
An object $5cm$ in length is held $25cm$ away from a converging lens of focal length $10cm$. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and nature of the image formed.
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint
A convex lens is also known as a converging lens. The object is situated behind the lens, so image distance would be taken negative, the focal length of a convex lens is always positive, the height is also taken positive. To find the position, we use the lens formula.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$ (Lens formula)
$\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{v}{u} = \dfrac{{{h_v}}}{{{h_u}}}$ (magnification)
Complete step by step answer
To find the position of image:
We have, the distance of an object from the lens $u = - 25cm$
Height of the object, ${h_u} = 5cm$
Focal length of the lens $f = 10cm$
Applying the lens formula here,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \left( {\dfrac{1}{{ - 25}}} \right) + \dfrac{1}{{10}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{{5 - 2}}{{50}} = \dfrac{3}{{50}}$
$\therefore v = \dfrac{{50}}{3} = 16.66{\text{ cm}}$
Therefore the image is formed on the right of the lens (Assuming that incident ray travels from left to right) at a distance $16.66{\text{ cm}}$.
Now magnification can be calculated by,
$\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{v}{u}$
$\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{16.66}}{{ - 25}} = - 0.66$
Since, magnification is also defined as,
$\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{{h_v}}}{{{h_u}}}$
Here ${h_v}{\text{ and }}{h_u}$are the heights of image and object respectively.
Height of image, ${h_v} = m{h_u}$
$\Rightarrow {h_v} = - 0.66 \times 5 = - 3.3{\text{ cm}}$
Therefore, the image is diminished in size and has a height of $3.3{\text{ cm}}$. Also, it has a negative sign, which tells that the image is real and inverted.
So,the position of the image,$v = - 16.66cm$
Height of image ${h_v} = - 3.3cm$
Nature of the image is real, diminished and inverted.
Ray diagram:
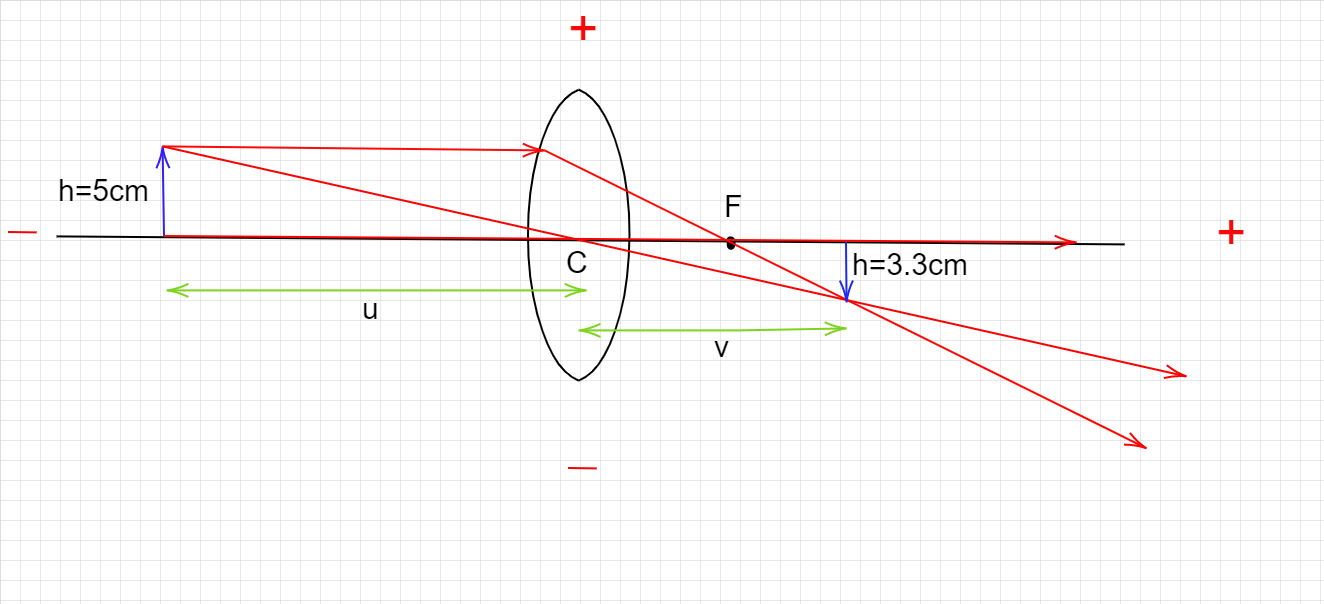
To draw this ray diagram, we take 3 rays.
-First ray originates from the top of the object, is incident parallel on the lens, after refraction, it passes through the focus.
-Second ray originates from the top of the object, passes through the optical centre and continues on the same path.
-Third ray originates from the bottom of the object, it is horizontal and passes through the optical centre as well as focus.
Note
Write the signs of u, v, f and m correctly, they play an important role in determining the nature of the image. For your convenience, you can also draw the Cartesian signs on the ray diagram itself (as done in the above ray diagram).
A convex lens is also known as a converging lens. The object is situated behind the lens, so image distance would be taken negative, the focal length of a convex lens is always positive, the height is also taken positive. To find the position, we use the lens formula.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$ (Lens formula)
$\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{v}{u} = \dfrac{{{h_v}}}{{{h_u}}}$ (magnification)
Complete step by step answer
To find the position of image:
We have, the distance of an object from the lens $u = - 25cm$
Height of the object, ${h_u} = 5cm$
Focal length of the lens $f = 10cm$
Applying the lens formula here,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \left( {\dfrac{1}{{ - 25}}} \right) + \dfrac{1}{{10}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{{5 - 2}}{{50}} = \dfrac{3}{{50}}$
$\therefore v = \dfrac{{50}}{3} = 16.66{\text{ cm}}$
Therefore the image is formed on the right of the lens (Assuming that incident ray travels from left to right) at a distance $16.66{\text{ cm}}$.
Now magnification can be calculated by,
$\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{v}{u}$
$\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{16.66}}{{ - 25}} = - 0.66$
Since, magnification is also defined as,
$\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{{h_v}}}{{{h_u}}}$
Here ${h_v}{\text{ and }}{h_u}$are the heights of image and object respectively.
Height of image, ${h_v} = m{h_u}$
$\Rightarrow {h_v} = - 0.66 \times 5 = - 3.3{\text{ cm}}$
Therefore, the image is diminished in size and has a height of $3.3{\text{ cm}}$. Also, it has a negative sign, which tells that the image is real and inverted.
So,the position of the image,$v = - 16.66cm$
Height of image ${h_v} = - 3.3cm$
Nature of the image is real, diminished and inverted.
Ray diagram:

To draw this ray diagram, we take 3 rays.
-First ray originates from the top of the object, is incident parallel on the lens, after refraction, it passes through the focus.
-Second ray originates from the top of the object, passes through the optical centre and continues on the same path.
-Third ray originates from the bottom of the object, it is horizontal and passes through the optical centre as well as focus.
Note
Write the signs of u, v, f and m correctly, they play an important role in determining the nature of the image. For your convenience, you can also draw the Cartesian signs on the ray diagram itself (as done in the above ray diagram).
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




