
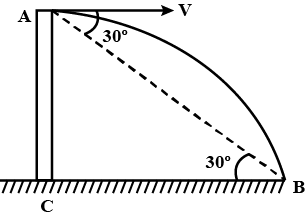
An object is thrown horizontally from point A from a tower and hit the ground 3s later at B. The line from A to B makes the angle of ${30^ \circ }$ with the horizontal. The initial velocity of the object is: (take $g = 10m/s$ )
A.$15\sqrt 3 m/s$
B.$15m/s$
C.$10\sqrt 3 m/s$
D.$\dfrac{{25}}{{\sqrt 3 }}m/s$

Answer
496.5k+ views
Hint: All objects irrespective of their mass experience the same acceleration g while falling freely under the influence of gravity at the same point on the earth. Also, gravity works towards the center of the Earth. The mass of the object and the gravitational constant determine the magnitude of the gravitational force.
Formula used:
From the equation of motion
$h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ ……………….. (1)
Where $u$ = initial velocity, $t$ = time taken by the motion, $g$ gravity
Complete answer:
From the figure, we can say that $h = AC$ ……… (2)
From equation (1)
$h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
$u = 0$
We get $h = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ ……….. (3)
It is given that the object takes $3s$ to fall so $t = 3s$
And $g = 10m/s$
By putting the value of $g$ and $t$ in equation (3)
We get $h = \dfrac{{10 \times {3^2}}}{2}$
$h = \dfrac{{90}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow h = 45m$
From the figure we can write
$\tan 30 = \dfrac{{AC}}{{BC}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan 30 = \dfrac{{AC}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AC}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
From equation (2) $AC = h$
We get $\dfrac{h}{{BC}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{45}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
$BC = 45\sqrt 3 m$
The object covers $45\sqrt 3 m$ in $3s$ so the initial velocity $u = \dfrac{{\text{d}}}{{\text{t}}}$
$u = \dfrac{{45\sqrt 3 }}{3}$
$ \Rightarrow u = 15\sqrt 3 m/s$
So the correct option is (a).
Note:
According to general relativity, gravity is not the force between masses. Instead, Einstein said that gravity is an effect of wrapping of space and time due to mass. Without a force upon an object, it can move in a straight line, this explains why every object falls at the same rate.
Most scientists have claimed that gravitational waves exist but none have ever proved their existence.
If our planet loses gravity for 5sec then that would be the end of our earth.
Formula used:
From the equation of motion
$h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ ……………….. (1)
Where $u$ = initial velocity, $t$ = time taken by the motion, $g$ gravity
Complete answer:
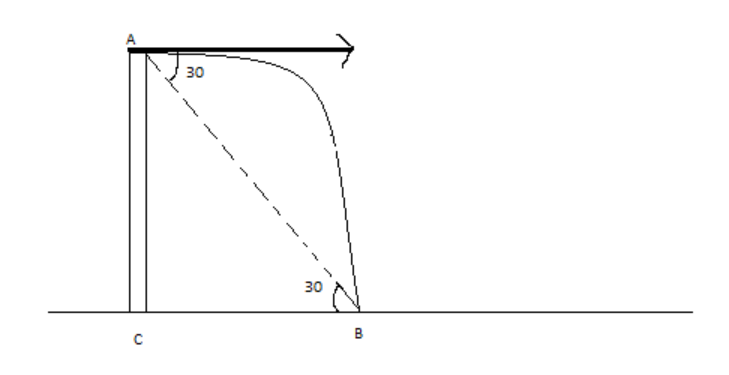
From the figure, we can say that $h = AC$ ……… (2)

From equation (1)
$h = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
$u = 0$
We get $h = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ ……….. (3)
It is given that the object takes $3s$ to fall so $t = 3s$
And $g = 10m/s$
By putting the value of $g$ and $t$ in equation (3)
We get $h = \dfrac{{10 \times {3^2}}}{2}$
$h = \dfrac{{90}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow h = 45m$
From the figure we can write
$\tan 30 = \dfrac{{AC}}{{BC}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan 30 = \dfrac{{AC}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AC}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
From equation (2) $AC = h$
We get $\dfrac{h}{{BC}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{45}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
$BC = 45\sqrt 3 m$
The object covers $45\sqrt 3 m$ in $3s$ so the initial velocity $u = \dfrac{{\text{d}}}{{\text{t}}}$
$u = \dfrac{{45\sqrt 3 }}{3}$
$ \Rightarrow u = 15\sqrt 3 m/s$
So the correct option is (a).
Note:
According to general relativity, gravity is not the force between masses. Instead, Einstein said that gravity is an effect of wrapping of space and time due to mass. Without a force upon an object, it can move in a straight line, this explains why every object falls at the same rate.
Most scientists have claimed that gravitational waves exist but none have ever proved their existence.
If our planet loses gravity for 5sec then that would be the end of our earth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




