
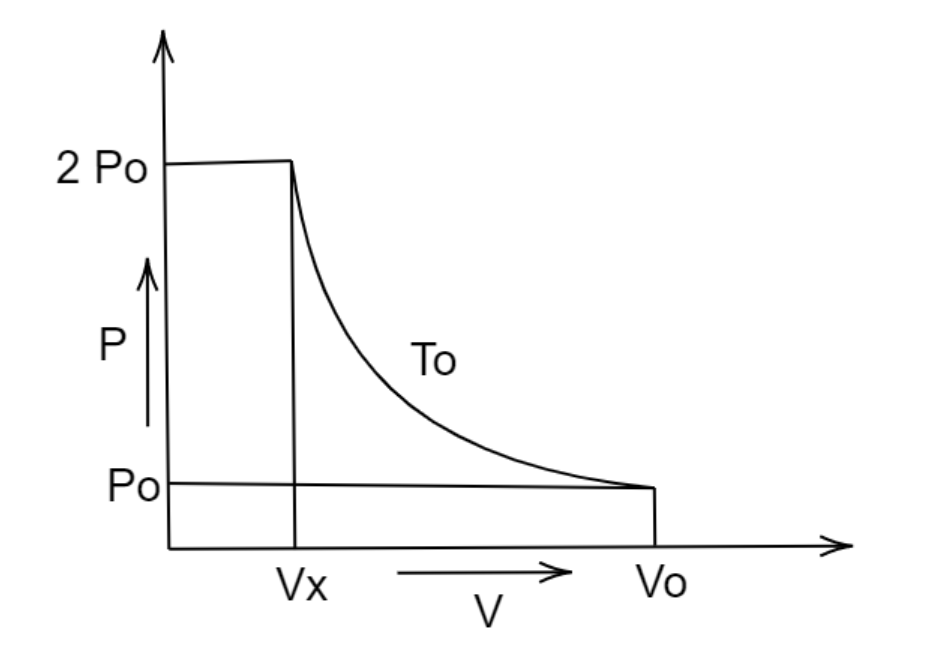
An ideal gas undergoes a state change according to a PV diagram. What is the value of \[Vx\]?
A. \[\dfrac{{V_o}}{2}\]
B. \[V_o\]
C. \[2V_o\]
D. \[\dfrac{{V_o}}{4}\]

Answer
497.4k+ views
Hint: In this question, a PV graph is given. A relation between pressure and the volume of an ideal gas is given. An ideal gas is a hypothetical gas and its behavior is described by kinetic molecular theory of gases.
Complete answer:
An ideal gas law is simply the combination of simple gas law such as Boyle’s law, Charles law and Avogadro’s law. The ideal gas equation is \[PV = nRT\]
Let’s first understand each gas law:
1. Boyle’s law- This law describes the inverse relation between the pressure and volume at a constant temperature and a fixed volume of a gas.
\[P \propto \dfrac{1}{V}\]
2. Charles’s law- This law describes the directly proportional relation between the volume and temperature of a gas where pressure and amount of a gas is kept constant.
\[V \propto T\]
3. Avogadro’s law- This law describes that volume of a gas is directly proportional to the amount of a gas at a constant pressure and temperature.
\[V \propto n\]
By combining all the above law, we get ideal gas equation i.e. \[PV = nRT\]
According to this question, the relation between pressure and volume of a gas is given, so we use Boyle’s law which states that the pressure exerted by a given mass of a gas is inversely proportional to the volume if the temperature and amount of a gas is kept constant.
\[P \propto \dfrac{1}{V}\]
We can also write it as: \[{P_1}{V_1} = {P_2}{V_2}\]
In this question, it is given:
Initial pressure and volume,
\[{P_1}\, = {P_o}\]
\[{V_1} = \,{V_o}\]
Final pressure and volume,
\[{P_2}\, = 2{P_o}\]
\[{V_2}\, = \,{V_x}\]
Put all the values in this equation \[{P_1}{V_1} = {P_2}{V_2}\]
We get,
\[{P_o}\,{V_o}\, = 2{P_o}\,{V_x}\]
\[{V_x} = \dfrac{{{V_o}}}{2}\]
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note:
There is another law which makes the ideal gas equation i.e. Amonton’s law which state that pressure of a gas is directly proportional to temperature at a constant volume and amount of a gas i.e. \[P \propto T\]. It must be noted that no such ideal gas exists in reality. It is just a hypothetical gas which is used to study real gases.
Complete answer:
An ideal gas law is simply the combination of simple gas law such as Boyle’s law, Charles law and Avogadro’s law. The ideal gas equation is \[PV = nRT\]
Let’s first understand each gas law:
1. Boyle’s law- This law describes the inverse relation between the pressure and volume at a constant temperature and a fixed volume of a gas.
\[P \propto \dfrac{1}{V}\]
2. Charles’s law- This law describes the directly proportional relation between the volume and temperature of a gas where pressure and amount of a gas is kept constant.
\[V \propto T\]
3. Avogadro’s law- This law describes that volume of a gas is directly proportional to the amount of a gas at a constant pressure and temperature.
\[V \propto n\]
By combining all the above law, we get ideal gas equation i.e. \[PV = nRT\]
According to this question, the relation between pressure and volume of a gas is given, so we use Boyle’s law which states that the pressure exerted by a given mass of a gas is inversely proportional to the volume if the temperature and amount of a gas is kept constant.
\[P \propto \dfrac{1}{V}\]
We can also write it as: \[{P_1}{V_1} = {P_2}{V_2}\]
In this question, it is given:
Initial pressure and volume,
\[{P_1}\, = {P_o}\]
\[{V_1} = \,{V_o}\]
Final pressure and volume,
\[{P_2}\, = 2{P_o}\]
\[{V_2}\, = \,{V_x}\]
Put all the values in this equation \[{P_1}{V_1} = {P_2}{V_2}\]
We get,
\[{P_o}\,{V_o}\, = 2{P_o}\,{V_x}\]
\[{V_x} = \dfrac{{{V_o}}}{2}\]
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note:
There is another law which makes the ideal gas equation i.e. Amonton’s law which state that pressure of a gas is directly proportional to temperature at a constant volume and amount of a gas i.e. \[P \propto T\]. It must be noted that no such ideal gas exists in reality. It is just a hypothetical gas which is used to study real gases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




