
An isosceles triangle has a base of 12 cm with equal sides of 20 cm each. How do you determine the area of this triangle accurate to the nearest square centimetre?
Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: We first describe the formula of area for the isosceles triangle with its sides’ length being $a,b,c$. We need to also find the semi-perimeter value. We put those values in the equation of $A=\sqrt{S\left( S-a \right)\left( S-b \right)\left( S-c \right)}$ to find the solution for the area.
Complete step by step answer:
We have been given an isosceles triangle which has a base of 12 cm with equal sides of 20 cm each.
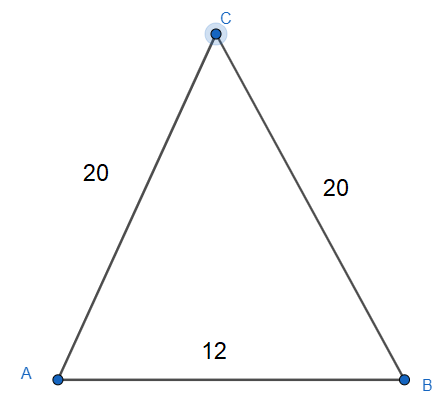
We are going to apply the formula of the area of the isosceles triangle whose sides are given.
For an isosceles triangle with their sides’ length being $a,b,c$ we can have its area as A and the perimeter as 2S.
Therefore, $2S=a+b+c$.
The formula of area for the isosceles triangle will be $A=\sqrt{S\left( S-a \right)\left( S-b \right)\left( S-c \right)}$.
The given values for the sides of our isosceles triangle are $12,20,20$.
We put the values in the equation $2S=a+b+c$ to find the value of S.
So, $2S=a+b+c=12+20+20=52$ which gives $S=\dfrac{52}{2}=26$.
Now we try to find the values of the terms $\left( S-a \right),\left( S-b \right),\left( S-c \right)$.
Therefore, $\left( S-a \right)=26-12=14$
$\left( S-b \right)=26-20=6$
$\left( S-c \right)=26-20=6$
Now we put the values in the equation of $A=\sqrt{S\left( S-a \right)\left( S-b \right)\left( S-c \right)}$.
$A=\sqrt{26\times 14\times 6\times 6}=12\sqrt{91}$.
We need to find the area of this triangle accurate to the nearest square centimetre.
The value of $12\sqrt{91}$ is approximated to $114.47\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$.
Therefore, the area of the isosceles triangle is $114.47\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$ accurate to the nearest square centimetre.
Note: We need to remember that the formula for area $A=\sqrt{S\left( S-a \right)\left( S-b \right)\left( S-c \right)}$ is applicable for any triangle with given sides’ length. The value of S is called the semi-perimeter of that triangle. The formula deals with semi-perimeter only. We can never use perimeter as S. The differences of the sides from the semi-perimeter is multiplied in the formula.
Complete step by step answer:
We have been given an isosceles triangle which has a base of 12 cm with equal sides of 20 cm each.

We are going to apply the formula of the area of the isosceles triangle whose sides are given.
For an isosceles triangle with their sides’ length being $a,b,c$ we can have its area as A and the perimeter as 2S.
Therefore, $2S=a+b+c$.
The formula of area for the isosceles triangle will be $A=\sqrt{S\left( S-a \right)\left( S-b \right)\left( S-c \right)}$.
The given values for the sides of our isosceles triangle are $12,20,20$.
We put the values in the equation $2S=a+b+c$ to find the value of S.
So, $2S=a+b+c=12+20+20=52$ which gives $S=\dfrac{52}{2}=26$.
Now we try to find the values of the terms $\left( S-a \right),\left( S-b \right),\left( S-c \right)$.
Therefore, $\left( S-a \right)=26-12=14$
$\left( S-b \right)=26-20=6$
$\left( S-c \right)=26-20=6$
Now we put the values in the equation of $A=\sqrt{S\left( S-a \right)\left( S-b \right)\left( S-c \right)}$.
$A=\sqrt{26\times 14\times 6\times 6}=12\sqrt{91}$.
We need to find the area of this triangle accurate to the nearest square centimetre.
The value of $12\sqrt{91}$ is approximated to $114.47\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$.
Therefore, the area of the isosceles triangle is $114.47\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$ accurate to the nearest square centimetre.
Note: We need to remember that the formula for area $A=\sqrt{S\left( S-a \right)\left( S-b \right)\left( S-c \right)}$ is applicable for any triangle with given sides’ length. The value of S is called the semi-perimeter of that triangle. The formula deals with semi-perimeter only. We can never use perimeter as S. The differences of the sides from the semi-perimeter is multiplied in the formula.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




