
An example of nitrogenous fertilizer is _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _.
(A) sugar-phosphate
(B) urea
(C) potassium sulphate
(D) potassium chloride
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: The example of nitrogenous fertilizer will be the one that will contain nitrogen elements in the compound. The nitrogen is given to plants in two forms - ammonium nitrogen or nitrate. This is because the plants can take only these forms. So, the compound will contain nitrogen in any of these forms.
Complete step by step solution:
Nitrogen is an important constituent for plant growth and development. It is required during both the vegetative and the reproductive phases of the plant growth. Nitrogen deficiency in plants can be seen in various parts of the plant. So, to fully fill this deficiency, nitrogenous fertilizer is given to plants.
So, what a nitrogenous fertilizer is.
A nitrogenous fertilizer is a nitrogen-based fertilizer. It contains the element nitrogen with other organic masses.
Let us see the options given to us above. The option with a Nitrogen-A element in its structure will be the nitrogenous fertilizer.
The option a.) is the sugar-phosphate. Such kind of fertilizer contains the sugar and the phosphate as components. So, this is not the correct answer.
The option b.) is the urea. We have the structure of urea as -
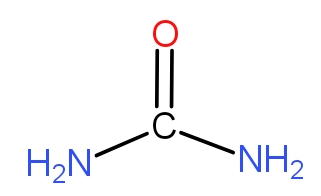
The urea molecule contains two $N{H_2}$units. SO, this will provide nitrogen to the plants and thus urea can act as nitrogenous fertilizer.
So, the correct option is option (B).
The third option we have is potassium sulphate. This fertilizer contains potassium metal and sulphate ions. So, it is not nitrogenous based fertilizer. Thus, the option c.) is not the correct answer.
The last option is potassium chloride. It will also contain the potassium ions and chloride ions and thus will not be nitrogenous based fertilizer. So, even this is the wrong option.
Note: The ammonium nitrogen fertilizers gradually lower the pH of soil. The ammonium nitrogen has a positive charge and soil particles are able to absorb it. Thus, it makes the soil acidic. The urea increases the pH of soil temporarily and this may lead to the burning of the plant roots even.
Complete step by step solution:
Nitrogen is an important constituent for plant growth and development. It is required during both the vegetative and the reproductive phases of the plant growth. Nitrogen deficiency in plants can be seen in various parts of the plant. So, to fully fill this deficiency, nitrogenous fertilizer is given to plants.
So, what a nitrogenous fertilizer is.
A nitrogenous fertilizer is a nitrogen-based fertilizer. It contains the element nitrogen with other organic masses.
Let us see the options given to us above. The option with a Nitrogen-A element in its structure will be the nitrogenous fertilizer.
The option a.) is the sugar-phosphate. Such kind of fertilizer contains the sugar and the phosphate as components. So, this is not the correct answer.
The option b.) is the urea. We have the structure of urea as -

The urea molecule contains two $N{H_2}$units. SO, this will provide nitrogen to the plants and thus urea can act as nitrogenous fertilizer.
So, the correct option is option (B).
The third option we have is potassium sulphate. This fertilizer contains potassium metal and sulphate ions. So, it is not nitrogenous based fertilizer. Thus, the option c.) is not the correct answer.
The last option is potassium chloride. It will also contain the potassium ions and chloride ions and thus will not be nitrogenous based fertilizer. So, even this is the wrong option.
Note: The ammonium nitrogen fertilizers gradually lower the pH of soil. The ammonium nitrogen has a positive charge and soil particles are able to absorb it. Thus, it makes the soil acidic. The urea increases the pH of soil temporarily and this may lead to the burning of the plant roots even.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




