
An elevator accelerates upward at a constant rate. A uniform string of length \[\;L\;\]and mass\[M\]supports a small block of mass\[M\]that hangs from the ceiling of the elevator. The tension at distance\[l\]from the ceiling is\[T\]. The acceleration of the elevator is
A. \[\dfrac{T}{{M + m - \dfrac{{ml}}{L}}} - g\]
B. \[\dfrac{T}{{2M + m - \dfrac{{ml}}{L}}} - g\]
C. \[\dfrac{T}{{M + \dfrac{{ml}}{L}}} - g\]
D. \[\dfrac{T}{{2M - m + \dfrac{{ml}}{L}}} - g\]
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: Here the elevator moves with a constant acceleration upwards. The elevator consists of a small block and a string inside it. Therefore the string and the block also move with the same constant acceleration. They have said that a small part of the string with length \[l\] has tension \[T\]. We need to find out the equation of motion of both the parts of the string in order to find the acceleration of the elevator.
Complete step by step solution:
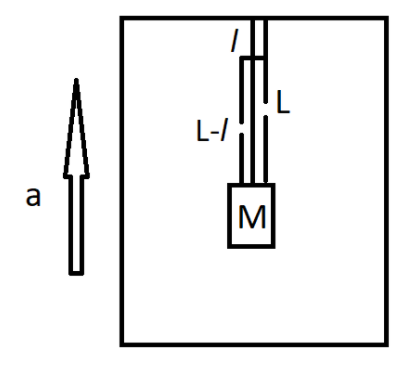
First, we need to find the equation of motion of the lower part. That is the part of the string whose length is \[L - l\]along with the small block of the mass \[M\]
We know the total mass of the string is \[m\].
The mass of the string of length \[L - l\] is given by,
\[{m_{L - l}} = \dfrac{m}{L}(L - l)\]
Here,\[{m_{L - l}}\] is the mass of the part of the string whose length is \[L - l\]
\[m\] is the total mass of the string inside the elevator.
\[L\] is the total length of the string inside the elevator.
We know the equation of motion,
\[T - mg = ma\]
We are using \[T\] in the place of a force because tension is a kind of force that acts on the string. We can draw the free body diagram of above mentioned lower part as
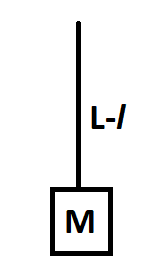
The mass of the part of the string whose length is \[L - l\] is \[{m_{L - l}} = \dfrac{m}{L}(L - l)\]. We also know the mass of the small block is\[M\].
Substituting this in the equation of motion,
\[T - \dfrac{m}{L}(L - l)g - Mg = \left[ {\dfrac{m}{L}(L - l) + M} \right]a\]
Rearranging the above equation to find acceleration we get,
\[\dfrac{{T - \left[ {\dfrac{m}{L}(L - l) + M} \right]g}}{{\dfrac{m}{L}(L - l) + M}}\]\[ = a\]
If we expand and write the above equation we get,
\[\dfrac{T}{{\dfrac{m}{L}(L - l) + M}} - g = a\]
\[\dfrac{T}{{M + m - \dfrac{{ml}}{L}}} - g = a\]
Therefore the correct option is A.
Note:
Note that we have found the acceleration only for the lower part and not for the elevator. But we can say that the elevator will also have the same acceleration because the string is inside the elevator therefore both string and the elevator will have the same acceleration.
Complete step by step solution:

First, we need to find the equation of motion of the lower part. That is the part of the string whose length is \[L - l\]along with the small block of the mass \[M\]
We know the total mass of the string is \[m\].
The mass of the string of length \[L - l\] is given by,
\[{m_{L - l}} = \dfrac{m}{L}(L - l)\]
Here,\[{m_{L - l}}\] is the mass of the part of the string whose length is \[L - l\]
\[m\] is the total mass of the string inside the elevator.
\[L\] is the total length of the string inside the elevator.
We know the equation of motion,
\[T - mg = ma\]
We are using \[T\] in the place of a force because tension is a kind of force that acts on the string. We can draw the free body diagram of above mentioned lower part as
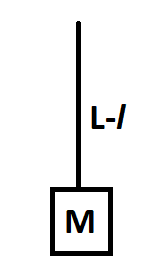
The mass of the part of the string whose length is \[L - l\] is \[{m_{L - l}} = \dfrac{m}{L}(L - l)\]. We also know the mass of the small block is\[M\].
Substituting this in the equation of motion,
\[T - \dfrac{m}{L}(L - l)g - Mg = \left[ {\dfrac{m}{L}(L - l) + M} \right]a\]
Rearranging the above equation to find acceleration we get,
\[\dfrac{{T - \left[ {\dfrac{m}{L}(L - l) + M} \right]g}}{{\dfrac{m}{L}(L - l) + M}}\]\[ = a\]
If we expand and write the above equation we get,
\[\dfrac{T}{{\dfrac{m}{L}(L - l) + M}} - g = a\]
\[\dfrac{T}{{M + m - \dfrac{{ml}}{L}}} - g = a\]
Therefore the correct option is A.
Note:
Note that we have found the acceleration only for the lower part and not for the elevator. But we can say that the elevator will also have the same acceleration because the string is inside the elevator therefore both string and the elevator will have the same acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




