
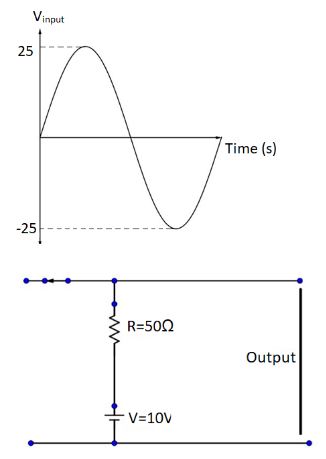
An ideal diode is connected in a circuit with resistance $ R = 50\Omega $ and $ V = 10V $ as shown in figure maximum and minimum value of output voltage. When no load applied is:
(A) 10V,-25V
(B) 10V,-15V

Answer
566.1k+ views
Hint : An ideal diode has zero resistance when it is forward biased and infinity resistance when it is reverse biased. From the arrow, it is evident that the circuit is reverse biased.
Complete step by step answer
An ideal diode is a diode that acts like a perfect conductor when voltage is applied forward biased and like a perfect insulator when voltage is applied reverse biased.
So when positive voltage is applied across the anode to the cathode, the diode conducts forward current instantly. When voltage is applied in reverse, the diode conducts no current at all. It thus behaves like an open circuit.
Given that, an ideal diode is connected in a circuit with resistance $ R = 50\Omega $ and $ V = 10V $ . The a.c. voltage is shown in terms of a sinusoidal wave whose maximum value is 25V and minimum value is-25V.
During the first half cycle, the N-portion is at high potential, since the arrow head is the negative end of the diode. Thus the diode is in reverse bias. The positive end of the diode is thus at negative potential. Thus, no current flows during the positive half cycle.
The output voltage shall thus be equal to the voltage of the battery. Thus, 10V is the value of output voltage.
During the second half cycle, the N-end of the diode is connected to the negative potential, as a result of which, the circuit is in forward bias. The peak voltage shall thus be, -25V.
Hence the correct answer is Option A.
Note
In forward bias, a positive voltage is applied to the p-type side with respect to the n-type side of the junction. With a voltage applied in this way, the holes in the p-type region and the electrons in the n-type region are forced towards the junction. The positive charge applied to the p-type material repels the holes, while the negative charge applied to the n-type material repels the electrons.
Reverse bias usually refers to how a diode is used in a circuit. If a diode is reverse biased, the voltage at the cathode is higher than that at the anode. Therefore, no current will flow until the electric field is so high that the diode breaks down.
Complete step by step answer
An ideal diode is a diode that acts like a perfect conductor when voltage is applied forward biased and like a perfect insulator when voltage is applied reverse biased.
So when positive voltage is applied across the anode to the cathode, the diode conducts forward current instantly. When voltage is applied in reverse, the diode conducts no current at all. It thus behaves like an open circuit.
Given that, an ideal diode is connected in a circuit with resistance $ R = 50\Omega $ and $ V = 10V $ . The a.c. voltage is shown in terms of a sinusoidal wave whose maximum value is 25V and minimum value is-25V.
During the first half cycle, the N-portion is at high potential, since the arrow head is the negative end of the diode. Thus the diode is in reverse bias. The positive end of the diode is thus at negative potential. Thus, no current flows during the positive half cycle.
The output voltage shall thus be equal to the voltage of the battery. Thus, 10V is the value of output voltage.
During the second half cycle, the N-end of the diode is connected to the negative potential, as a result of which, the circuit is in forward bias. The peak voltage shall thus be, -25V.
Hence the correct answer is Option A.
Note
In forward bias, a positive voltage is applied to the p-type side with respect to the n-type side of the junction. With a voltage applied in this way, the holes in the p-type region and the electrons in the n-type region are forced towards the junction. The positive charge applied to the p-type material repels the holes, while the negative charge applied to the n-type material repels the electrons.
Reverse bias usually refers to how a diode is used in a circuit. If a diode is reverse biased, the voltage at the cathode is higher than that at the anode. Therefore, no current will flow until the electric field is so high that the diode breaks down.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




