
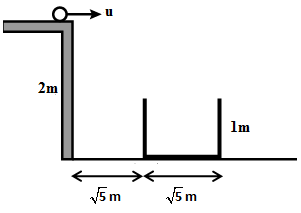
An open box of height 1 m is placed near a 2 m high table as shown. Marbles roll on the table and are collected in the box. \[{u_{\max }}\] and \[{u_{\min }}\] are the maximum and minimum values of velocity of marbles to fall into the box. Find the value of \[{u_{\max }} - {u_{\min }}\] (in m/s).

Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:The vertical component of the initial velocity of marble is zero. We can use a kinematic equation in vertical direction to determine the time taken by the marble to fall in the box. Then we can use the kinematic equation in the horizontal direction to determine the initial velocity for both the cases.
Formula used:
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
Here, s is the distance, u is the initial velocity, a is the acceleration and t is the time.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to find the time required for the marbles to fall into the box. If we use the kinematic equation in the vertical direction, we can find the time as follows,
\[{s_y} = {u_y}t + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}\]
Here, \[{s_y}\] is the vertical distance covered by the marble which is 1 m, \[{u_y}\] is the vertical component of initial velocity, g is the acceleration due to gravity and t is the time.
We can observe here that the marbles were sliding horizontally on the table. Therefore, their initial velocity has only horizontal component and vertical component is zero.
We substitute 1 m for \[{s_y}\], 0 for \[{u_y}\] and \[10\,m/{s^2}\] for g in the above equation.
\[1 = \left( 0 \right)t + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {10} \right){t^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {t^2} = \dfrac{1}{5}\]
\[ \Rightarrow t = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}\]
The time to fall into the box will be the same for both the cases.
We now, use the kinematic equation in horizontal direction as follows,
\[{s_x} = {u_x}t\] …… (1)
We see in the above equation, the term of acceleration due to gravity is absent since the acceleration due to gravity does not affect the horizontal motion of the object.For minimum initial velocity, we substitute \[\sqrt 5 \,m\] for \[{s_x}\] and \[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}\] for t in the above equation.
\[\sqrt 5 = {u_{\min }}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {u_{\min }} = \sqrt 5 \sqrt 5 \]
\[ \Rightarrow {u_{\min }} = 5\,m/s\]
For maximum initial velocity, we substitute \[\left( {\sqrt 5 + \sqrt 5 \,} \right)m\] for \[{s_x}\] and \[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}\] for t in equation (1) equation.
\[\sqrt 5 + \sqrt 5 = {u_{\max }}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {4.472} \right)\sqrt 5 = {u_{\max }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {u_{\max }} = 10m/s\]
Now, we have to determine the value of \[{u_{\max }} - {u_{\min }}\], therefore,
\[{u_{\max }} - {u_{\min }} = 10 - 5\]
\[ \therefore {u_{\max }} - {u_{\min }} = 5\,m/s\]
Therefore, the value of \[{u_{\max }} - {u_{\min }}\] is 5 m/s.
Note:Students should always take the sign of acceleration due to gravity as positive for the downward motion of the body and for the upward motion, take acceleration due to gravity as negative. For the horizontal motion of the body, we can directly use the relation \[s = ut\], where, s is distance, u is the initial velocity and t is the time. Students should
understand which kinematic equation should be used for different kinds of questions. For this question we don’t know the final velocity of the marble. Therefore, we have taken the kinematic equation which does not have the term final velocity.
Formula used:
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
Here, s is the distance, u is the initial velocity, a is the acceleration and t is the time.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to find the time required for the marbles to fall into the box. If we use the kinematic equation in the vertical direction, we can find the time as follows,
\[{s_y} = {u_y}t + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}\]
Here, \[{s_y}\] is the vertical distance covered by the marble which is 1 m, \[{u_y}\] is the vertical component of initial velocity, g is the acceleration due to gravity and t is the time.
We can observe here that the marbles were sliding horizontally on the table. Therefore, their initial velocity has only horizontal component and vertical component is zero.
We substitute 1 m for \[{s_y}\], 0 for \[{u_y}\] and \[10\,m/{s^2}\] for g in the above equation.
\[1 = \left( 0 \right)t + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {10} \right){t^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {t^2} = \dfrac{1}{5}\]
\[ \Rightarrow t = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}\]
The time to fall into the box will be the same for both the cases.
We now, use the kinematic equation in horizontal direction as follows,
\[{s_x} = {u_x}t\] …… (1)
We see in the above equation, the term of acceleration due to gravity is absent since the acceleration due to gravity does not affect the horizontal motion of the object.For minimum initial velocity, we substitute \[\sqrt 5 \,m\] for \[{s_x}\] and \[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}\] for t in the above equation.
\[\sqrt 5 = {u_{\min }}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {u_{\min }} = \sqrt 5 \sqrt 5 \]
\[ \Rightarrow {u_{\min }} = 5\,m/s\]
For maximum initial velocity, we substitute \[\left( {\sqrt 5 + \sqrt 5 \,} \right)m\] for \[{s_x}\] and \[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}\] for t in equation (1) equation.
\[\sqrt 5 + \sqrt 5 = {u_{\max }}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {4.472} \right)\sqrt 5 = {u_{\max }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {u_{\max }} = 10m/s\]
Now, we have to determine the value of \[{u_{\max }} - {u_{\min }}\], therefore,
\[{u_{\max }} - {u_{\min }} = 10 - 5\]
\[ \therefore {u_{\max }} - {u_{\min }} = 5\,m/s\]
Therefore, the value of \[{u_{\max }} - {u_{\min }}\] is 5 m/s.
Note:Students should always take the sign of acceleration due to gravity as positive for the downward motion of the body and for the upward motion, take acceleration due to gravity as negative. For the horizontal motion of the body, we can directly use the relation \[s = ut\], where, s is distance, u is the initial velocity and t is the time. Students should
understand which kinematic equation should be used for different kinds of questions. For this question we don’t know the final velocity of the marble. Therefore, we have taken the kinematic equation which does not have the term final velocity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




