
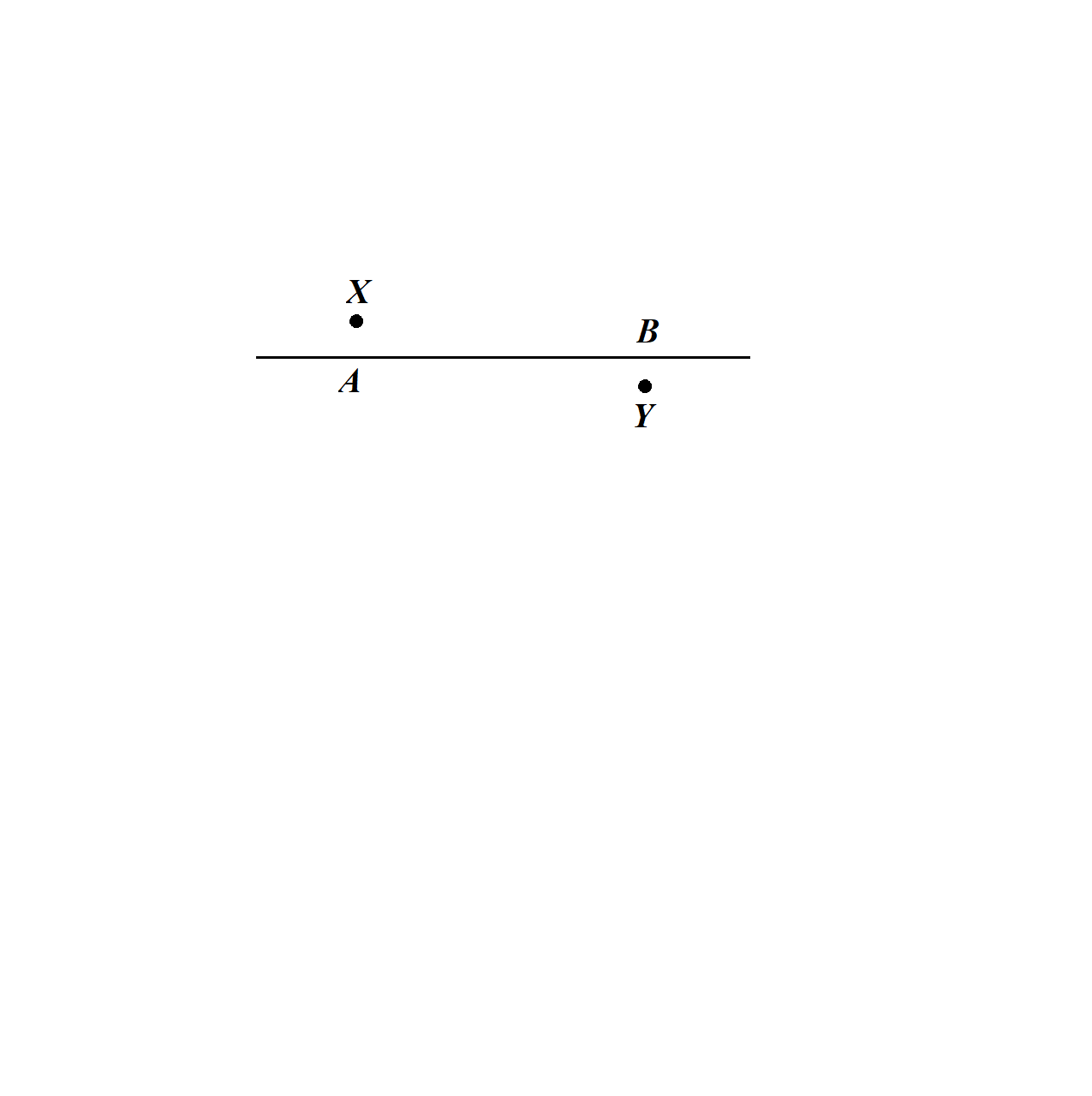
An image Y is formed of a point object X by a lens whose optic axis is AB as shown in figure. Draw a ray diagram to locate the lens and its focus. If the image Y of object X is formed by a concave mirror (having the same optic axis AB) instead of lens, draw another ray diagram to locate the mirror and its focus. Write down the steps of construction of the ray diagrams.

Answer
599.4k+ views
Hint: In the first case, the image obtained is inverted. Thus, the lens used is a convex lens. We will draw the ray diagram with the help of different references such as Optical centre, Focus, and Radius of curvature.
Complete step by step answer:
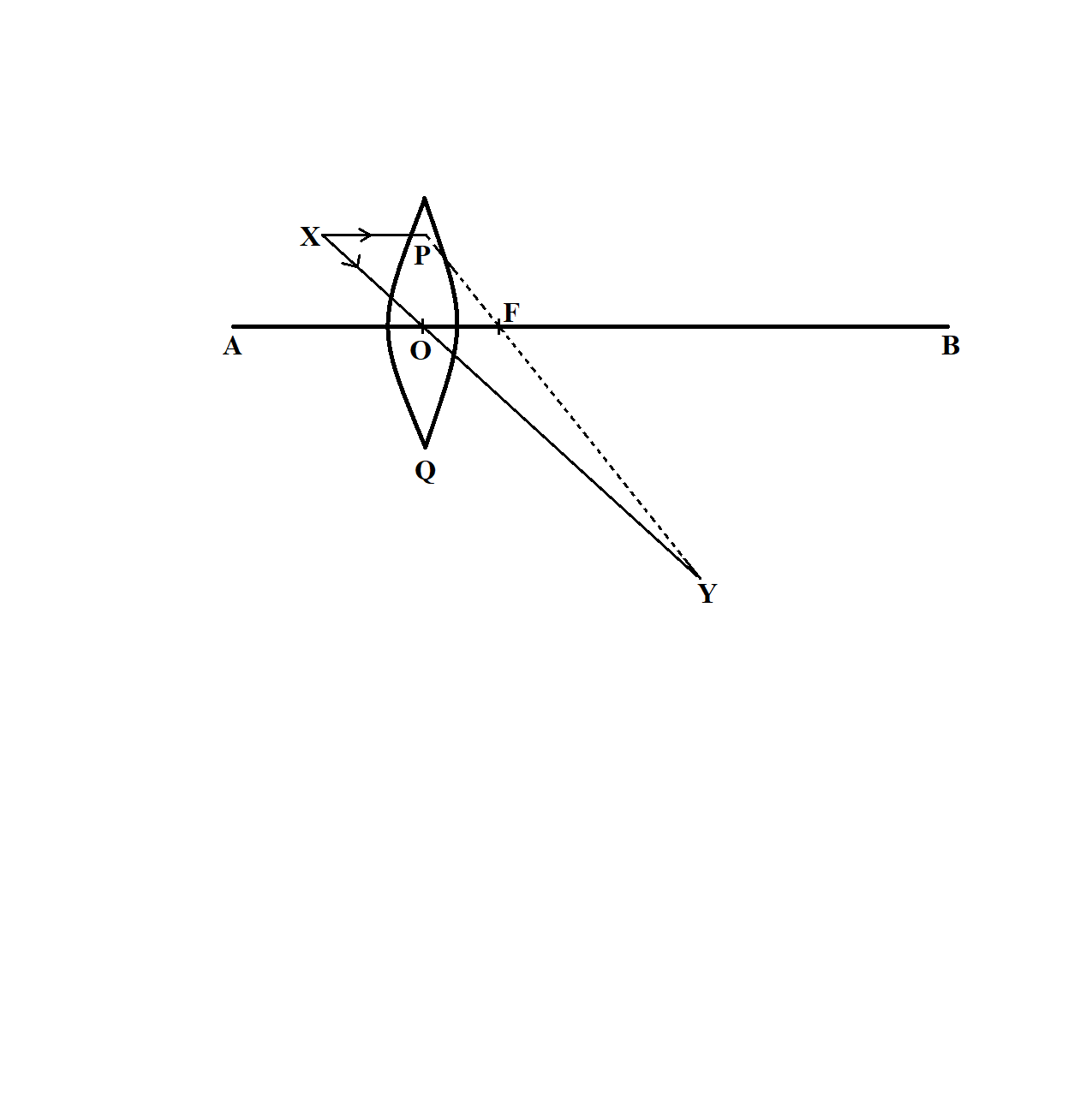
For the first case,
Steps to be followed:
Join the line XY, which intersects the line AB at O.
A line PQ passing through O and perpendicular to AB will represent the position of the lens.
Draw the line from X parallel to AB. Join P to Y, and this line intersects AB at F.
OF is represented as the focal length of the lens.
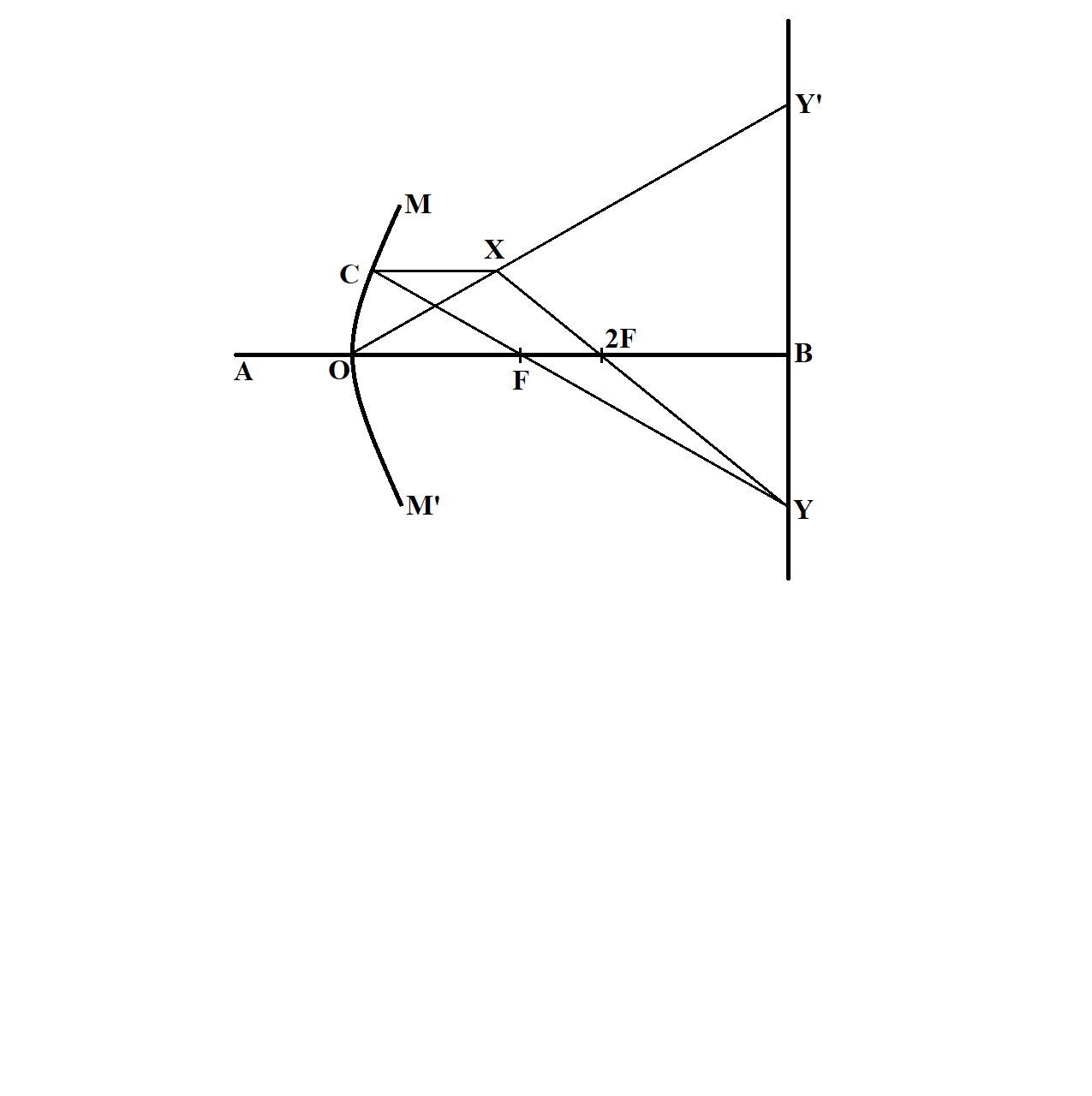
For the second case,
Steps to be followed:
Draw a line Y’BY perpendicular to AB. Take BY=BY’.
Join XY’ and extend it to O. O is the pole of the concave mirror.
Join XY which intersects AB at 2F.
Take 2F as centre of mirror and O to 2F as the radius of curvature of mirror.
Draw an arc MOM’. This arc represents the position of the concave mirror.
Draw XC parallel to AB. Join CY- Intersects AB at F, which is the focus of the concave mirror.
Note: Students should note the following points while constructing ray diagrams:
Note the position of the object carefully.
Understand all the rules of drawing a ray diagram.
Use an appropriate scale for finding the required distances.
Memorize all the formulas, sign conventions, and rules for drawing the diagrams.
Complete step by step answer:
For the first case,
Steps to be followed:
Join the line XY, which intersects the line AB at O.
A line PQ passing through O and perpendicular to AB will represent the position of the lens.
Draw the line from X parallel to AB. Join P to Y, and this line intersects AB at F.
OF is represented as the focal length of the lens.

For the second case,
Steps to be followed:
Draw a line Y’BY perpendicular to AB. Take BY=BY’.
Join XY’ and extend it to O. O is the pole of the concave mirror.
Join XY which intersects AB at 2F.
Take 2F as centre of mirror and O to 2F as the radius of curvature of mirror.
Draw an arc MOM’. This arc represents the position of the concave mirror.
Draw XC parallel to AB. Join CY- Intersects AB at F, which is the focus of the concave mirror.

Note: Students should note the following points while constructing ray diagrams:
Note the position of the object carefully.
Understand all the rules of drawing a ray diagram.
Use an appropriate scale for finding the required distances.
Memorize all the formulas, sign conventions, and rules for drawing the diagrams.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




