
An object is thrown vertically upward from a height of 2m at $7m{{s}^{-1}}$. How long will it take for the object to hit the ground?
Answer
552.9k+ views
Hint: We shall analyze the velocity of the object at various points of its motion and apply the equations of motion at those points. However, before applying the equations of motion, we will first break down the journey of the object into two parts.
Complete answer:
We have marked three points in the journey of the object that are A, B and C respectively. Also, we break up the motion of the object into two parts, from A to B and from B to C.
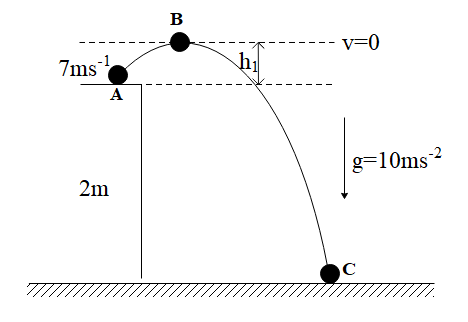
We shall first look into the motion of the object from A to B.
At point A, the object has an initial velocity of $7m{{s}^{-1}}$. When it is thrown vertically, it does not fall downwards directly rather it goes upward to reach its maximum height. At the maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero. Thus, the acceleration acting on it is negative of the acceleration due to gravity, that is,$-10m{{s}^{2}}$. Let the time taken to complete this journey be ${{t}_{1}}$.
Applying the equation of motion, $v=u+at$ and substituting values, $v=0m{{s}^{-1}},u=7m{{s}^{-1}},a=-10m{{s}^{-2}},t={{t}_{1}}$, we get
$\Rightarrow 0=7+\left( -10 \right){{t}_{1}}$
$\Rightarrow 10{{t}_{1}}=7$
Dividing both sides by 7, we get
$\Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{7}{10}s$
Also, ${{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}}{2a}$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{0-{{7}^{2}}}{2\left( -10 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{49}{20}m \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow {{h}_{1}}=2.45m$
Now, when the object travels from point B to C, the object is freely falling under the force of gravity from its maximum height. Applying the equation of motion, $s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$ and substituting the values, $s=2m+{{h}_{1}},u=0m{{s}^{-1}},a=10m{{s}^{-2}},t={{t}_{2}}$ , we get
$\Rightarrow 2+2.45=\left( 0 \right){{t}_{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 10 \right)t_{2}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow 4.45=5t_{2}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{4.45}{5}}s$
Thus, the total time of motion of the object is ${{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}$.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow t=\dfrac{7}{10}+\sqrt{\dfrac{4.45}{5}} \\
& \Rightarrow t=0.7+0.94 \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow t=1.64s$
Therefore, time taken for the object to hit the ground is 1.64 seconds.
Note:
In motion from A to B, we have taken the acceleration of the object as negative of acceleration due to gravity because it is going in the exact opposite of the acceleration due to gravity. However, in motion from B to C, we have taken the acceleration to be positive acceleration due to gravity because then the object is moving in the same direction as that of the acceleration due to gravity.
Complete answer:
We have marked three points in the journey of the object that are A, B and C respectively. Also, we break up the motion of the object into two parts, from A to B and from B to C.

We shall first look into the motion of the object from A to B.
At point A, the object has an initial velocity of $7m{{s}^{-1}}$. When it is thrown vertically, it does not fall downwards directly rather it goes upward to reach its maximum height. At the maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero. Thus, the acceleration acting on it is negative of the acceleration due to gravity, that is,$-10m{{s}^{2}}$. Let the time taken to complete this journey be ${{t}_{1}}$.
Applying the equation of motion, $v=u+at$ and substituting values, $v=0m{{s}^{-1}},u=7m{{s}^{-1}},a=-10m{{s}^{-2}},t={{t}_{1}}$, we get
$\Rightarrow 0=7+\left( -10 \right){{t}_{1}}$
$\Rightarrow 10{{t}_{1}}=7$
Dividing both sides by 7, we get
$\Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{7}{10}s$
Also, ${{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}}{2a}$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{0-{{7}^{2}}}{2\left( -10 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{49}{20}m \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow {{h}_{1}}=2.45m$
Now, when the object travels from point B to C, the object is freely falling under the force of gravity from its maximum height. Applying the equation of motion, $s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$ and substituting the values, $s=2m+{{h}_{1}},u=0m{{s}^{-1}},a=10m{{s}^{-2}},t={{t}_{2}}$ , we get
$\Rightarrow 2+2.45=\left( 0 \right){{t}_{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 10 \right)t_{2}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow 4.45=5t_{2}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow {{t}_{2}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{4.45}{5}}s$
Thus, the total time of motion of the object is ${{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}$.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow t=\dfrac{7}{10}+\sqrt{\dfrac{4.45}{5}} \\
& \Rightarrow t=0.7+0.94 \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow t=1.64s$
Therefore, time taken for the object to hit the ground is 1.64 seconds.
Note:
In motion from A to B, we have taken the acceleration of the object as negative of acceleration due to gravity because it is going in the exact opposite of the acceleration due to gravity. However, in motion from B to C, we have taken the acceleration to be positive acceleration due to gravity because then the object is moving in the same direction as that of the acceleration due to gravity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




