
An electric heater which is connected to a 220 V supply line has two resistance coils. A and B of 240Ω resistance each, these coils can be used separately (one at a time), in series or in parallel. Calculate the current drawn when:
i) only one coil A is used
ii) coils A and B are used in series.
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: The resistance of the resistance coils and the given voltage can be used in Ohm’s law to find the current drawn. While finding the current drawn when the coils A and B are connected in series, we must first find the equivalent resistance of the coils. Then, we can use Ohm’s law to find the current drawn.
Formula used:
$\eqalign{
& V = IR \cr
& {R_{series}} = {R_1} + {R_2} \cr} $
Complete answer:
Firstly, we are going to draw the electric circuit, for better understanding. The circuit when only one coil A is used is drawn below.
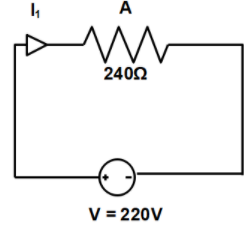
Now, let the resistance of A be ‘${R_A}$’, then in the circuit drawn above the current ‘${I_1}$' can be found by applying Ohm’s law as follows,
$\eqalign{
& V = {I_1}{R_A} \Rightarrow {I_1} = \dfrac{V}{{{R_A}}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_1} = \dfrac{{220V}}{{240\Omega }} \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_1} = 0.917A \cr} $
Therefore, the current drawn by the electric heater when only coil A is used is $0.917A$.
Next, we’ll draw the circuit diagram when the coils A and B are connected in series.
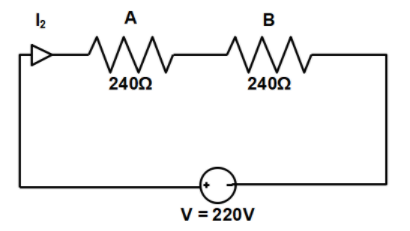
As the resistance coils are connected in series, the equivalent resistance of the circuit coils will be
$\eqalign{
& {R_{eq}} = {R_A} + {R_B} \cr
& \Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = 240\Omega + 240\Omega \cr
& \Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = 480\Omega \cr} $
If we assume that ‘${I_2}$’ is the current drawn when the coils are connected in series, by Ohm’s law we have
$\eqalign{
& V = {I_2}{R_{eq}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_2} = \dfrac{V}{{{R_{eq}}}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_2} = \dfrac{{220V}}{{480\Omega }} = 0.458A \cr
& \therefore {I_2} = 0.458A \cr} $
Therefore, the current drawn when the coils A and B are connected in series is $0.458A$.
Note:
The resistance coils are used in the electric heaters due to the property of their heat dissipation.
Here, we’re representing the electric heater as a resistor, instead of using the standard symbol for an electric heater, as we’re only concerned with the resistor properties of the electric heater. This also applies to all the problems in which heating coils are used, like an electric kettle.
Formula used:
$\eqalign{
& V = IR \cr
& {R_{series}} = {R_1} + {R_2} \cr} $
Complete answer:
Firstly, we are going to draw the electric circuit, for better understanding. The circuit when only one coil A is used is drawn below.

Now, let the resistance of A be ‘${R_A}$’, then in the circuit drawn above the current ‘${I_1}$' can be found by applying Ohm’s law as follows,
$\eqalign{
& V = {I_1}{R_A} \Rightarrow {I_1} = \dfrac{V}{{{R_A}}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_1} = \dfrac{{220V}}{{240\Omega }} \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_1} = 0.917A \cr} $
Therefore, the current drawn by the electric heater when only coil A is used is $0.917A$.
Next, we’ll draw the circuit diagram when the coils A and B are connected in series.

As the resistance coils are connected in series, the equivalent resistance of the circuit coils will be
$\eqalign{
& {R_{eq}} = {R_A} + {R_B} \cr
& \Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = 240\Omega + 240\Omega \cr
& \Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = 480\Omega \cr} $
If we assume that ‘${I_2}$’ is the current drawn when the coils are connected in series, by Ohm’s law we have
$\eqalign{
& V = {I_2}{R_{eq}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_2} = \dfrac{V}{{{R_{eq}}}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {I_2} = \dfrac{{220V}}{{480\Omega }} = 0.458A \cr
& \therefore {I_2} = 0.458A \cr} $
Therefore, the current drawn when the coils A and B are connected in series is $0.458A$.
Note:
The resistance coils are used in the electric heaters due to the property of their heat dissipation.
Here, we’re representing the electric heater as a resistor, instead of using the standard symbol for an electric heater, as we’re only concerned with the resistor properties of the electric heater. This also applies to all the problems in which heating coils are used, like an electric kettle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




