
An object is observed from three points A, B and C in the same horizontal line passing through the base of the object. The angle of elevation at B is twice and at C thrice that of A. If AB = a, BC = b, then the height of the object is
a.\[\dfrac{a}{2b}\sqrt{\left( a+b \right)\left( 3b-a \right)}\]
b.\[\dfrac{a}{2b}\sqrt{\left( a-b \right)\left( 3b-a \right)}\]
c.\[\dfrac{a}{2b}\sqrt{\left( a-b \right)\left( 3b+a \right)}\]
d.\[\dfrac{a}{2b}\sqrt{\left( a+b \right)\left( 3b+a \right)}\]
Answer
603k+ views
Hint: Assume the angle of elevation at A be \[\alpha \] . The angle of elevation at B and will be \[2\alpha \] and \[3\alpha \] respectively. Now, find \[\angle PBA\] and \[\angle PCA\] using a linear pair of angles. As we know that the sum of all angles of a triangle is \[\pi \] , so using this find \[\angle BPA\] and \[\angle CPB\] . We will get BP=BA(sides opposite to equal angles are also equal). Now use the sine formula in the \[\Delta PCB\] and get the value of \[\sin \alpha \] . Using the identity, \[{{\sin }^{2}}\alpha +{{\cos }^{2}}\alpha =1\] , get the value of \[\cos \alpha \] . We know that \[\sin 2\alpha =2\sin \alpha \cos \alpha \] . In \[\Delta PQB\] , apply \[\sin 2\alpha \] . Then, put the value of \[\sin \alpha \] , \[\cos \alpha \] , and BP=a. Solve further and get the value of PQ.
Complete step-by-step answer:
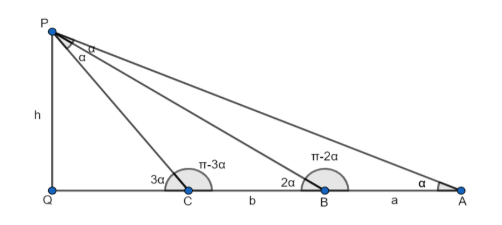
Let the angle of elevation at A be \[\alpha \] .
\[\angle PAQ=\alpha \] ……………………(1)
According to the question, it is given that the angle of elevation at B is twice and at C thrice that of A.
The angle of elevation at B that is \[\angle PBQ\] = \[2\alpha \] ………………….(2)
The angle of elevation at B that is \[\angle PCQ\] = \[3\alpha \] ………………………..(3)
\[\angle PBQ+\angle PBA=\pi \] (linear pair)
From equation (2), we can write \[\angle PBA=\pi -2\alpha \] ……………………………..(4)
Similarly, \[\angle PCQ+\angle PCA=\pi \] (linear pair)
From equation (3), we can write \[\angle PCA=\pi -3\alpha \] ……………………………..(5)
In \[\Delta PBA\] , we have
\[\angle BPA+\angle PAQ+\angle PBA=\pi \,(sum\text{ }of\text{ }all\text{ }angles\text{ }of\text{ }a\text{ }triangle\text{ }is\text{ }\pi )\] ………………………..(6)
Now, using equation (1) and equation (4), we can write equation (6) as,
\[\begin{align}
& \angle BPA+\angle PAQ+\angle PBA=\pi \\
& \Rightarrow \,\angle BPA+\alpha +\pi -2\alpha =\pi \\
& \Rightarrow \angle BPA-\alpha =0 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle BPA=\alpha \] ………………………….(7)
In \[\Delta PCB\] , we have
\[\angle PCB+\angle CPB+\angle PBC=\pi \,(sum\text{ }of\text{ }all\text{ }angles\text{ }of\text{ }a\text{ }triangle\text{ }is\text{ }\pi )\] ………………………..(8)
Now, using equation (2) and equation (5), we can write equation (8) as,
\[\begin{align}
& \angle PCB+\angle CPB+\angle PBC=\pi \, \\
& \Rightarrow \,\pi -3\alpha +\angle CPB+2\alpha =\pi \\
& \Rightarrow \angle CPB-\alpha =0 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle CPB=\alpha \] ………………………….(9)
We know the sine formula of a triangle.
We know the sine formula of a triangle, \[\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}\] .
Now, applying sine formula in the \[\Delta PCB\] ,
\[\dfrac{BC}{\sin \alpha }=\dfrac{PB}{\sin (\pi -3\alpha )}\]
We know the formula that, \[\sin 3\alpha =3\sin \alpha -4{{\sin }^{3}}\alpha \] and \[\sin \left( \pi -\theta \right)=\sin \theta \] . Using this formula, we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{b}{\sin \alpha }=\dfrac{PB}{\sin 3\alpha }\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{b}{\sin \alpha }=\dfrac{PB}{3\sin \alpha -4{{\sin }^{3}}\alpha } \\
& \Rightarrow b(3-4si{{n}^{2}}\alpha )=PB \\
\end{align}\]
We have, \[\angle BPA=\alpha \] and \[\angle PAB=\alpha \] .
So, PB = BA = a (sides opposite to equal angles are equal).
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow b(3-4si{{n}^{2}}\alpha )=a \\
& \Rightarrow 3b-a=4b{{\sin }^{2}}\alpha \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( 3b-a \right)}{4b}={{\sin }^{2}}\alpha \]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{\dfrac{\left( 3b-a \right)}{4b}}=\sin \alpha \] ………………….(10)
We know the identity, \[{{\sin }^{2}}\alpha +{{\cos }^{2}}\alpha =1\] . Now putting the value of \[\sin \alpha \] from equation (10) in the identity, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( 3b-a \right)}{4b}+{{\cos }^{2}}\alpha =1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}\alpha =1-\dfrac{\left( 3b-a \right)}{4b} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}\alpha =\dfrac{4b-3b+a}{4b} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}\alpha =\dfrac{a+b}{4b} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow \cos \alpha =\sqrt{\dfrac{a+b}{4b}}\] ………………………(11)
In \[\Delta PQB\] , we have
\[\dfrac{PQ}{BP}=\sin 2\alpha \]
\[\Rightarrow PQ=BP\sin 2\alpha \]
We have, \[\angle BPA=\alpha \] and \[\angle PAB=\alpha \] .
So, PB = BA = a (sides opposite to equal angles are equal).
\[\Rightarrow PQ=BA\sin 2\alpha \]
\[\Rightarrow PQ=a\sin 2\alpha \] ……………………(12)
We know the formula, \[\sin 2\alpha =2\sin \alpha \cos \alpha \] .
From equation (10), equation (11) and equation (12), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow PQ=a.2\sin \alpha \cos \alpha \\
& \Rightarrow PQ=a.2\sqrt{\dfrac{\left( 3b-a \right)}{4b}}\sqrt{\dfrac{a+b}{4b}} \\
& \Rightarrow PQ=2a\dfrac{\sqrt{\left( 3b-a \right)\left( a+b \right)}}{4b} \\
& \Rightarrow PQ=\dfrac{a}{2b}\sqrt{\left( 3b-a \right)\left( a+b \right)} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, option (A) is the correct option.
Note: To solve this question, one may think to apply tan formulas in the \[\Delta PQC\] , \[\Delta PQB\] , and \[\Delta PQA\] . If we do so then we will get complex equations which will be difficult to solve. So, we don’t have to approach this question by applying a tan formula.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Let the angle of elevation at A be \[\alpha \] .
\[\angle PAQ=\alpha \] ……………………(1)
According to the question, it is given that the angle of elevation at B is twice and at C thrice that of A.
The angle of elevation at B that is \[\angle PBQ\] = \[2\alpha \] ………………….(2)
The angle of elevation at B that is \[\angle PCQ\] = \[3\alpha \] ………………………..(3)
\[\angle PBQ+\angle PBA=\pi \] (linear pair)
From equation (2), we can write \[\angle PBA=\pi -2\alpha \] ……………………………..(4)
Similarly, \[\angle PCQ+\angle PCA=\pi \] (linear pair)
From equation (3), we can write \[\angle PCA=\pi -3\alpha \] ……………………………..(5)
In \[\Delta PBA\] , we have
\[\angle BPA+\angle PAQ+\angle PBA=\pi \,(sum\text{ }of\text{ }all\text{ }angles\text{ }of\text{ }a\text{ }triangle\text{ }is\text{ }\pi )\] ………………………..(6)
Now, using equation (1) and equation (4), we can write equation (6) as,
\[\begin{align}
& \angle BPA+\angle PAQ+\angle PBA=\pi \\
& \Rightarrow \,\angle BPA+\alpha +\pi -2\alpha =\pi \\
& \Rightarrow \angle BPA-\alpha =0 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle BPA=\alpha \] ………………………….(7)
In \[\Delta PCB\] , we have
\[\angle PCB+\angle CPB+\angle PBC=\pi \,(sum\text{ }of\text{ }all\text{ }angles\text{ }of\text{ }a\text{ }triangle\text{ }is\text{ }\pi )\] ………………………..(8)
Now, using equation (2) and equation (5), we can write equation (8) as,
\[\begin{align}
& \angle PCB+\angle CPB+\angle PBC=\pi \, \\
& \Rightarrow \,\pi -3\alpha +\angle CPB+2\alpha =\pi \\
& \Rightarrow \angle CPB-\alpha =0 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle CPB=\alpha \] ………………………….(9)
We know the sine formula of a triangle.
We know the sine formula of a triangle, \[\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}\] .
Now, applying sine formula in the \[\Delta PCB\] ,
\[\dfrac{BC}{\sin \alpha }=\dfrac{PB}{\sin (\pi -3\alpha )}\]
We know the formula that, \[\sin 3\alpha =3\sin \alpha -4{{\sin }^{3}}\alpha \] and \[\sin \left( \pi -\theta \right)=\sin \theta \] . Using this formula, we get
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{b}{\sin \alpha }=\dfrac{PB}{\sin 3\alpha }\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{b}{\sin \alpha }=\dfrac{PB}{3\sin \alpha -4{{\sin }^{3}}\alpha } \\
& \Rightarrow b(3-4si{{n}^{2}}\alpha )=PB \\
\end{align}\]
We have, \[\angle BPA=\alpha \] and \[\angle PAB=\alpha \] .
So, PB = BA = a (sides opposite to equal angles are equal).
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow b(3-4si{{n}^{2}}\alpha )=a \\
& \Rightarrow 3b-a=4b{{\sin }^{2}}\alpha \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( 3b-a \right)}{4b}={{\sin }^{2}}\alpha \]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{\dfrac{\left( 3b-a \right)}{4b}}=\sin \alpha \] ………………….(10)
We know the identity, \[{{\sin }^{2}}\alpha +{{\cos }^{2}}\alpha =1\] . Now putting the value of \[\sin \alpha \] from equation (10) in the identity, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( 3b-a \right)}{4b}+{{\cos }^{2}}\alpha =1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}\alpha =1-\dfrac{\left( 3b-a \right)}{4b} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}\alpha =\dfrac{4b-3b+a}{4b} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}\alpha =\dfrac{a+b}{4b} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow \cos \alpha =\sqrt{\dfrac{a+b}{4b}}\] ………………………(11)
In \[\Delta PQB\] , we have
\[\dfrac{PQ}{BP}=\sin 2\alpha \]
\[\Rightarrow PQ=BP\sin 2\alpha \]
We have, \[\angle BPA=\alpha \] and \[\angle PAB=\alpha \] .
So, PB = BA = a (sides opposite to equal angles are equal).
\[\Rightarrow PQ=BA\sin 2\alpha \]
\[\Rightarrow PQ=a\sin 2\alpha \] ……………………(12)
We know the formula, \[\sin 2\alpha =2\sin \alpha \cos \alpha \] .
From equation (10), equation (11) and equation (12), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow PQ=a.2\sin \alpha \cos \alpha \\
& \Rightarrow PQ=a.2\sqrt{\dfrac{\left( 3b-a \right)}{4b}}\sqrt{\dfrac{a+b}{4b}} \\
& \Rightarrow PQ=2a\dfrac{\sqrt{\left( 3b-a \right)\left( a+b \right)}}{4b} \\
& \Rightarrow PQ=\dfrac{a}{2b}\sqrt{\left( 3b-a \right)\left( a+b \right)} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, option (A) is the correct option.
Note: To solve this question, one may think to apply tan formulas in the \[\Delta PQC\] , \[\Delta PQB\] , and \[\Delta PQA\] . If we do so then we will get complex equations which will be difficult to solve. So, we don’t have to approach this question by applying a tan formula.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




