
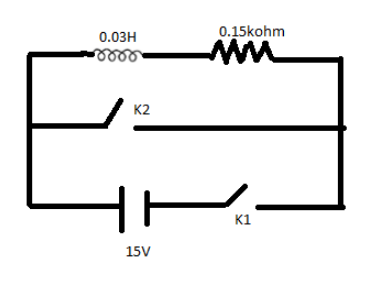
An inductor $(L = 0.03H)$ and a resistor $(R = 0.15K\Omega )$ are connected in series to a battery of $15V$ EMF in a circuit shown below. The key ${K_1}$ has been kept closed for a long time. Then at $t = 0$, ${K_1}$ is opened and key ${K_2}$ is closed simultaneously. At $t = 1ms$,the current in the circuit will be: $({e^5} \cong 150)$
(A) $100mA$
(B) $67mA$
(C) $6.7mA$
(D) $0.67mA$

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint:Here first we have to find the inductor current. Then we have to use KCL to find the inductor equation and then use the current expression in the LR series circuit to find the final current after decay.
Complete step by step answer:
Now first let us see what LR series circuit is-
A LR series circuit consists fundamentally of an inductance inductor,$L$ linked in series to a resistance resistor $R$. The $R$ resistance is the DC resistive value of the wire turns or loops that make up the coil of the inductors.The LR series circuit’s time constant is given as $L/R$ in which $V/R$,after five time constant values, represents the final steady state current value.
Given,
Inductor, $L = 0.03H$
Resistor, $R = 0.15K\Omega $
EMF$ = 15V$
At $t = 0$, ${K_1}$ is closed and key ${K_2}$ is opened simultaneously and the inductor is short circuited.
Let current $i$ be flowing through the circuit, then,
$i = \dfrac{{EMF}}{R} \\
= \dfrac{{15}}{{0.15 \times {{10}^3}}}\,A \\ $
When ${K_1}$is opened and key ${K_2}$ is closed simultaneously, then current will start to decay.
Here the inductor will behave as source and current at any time can be found using KCL-
$ - L\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}} - IR = 0$
...... (i)
Integrating the equation (i), we get-
$\log \dfrac{i}{{{i_ \circ }}} = - t \\
\Rightarrow i = {i_ \circ }{e^{\dfrac{{ - Rt}}
{L}}} \\ $
The decay current is given by-
$i = {i_ \circ }{e^{\dfrac{{ - Rt}}{L}}}$
At time $t = 1ms$ and putting the values of inductor and resistor we get-
$i = 0.67mA$
Hence, at $t = 1ms$,the current in the circuit will be: $i = 0.67mA$
Therefore, option D is correct.
Note:Current in the LR circuit will easily decrease if the resistor is large. To prevent this scenario, the inductor is retained high enough to render $L/R$ so that current will steadily decrease.The decay is slow for large time constant and fast for small time constant.
Complete step by step answer:
Now first let us see what LR series circuit is-
A LR series circuit consists fundamentally of an inductance inductor,$L$ linked in series to a resistance resistor $R$. The $R$ resistance is the DC resistive value of the wire turns or loops that make up the coil of the inductors.The LR series circuit’s time constant is given as $L/R$ in which $V/R$,after five time constant values, represents the final steady state current value.
Given,
Inductor, $L = 0.03H$
Resistor, $R = 0.15K\Omega $
EMF$ = 15V$
At $t = 0$, ${K_1}$ is closed and key ${K_2}$ is opened simultaneously and the inductor is short circuited.
Let current $i$ be flowing through the circuit, then,
$i = \dfrac{{EMF}}{R} \\
= \dfrac{{15}}{{0.15 \times {{10}^3}}}\,A \\ $
When ${K_1}$is opened and key ${K_2}$ is closed simultaneously, then current will start to decay.
Here the inductor will behave as source and current at any time can be found using KCL-
$ - L\dfrac{{di}}{{dt}} - IR = 0$
...... (i)
Integrating the equation (i), we get-
$\log \dfrac{i}{{{i_ \circ }}} = - t \\
\Rightarrow i = {i_ \circ }{e^{\dfrac{{ - Rt}}
{L}}} \\ $
The decay current is given by-
$i = {i_ \circ }{e^{\dfrac{{ - Rt}}{L}}}$
At time $t = 1ms$ and putting the values of inductor and resistor we get-
$i = 0.67mA$
Hence, at $t = 1ms$,the current in the circuit will be: $i = 0.67mA$
Therefore, option D is correct.
Note:Current in the LR circuit will easily decrease if the resistor is large. To prevent this scenario, the inductor is retained high enough to render $L/R$ so that current will steadily decrease.The decay is slow for large time constant and fast for small time constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




