
An elevator is accelerating upwards with an acceleration of $6m/{s^2}$. Inside it, a person of mass \[50kg\] is standing on a weighing machine which is kept on an inclined plane having an angle of inclination ${60^0}$. The reading of the weighing machine is:
A. $40kg$
B. \[\;160kg\]
C. \[80kg\]
D. \[50kg\]
Answer
495k+ views
Hint:Weight is simply defined by the gravitational force acting on an object. While dealing with elevator questions we also come across another term called apparent weight. Apparent weight simply means how heavy or light an object feels. The normal force acting on the weighing machine will give us the weight of the person.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first write the information given in the question.
$a = 6m/{s^2}$, $m = 50kg$, $inclination = {60^o}$
We have to find the reading of the weighing machine.
We will first draw the free body diagram of the weighing machine. That is first we will write all the forces acting on the weighing machine only in the horizontal and vertical direction as shown in the following figure.
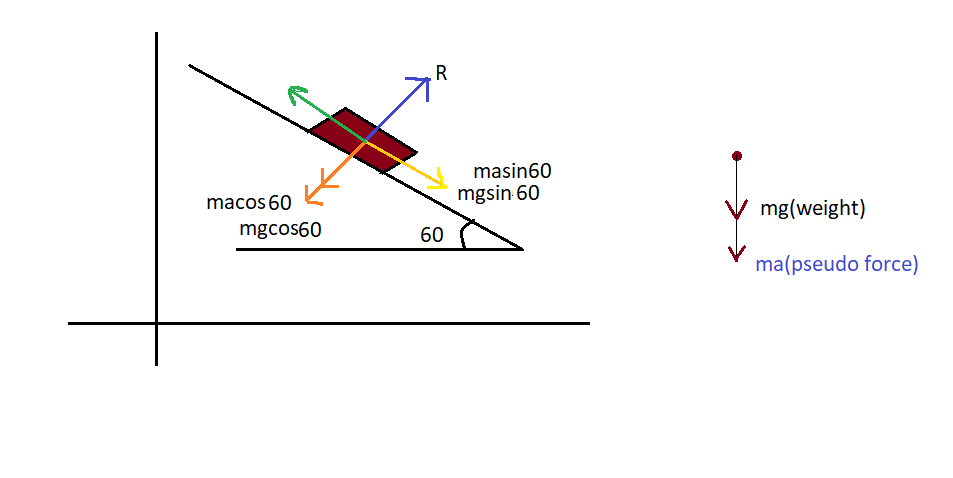
From the figure, we can write the normal force as below.
$R = mg\cos \theta + ma\cos \theta $
Let us substitute the values.
$R = 50 \times 10\cos 60 + 50 \times 6\cos 60$
On further simplifying.
$R = 500 \times \dfrac{1}{2} + 300 \times \dfrac{1}{2} = 400N$
So, the normal force on the machine is 400N. Let us divide it by acceleration due to gravity to find weight.
${W_{MachineReading}} = \dfrac{{400}}{{10}} = 40kg$
Hence, the correct option is (A) $40kg$.
Note:
The weight of an object is calculated by $W = mg$, where $m$ is the mass of the object and $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
When a person is in the elevator and the elevator is accelerating upwards, then the apparent weight is more than the actual weight.
Similarly, when the elevator accelerates downwards, the apparent weight is less than the actual weight.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first write the information given in the question.
$a = 6m/{s^2}$, $m = 50kg$, $inclination = {60^o}$
We have to find the reading of the weighing machine.
We will first draw the free body diagram of the weighing machine. That is first we will write all the forces acting on the weighing machine only in the horizontal and vertical direction as shown in the following figure.

From the figure, we can write the normal force as below.
$R = mg\cos \theta + ma\cos \theta $
Let us substitute the values.
$R = 50 \times 10\cos 60 + 50 \times 6\cos 60$
On further simplifying.
$R = 500 \times \dfrac{1}{2} + 300 \times \dfrac{1}{2} = 400N$
So, the normal force on the machine is 400N. Let us divide it by acceleration due to gravity to find weight.
${W_{MachineReading}} = \dfrac{{400}}{{10}} = 40kg$
Hence, the correct option is (A) $40kg$.
Note:
The weight of an object is calculated by $W = mg$, where $m$ is the mass of the object and $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
When a person is in the elevator and the elevator is accelerating upwards, then the apparent weight is more than the actual weight.
Similarly, when the elevator accelerates downwards, the apparent weight is less than the actual weight.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




