
An open U-tube contains mercury. When $13.6cm$ of water is poured into one of the arms of the tube then the mercury rise in the other arm from its initial level is:
A. $1cm$
B. $0.5cm$
C. $10cm$
D. $5cm$
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: We can solve this problem with the help of Pascal’s law. Pascal’s law states that if the pressure is applied on fluid in an enclosed container , it is transmitted equally through the container and also to the wall of the container. In this question, U- tube is the container which we have, so when some water is poured in its one arm it applies some pressure which causes an increase of mercury column in the second arm and decreases of mercury column in the first arm. So we apply this concept in our question.
Complete answer:
The mathematical equation of Pascal’s law is:
$P = \rho gh$ or $F = PA$
Where $F$ is the force applied , $A$is the cross-sectional area of the container, $P$ is the pressure change at two points in the fluids column, $\rho $ is the fluid density , $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $h$ is the height change in the fluid column.
Both the above equation is the expression of pascal’s law, and both are used to find the hydrostatic pressure but essentially they are the same, according to the use of the question we can apply to anyone.
Initial condition before adding water is $A$ and after adding $13.6cm$ of water is $B$
Figure A
Figure B
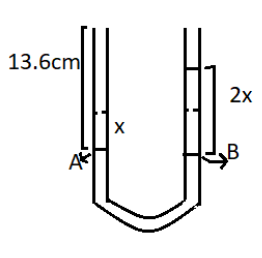
There is a decrease in the level of mercury $x$. On the other side total increase is $2x$. According to pascal’s law , pressure at the same level is equal in the both arms of the U-tube.
${P_A} = {P_B}$
$13.6 \times 1 \times g = 2x \times 13.6 \times g$
$1 = 2x \Rightarrow x = 0.5$
then the mercury rise in the other arm from its initial level is .$0.5cm$.
So option B is correct.
Note:
A typical application of Pascal's law is the hydraulic lifts. If a U-tube is filled with water and the pistons are placed at both the ends , pressure is applied on the left arm of the tube then it is transmitted throughout the liquid and exert the same pressure on the right side on the arm of the tube . it is the best example of Pascal’s law.
Complete answer:
The mathematical equation of Pascal’s law is:
$P = \rho gh$ or $F = PA$
Where $F$ is the force applied , $A$is the cross-sectional area of the container, $P$ is the pressure change at two points in the fluids column, $\rho $ is the fluid density , $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $h$ is the height change in the fluid column.
Both the above equation is the expression of pascal’s law, and both are used to find the hydrostatic pressure but essentially they are the same, according to the use of the question we can apply to anyone.
Initial condition before adding water is $A$ and after adding $13.6cm$ of water is $B$
Figure A

Figure B

There is a decrease in the level of mercury $x$. On the other side total increase is $2x$. According to pascal’s law , pressure at the same level is equal in the both arms of the U-tube.
${P_A} = {P_B}$
$13.6 \times 1 \times g = 2x \times 13.6 \times g$
$1 = 2x \Rightarrow x = 0.5$
then the mercury rise in the other arm from its initial level is .$0.5cm$.
So option B is correct.
Note:
A typical application of Pascal's law is the hydraulic lifts. If a U-tube is filled with water and the pistons are placed at both the ends , pressure is applied on the left arm of the tube then it is transmitted throughout the liquid and exert the same pressure on the right side on the arm of the tube . it is the best example of Pascal’s law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




