
An element $X$ belongs to the\[{3^{rd}}\] period and group 16 of the modern periodic table. Write the molecular formula of the compound when $X$ reacts with hydrogen and write its electron dot structure?
Answer
550.8k+ views
Hint:The element belongs to group \[16\] . X belongs to the oxygen family. So, $X$ possesses valency of \[2\] . Therefore, its electronic configuration is \[2,{\text{ }}8,{\text{ }}6\] . Hence it has \[6\] valence electrons its valency is \[8 - 6\, = \,2{\text{ }}\left( { - 2} \right)\].
2) When reacting with hydrogen its molecular formula is hydride.
3) Lewis electron dot structure gives the valence structure present in the compound.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The molecular formula contains the chemical symbols for the constituent elements which are followed by numeric subscripts describing the number of atoms of each element present in the molecule. The constituent elements are represented by their chemical symbols and the number of atoms of each element present in each molecule is shown as in a subscript following that element’s symbol. The electronic configuration of an element describes how an electron is distributed in its atomic orbital. In the third group the electronic configuration is group \[16\] which is \[2,{\text{ }}8,{\text{ }}6\] . Hence its valency is \[2\] .
Similarly, when hydrogen is reacted with that compound the compound is called its hydride. The compound formed is $X{H_2}$ .
A Lewis electron dot diagram is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. As we know that the number of dots will be equal to the number of valence electrons in an atom.
So, the Lewis structure will be given as follows;
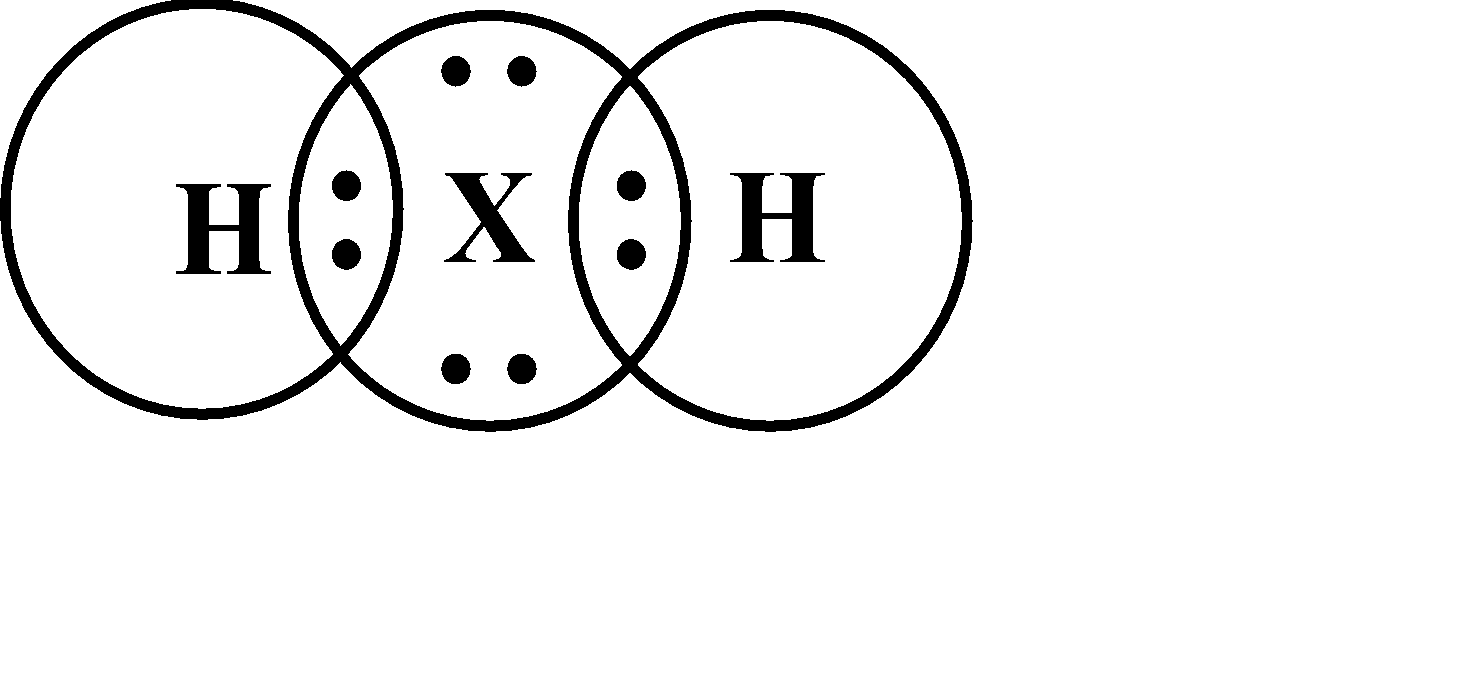
Note:A structural formula is for the indication of the number of atoms and also their arrangement in space. Therefore, the $X$ atom must be mostly non-metal according to the electronic configuration and the name of the element is sulfur. Since, sulfur has \[6\] valence electrons and valency is \[2\] .
2) When reacting with hydrogen its molecular formula is hydride.
3) Lewis electron dot structure gives the valence structure present in the compound.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The molecular formula contains the chemical symbols for the constituent elements which are followed by numeric subscripts describing the number of atoms of each element present in the molecule. The constituent elements are represented by their chemical symbols and the number of atoms of each element present in each molecule is shown as in a subscript following that element’s symbol. The electronic configuration of an element describes how an electron is distributed in its atomic orbital. In the third group the electronic configuration is group \[16\] which is \[2,{\text{ }}8,{\text{ }}6\] . Hence its valency is \[2\] .
Similarly, when hydrogen is reacted with that compound the compound is called its hydride. The compound formed is $X{H_2}$ .
A Lewis electron dot diagram is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. As we know that the number of dots will be equal to the number of valence electrons in an atom.
So, the Lewis structure will be given as follows;

Note:A structural formula is for the indication of the number of atoms and also their arrangement in space. Therefore, the $X$ atom must be mostly non-metal according to the electronic configuration and the name of the element is sulfur. Since, sulfur has \[6\] valence electrons and valency is \[2\] .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




