
An object is moving with constant speed in a circle of radius $r$. Calculate the distance and displacement,
A. When it completes half the circle.
B. When it completes $\dfrac{3}{4}th$ of the circle.
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint:The distance covered by an object when the object will cover half of the distance can be calculated by taking half of the circumference of the circle and displacement will be diameter of the circle. On the other hand, when the object will cover $\dfrac{3}{4}th$ of the circle, the distance will be $\dfrac{3}{4}th$ of the circumference and the displacement will be hypotenuse of the circle.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a circle of radius $r$ in which an object is moving with constant speed.
A. Now, consider a case in which the object will cover half of the circle as shown below
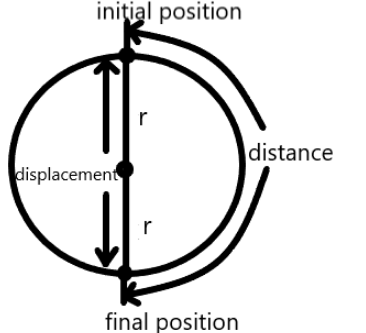
In the above figure, we have mentioned the initial and final positions of the body. The line joining the initial and final positions of an object is showing the displacement of the body. Also, the semicircle is representing the distance covered by the object. Therefore, the distance covered by the object can be calculated as given below
$s = \dfrac{{circumference}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \,s = \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \,s = \pi r$
Here, $s$ is the distance covered by an object.
Now, the displacement of an object can be calculated as shown below
Displacement $ = r + r = 2r$
Therefore, when the object is over half of the circle, the distance is $\pi r$ and the displacement is $2r$.
B. Now we will consider a case in which the object will cover $\dfrac{3}{4}th$ of the circle. Therefore, the distance covered by the object is given below;
$s = \dfrac{3}{4}\left( {circumference} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \,s = \dfrac{3}{4}\left( {2\pi r} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \,s = \dfrac{3}{2}\pi r$
Now, the displacement covered by the object will be the hypotenuse of the triangle as shown below
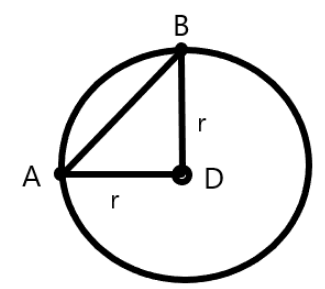
Therefore, displacement $ = AB$
Now, for calculating AB, we will use the Pythagoras formula as shown below
$A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \,A{B^2} = {r^2} + {r^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \,A{B^2} = 2{r^2}$
$ \therefore \,A{B^2} = \sqrt 2 r$
Therefore, when the object will cover $\dfrac{3}{4}th$ of the circle, the distance is $\dfrac{3}{2}\pi r$ and displacement is $\sqrt 2 r$.
Note:Remember that the distance in the first case is in the form of a semicircle, that is why, we have got the distance as circumference of semicircle. Also, the displacement of the body in the second case is in the form of hypotenuse of the right angled triangle. That is why we have used the Pythagoras theorem.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a circle of radius $r$ in which an object is moving with constant speed.
A. Now, consider a case in which the object will cover half of the circle as shown below

In the above figure, we have mentioned the initial and final positions of the body. The line joining the initial and final positions of an object is showing the displacement of the body. Also, the semicircle is representing the distance covered by the object. Therefore, the distance covered by the object can be calculated as given below
$s = \dfrac{{circumference}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \,s = \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \,s = \pi r$
Here, $s$ is the distance covered by an object.
Now, the displacement of an object can be calculated as shown below
Displacement $ = r + r = 2r$
Therefore, when the object is over half of the circle, the distance is $\pi r$ and the displacement is $2r$.
B. Now we will consider a case in which the object will cover $\dfrac{3}{4}th$ of the circle. Therefore, the distance covered by the object is given below;
$s = \dfrac{3}{4}\left( {circumference} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \,s = \dfrac{3}{4}\left( {2\pi r} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \,s = \dfrac{3}{2}\pi r$
Now, the displacement covered by the object will be the hypotenuse of the triangle as shown below

Therefore, displacement $ = AB$
Now, for calculating AB, we will use the Pythagoras formula as shown below
$A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \,A{B^2} = {r^2} + {r^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \,A{B^2} = 2{r^2}$
$ \therefore \,A{B^2} = \sqrt 2 r$
Therefore, when the object will cover $\dfrac{3}{4}th$ of the circle, the distance is $\dfrac{3}{2}\pi r$ and displacement is $\sqrt 2 r$.
Note:Remember that the distance in the first case is in the form of a semicircle, that is why, we have got the distance as circumference of semicircle. Also, the displacement of the body in the second case is in the form of hypotenuse of the right angled triangle. That is why we have used the Pythagoras theorem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




