
An ideal p-n junction diode can withstand currents up to 10mA under forward bias. The diode has a potential difference of 0.5V across it which is assumed to be independent of current. The maximum voltage of the battery used to forward bias the diode when a resistance of 200$\Omega $ is connected in series with it is
A. 2.5V
B. 2.6V
C. 2.7V
D. 2.8V
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: First we need to draw a circuit diagram showing a diode, a resistance and a battery as given in the question. Then we can apply Kirchoff's law to the circuit to obtain an equation linking the various parameters. Solving the equation for the voltage of the battery, we can get the required answer.
Complete answer:
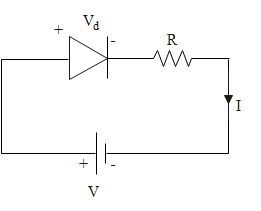
We are given an ideal pn junction diode which is connected to an external battery through a resistance R as shown in the diagram. We have V as the voltage of the battery, ${V_d}$ as the voltage of the diode, R is the value of the resistance attached to it while I is the maximum value of current flowing through the circuit that the diode can withstand without getting damaged. The diode has been forward biased by attaching the positive terminal of the battery to the p side of the diode. We are given the value of some of these parameters which are as follows:
$
I = 10mA = 10 \times {10^{ - 3}}A = {10^{ - 2}}A \\
{V_d} = 0.5V \\
R = 200\Omega \\
$
Now we can apply Kirchhoff's law to the above circuit. We will start from the battery moving in the clockwise direction. Doing so, we obtain the following expression.
$
- V + {V_d} + IR = 0 \\
V = {V_d} + IR \\
$
Now we can insert the known values. Doing so, we get
$V = 0.5 + {10^{ - 2}} \times 200 = 0.5 + 2 = 2.5V$
This is the required value of voltage.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
It should be noted that when a pn junction diode is forward biased then we have a certain amount of current flowing in the circuit due to majority charge carriers crossing the depletion layer. If the diode is reverse biased, then there is an extremely small amount of current flowing due to the minority charge carriers which are able to cross the depletion layer.
Complete answer:

We are given an ideal pn junction diode which is connected to an external battery through a resistance R as shown in the diagram. We have V as the voltage of the battery, ${V_d}$ as the voltage of the diode, R is the value of the resistance attached to it while I is the maximum value of current flowing through the circuit that the diode can withstand without getting damaged. The diode has been forward biased by attaching the positive terminal of the battery to the p side of the diode. We are given the value of some of these parameters which are as follows:
$
I = 10mA = 10 \times {10^{ - 3}}A = {10^{ - 2}}A \\
{V_d} = 0.5V \\
R = 200\Omega \\
$
Now we can apply Kirchhoff's law to the above circuit. We will start from the battery moving in the clockwise direction. Doing so, we obtain the following expression.
$
- V + {V_d} + IR = 0 \\
V = {V_d} + IR \\
$
Now we can insert the known values. Doing so, we get
$V = 0.5 + {10^{ - 2}} \times 200 = 0.5 + 2 = 2.5V$
This is the required value of voltage.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
It should be noted that when a pn junction diode is forward biased then we have a certain amount of current flowing in the circuit due to majority charge carriers crossing the depletion layer. If the diode is reverse biased, then there is an extremely small amount of current flowing due to the minority charge carriers which are able to cross the depletion layer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




