
An open metallic bucket is in the shape of a frustum of a cone mounted on a hollow cylindrical base made of metallic sheet. If the diameters of the two circular ends of the bucket are 45 cm and 25 cm, the total vertical height of the bucket is 30 cm and that of the cylindrical portion is 6 cm, find the area of the metallic sheet used to make the bucket. Also, find the volume of the water it can hold. (Take $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$ ).
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: To find the area of the metal sheet, we will find the curved surface area of the frustum, whose formula is given by, $\pi l\left( R+r \right)$, where l is the slant height which is given by the formula, $\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{\left( R-r \right)}^{2}}}$, and h is the height of the frustum and R, r are the radii of the base. We will then find the curved surface area of the cylinder by using the formula, $2\pi rh$, where r is the radius of the cylinder and h is its height. We will also find the area of the base and then add them. And to find the volume of each frustum and cylinder, we will use the respective formulas, $\dfrac{\pi h}{3}\left( {{R}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}}+Rr \right)$ and $\pi {{r}^{2}}h$.
Complete step by step solution:
In the question, we are given a small metallic bucket which is the shape of a frustum of a cone which is mounted on the top of a cylindrical base which is fully made up of metallic sheet. We are given that the diameters of the two circular ends of the frustum of the cone is 45 cm and 25 cm, and the vertical height is given as 30 cm. Out of this the height of the cylindrical portion is 6 cm. We have to find the area of the metallic sheet used to make the bucket and also the volume of water that it can hold. We will draw the figure according to the conditions given in the question as given below.
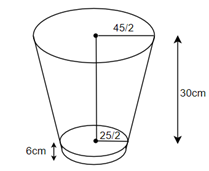
In order to find the area of the metallic sheet used to make the metallic bucket, we need to have the sum of the curved surface area of the frustum, curved surface area of the cylinder and the base area of the cylinder. As the diameters of the bases are given as 45 cm and 25 cm, we can say that the radius will be $\dfrac{45}{2}=22.5cm$ and $\dfrac{25}{2}=12.5cm$. So, the base radius of the cylinder will be 12.5 cm. The slant height of the frustum can be found by using the formula, $\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{\left( R-r \right)}^{2}}}$. The total vertical height of the bucket was given as 30 cm and that of the cylinder as 6 cm. Therefore, the height of the cone would be (30 - 6) = 24 cm. Thus, the value of h will be 24 cm and the values of R and r are 22.5 cm and 12.5 cm respectively. So, substituting these value sin the formula, we get,
$\begin{align}
& l=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{\left( R-r \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow l=\sqrt{{{\left( 24 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 22.5-12.5 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow l=\sqrt{576+100} \\
& \Rightarrow l=\sqrt{676} \\
& \Rightarrow l=26cm \\
\end{align}$
Thus, we get the value of the slant height l as 26 cm. We know that the curved surface area of the frustum is given by, $\pi l\left( R+r \right)$. So, by substituting the values of l = 26 cm, R = 22.5 cm and r = 12.5 cm, we get the curved surface area as,
$\begin{align}
& \pi l\left( R+r \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \pi \times 26\left( 22.5+12.5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \pi \times 26\times 35 \\
\end{align}$
We know the value of $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$, so substituting that, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{22}{7}\times 26\times 35 \\
& \Rightarrow 2860c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the curved surface area of the cylinder is $2\pi rh$, where r is the radius of the cylinder and h is its height. Here, we have the values of r = 12.5 cm and h = 6 cm, so the curved surface area of the cylinder will be,
\[2\pi rh=2\times \pi \times 12.5\times 6=150\pi \]
We will take the value of $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$, so substituting this value, we get,
$\begin{align}
& 150\times \dfrac{22}{7} \\
& \Rightarrow 471.43c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
The area of the base of the cylinder is $\pi {{r}^{2}}$, where r = 12.5 cm. So, putting that value and the value of $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{\left( 12.5 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 491.07c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
So, the total area of the metallic sheet will be, $2860c{{m}^{2}}+471.43c{{m}^{2}}+491.07c{{m}^{2}}=3822.5c{{m}^{2}}$.
Now, since we have to find the volume of water the bucket will hold, we have to find the volumes of both the frustum of the cone and that of the cylinder also. The formula for the volume of the frustum is given by, $\dfrac{\pi h}{3}\left( {{R}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}}+Rr \right)$. Here, we have h = 24 cm, R = 22.5 cm and r = 12.5 cm. So, substituting these values, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\pi }{3}\times 24\left( {{22.5}^{2}}+{{12.5}^{2}}+22.5\times 12.5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 8\pi \left( 943.75 \right) \\
\end{align}$
We know that the value of $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$, so we get,
$8\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 943.75=23728.57c{{m}^{3}}$
Similarly we will find the volume of the cylinder by using the formula, $\pi {{r}^{2}}h$, where r = 12.5 cm and h = 6 cm and $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$. So, substituting the values, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{\left( 12.5 \right)}^{2}}\times 6 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{625}{4}\times 6 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{22}{7}\times 937.5 \\
& \Rightarrow 2946.43c{{m}^{3}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the total volume of the structure is, $23728.57c{{m}^{3}}+2946.43c{{m}^{3}}=26675c{{m}^{3}}$.
Hence, the area of the metallic sheet to be used for the bucket is $3822.5c{{m}^{2}}$ and the volume of water it will hold is $26675c{{m}^{3}}$.
Note: While solving such questions, students generally forget to add or they miss out to add any one of the particular structures during the calculation of the area and volume. Some students get confused with the area, slant height and volume formulas for frustum, so they try to modify the formulas of cones to get it. For example, the slant height of the cone is given by, $\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$. In frustum, we have two radii, so we get the formula as $\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+\left( {{r}_{1}}^{2}-{{r}_{2}}^{2} \right)}$.
Complete step by step solution:
In the question, we are given a small metallic bucket which is the shape of a frustum of a cone which is mounted on the top of a cylindrical base which is fully made up of metallic sheet. We are given that the diameters of the two circular ends of the frustum of the cone is 45 cm and 25 cm, and the vertical height is given as 30 cm. Out of this the height of the cylindrical portion is 6 cm. We have to find the area of the metallic sheet used to make the bucket and also the volume of water that it can hold. We will draw the figure according to the conditions given in the question as given below.

In order to find the area of the metallic sheet used to make the metallic bucket, we need to have the sum of the curved surface area of the frustum, curved surface area of the cylinder and the base area of the cylinder. As the diameters of the bases are given as 45 cm and 25 cm, we can say that the radius will be $\dfrac{45}{2}=22.5cm$ and $\dfrac{25}{2}=12.5cm$. So, the base radius of the cylinder will be 12.5 cm. The slant height of the frustum can be found by using the formula, $\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{\left( R-r \right)}^{2}}}$. The total vertical height of the bucket was given as 30 cm and that of the cylinder as 6 cm. Therefore, the height of the cone would be (30 - 6) = 24 cm. Thus, the value of h will be 24 cm and the values of R and r are 22.5 cm and 12.5 cm respectively. So, substituting these value sin the formula, we get,
$\begin{align}
& l=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{\left( R-r \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow l=\sqrt{{{\left( 24 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 22.5-12.5 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow l=\sqrt{576+100} \\
& \Rightarrow l=\sqrt{676} \\
& \Rightarrow l=26cm \\
\end{align}$
Thus, we get the value of the slant height l as 26 cm. We know that the curved surface area of the frustum is given by, $\pi l\left( R+r \right)$. So, by substituting the values of l = 26 cm, R = 22.5 cm and r = 12.5 cm, we get the curved surface area as,
$\begin{align}
& \pi l\left( R+r \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \pi \times 26\left( 22.5+12.5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \pi \times 26\times 35 \\
\end{align}$
We know the value of $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$, so substituting that, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{22}{7}\times 26\times 35 \\
& \Rightarrow 2860c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the curved surface area of the cylinder is $2\pi rh$, where r is the radius of the cylinder and h is its height. Here, we have the values of r = 12.5 cm and h = 6 cm, so the curved surface area of the cylinder will be,
\[2\pi rh=2\times \pi \times 12.5\times 6=150\pi \]
We will take the value of $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$, so substituting this value, we get,
$\begin{align}
& 150\times \dfrac{22}{7} \\
& \Rightarrow 471.43c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
The area of the base of the cylinder is $\pi {{r}^{2}}$, where r = 12.5 cm. So, putting that value and the value of $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{\left( 12.5 \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 491.07c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
So, the total area of the metallic sheet will be, $2860c{{m}^{2}}+471.43c{{m}^{2}}+491.07c{{m}^{2}}=3822.5c{{m}^{2}}$.
Now, since we have to find the volume of water the bucket will hold, we have to find the volumes of both the frustum of the cone and that of the cylinder also. The formula for the volume of the frustum is given by, $\dfrac{\pi h}{3}\left( {{R}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}}+Rr \right)$. Here, we have h = 24 cm, R = 22.5 cm and r = 12.5 cm. So, substituting these values, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\pi }{3}\times 24\left( {{22.5}^{2}}+{{12.5}^{2}}+22.5\times 12.5 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 8\pi \left( 943.75 \right) \\
\end{align}$
We know that the value of $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$, so we get,
$8\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 943.75=23728.57c{{m}^{3}}$
Similarly we will find the volume of the cylinder by using the formula, $\pi {{r}^{2}}h$, where r = 12.5 cm and h = 6 cm and $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$. So, substituting the values, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{\left( 12.5 \right)}^{2}}\times 6 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{625}{4}\times 6 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{22}{7}\times 937.5 \\
& \Rightarrow 2946.43c{{m}^{3}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the total volume of the structure is, $23728.57c{{m}^{3}}+2946.43c{{m}^{3}}=26675c{{m}^{3}}$.
Hence, the area of the metallic sheet to be used for the bucket is $3822.5c{{m}^{2}}$ and the volume of water it will hold is $26675c{{m}^{3}}$.
Note: While solving such questions, students generally forget to add or they miss out to add any one of the particular structures during the calculation of the area and volume. Some students get confused with the area, slant height and volume formulas for frustum, so they try to modify the formulas of cones to get it. For example, the slant height of the cone is given by, $\sqrt{{{r}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}}$. In frustum, we have two radii, so we get the formula as $\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+\left( {{r}_{1}}^{2}-{{r}_{2}}^{2} \right)}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




