
An infinite cylinder of radius $ 'R' $ carrying charge density $ \rho = ar + b{r^2} $ where $ 'r' $ distance of point from the axis and $ a $ , $ b $ are non-zero constant. Find the ratio of $ \dfrac{a}{b} $ if the field out of the cylinder is zero.
$ \left( A \right)\dfrac{R}{4} \\
\left( B \right) - \dfrac{R}{4} \\
\left( C \right) - \dfrac{{3R}}{4} \\
\left( D \right)\dfrac{{3R}}{4} \\ $
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint : In order to solve this question, we are going to first draw a figure for the situation as given in the question, then by using the formulae for the flux and the net current and further simplifying the equations and solving for the ratio $ \dfrac{a}{b} $ , we can find the right answer.
The flux of the field is given by
$ \phi = \dfrac{{{q_{net}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} $
Where flux is the surface integral of an electric field.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
It is given that the radius of the infinite cylinder is $ 'R' $
The charge density is given by $ \rho = ar + b{r^2} $
The distance of point from the axis is $ 'r' $
If we construct a figure for the situation that is given
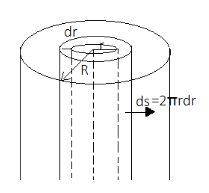
Now, as we know that the flux of the field is given by
$ \phi = \dfrac{{{q_{net}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} $
Where flux is the surface integral of an electric field.
Now, it is given that the field that is coming out of the cylinder is equal to zero, i.e.,
This implies from the formula given for the field, that the flux is also zero for this field
Then, we can see that,
$ {q_{net}} = 0 $
The formula for the net charge of a conductor is given by
$ {q_{net}} = \int\limits_0^R {\rho ds\, = 0} $
Putting the values for the charge density and the small area element, we get
$ {q_{net}} = \int\limits_0^R {\left( {ar + b{r^2}} \right)2\pi rdr = 0} $
Solving this on, we get
$ {q_{net}} = \int\limits_0^R {\left( {a{r^2} + b{r^3}} \right)dr = 0} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{a{R^3}}}{3} = - \dfrac{{b{R^4}}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{b} = - \dfrac{{3R}}{4} \\ $
Hence, the ratio of $ a $ and $ b $ i.e. $ \dfrac{a}{b} $ is $ - \dfrac{{3R}}{4} $
Hence, option $ \left( C \right) - \dfrac{{3R}}{4} $ is the correct answer.
Note :
When the electric field coming out of an infinite cylinder is zero, then it implies that the flux of the field of that cylinder is also zero. Now the zero flux implies that the total net charge stored inside the conductor is also zero. These implications are important in this question to get the ratio.
The flux of the field is given by
$ \phi = \dfrac{{{q_{net}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} $
Where flux is the surface integral of an electric field.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
It is given that the radius of the infinite cylinder is $ 'R' $
The charge density is given by $ \rho = ar + b{r^2} $
The distance of point from the axis is $ 'r' $
If we construct a figure for the situation that is given

Now, as we know that the flux of the field is given by
$ \phi = \dfrac{{{q_{net}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} $
Where flux is the surface integral of an electric field.
Now, it is given that the field that is coming out of the cylinder is equal to zero, i.e.,
This implies from the formula given for the field, that the flux is also zero for this field
Then, we can see that,
$ {q_{net}} = 0 $
The formula for the net charge of a conductor is given by
$ {q_{net}} = \int\limits_0^R {\rho ds\, = 0} $
Putting the values for the charge density and the small area element, we get
$ {q_{net}} = \int\limits_0^R {\left( {ar + b{r^2}} \right)2\pi rdr = 0} $
Solving this on, we get
$ {q_{net}} = \int\limits_0^R {\left( {a{r^2} + b{r^3}} \right)dr = 0} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{a{R^3}}}{3} = - \dfrac{{b{R^4}}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{b} = - \dfrac{{3R}}{4} \\ $
Hence, the ratio of $ a $ and $ b $ i.e. $ \dfrac{a}{b} $ is $ - \dfrac{{3R}}{4} $
Hence, option $ \left( C \right) - \dfrac{{3R}}{4} $ is the correct answer.
Note :
When the electric field coming out of an infinite cylinder is zero, then it implies that the flux of the field of that cylinder is also zero. Now the zero flux implies that the total net charge stored inside the conductor is also zero. These implications are important in this question to get the ratio.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




