
An ecological pyramid of biomass is often an inverted pyramid in which of the following ecosystems?
A) Desert
B) Ocean
C) Tundra
D) Rainforest
Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: The ecological pyramid of biomass becomes inverted when the mass of producers in an ecosystem is less than the successive consumers.
Complete answer:
Before we try to figure out where and how an ecological pyramid is inverted, first of all let’s define the ecological pyramids.
An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation of a food chain, depicting the interrelationships of different organisms, occupying different trophic levels based on their feeding habit.
In a typical ecological pyramid, the base is occupied by the producers, followed by the primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers and top carnivores. The ecological pyramids have a disadvantage that they do not provide appropriate representation of decomposers.
Now, there are following types of ecological pyramids:
1) Pyramid of energy that shows the flow of energy in an ecosystem. It is always upright because energy is lost at each trophic level in the form of heat and respiratory losses.
2) Pyramid of numbers that depicts the number of organisms at each trophic level. Generally, the producers are the largest in numbers, followed by a gradual decrease in number of consumer organisms. So, it is upright. A somewhat inverted pyramid of numbers is seen when a tree is a producer and is supporting a number of organisms.
3) Pyramid of biomass shows the relation between organisms occupying the different trophic levels based on their biomass. So, if in a given ecosystem, the producers are bulky, the pyramid of biomass will be upright and if the producers have low biomass, it becomes inverted.
An inverted pyramid of biomass is seen in oceans or aquatic ecosystems where the producers are phytoplanktons. Their number is quite large but their biomass is less than zooplanktons and so on.
An inverted pyramid of biomass in ocean is shown below:
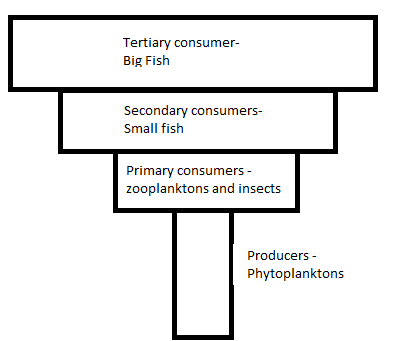
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note: The biomass of producers in desert and rainforest is way too more than the consumers, so they show an upright pyramid of biomass.
Complete answer:
Before we try to figure out where and how an ecological pyramid is inverted, first of all let’s define the ecological pyramids.
An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation of a food chain, depicting the interrelationships of different organisms, occupying different trophic levels based on their feeding habit.
In a typical ecological pyramid, the base is occupied by the producers, followed by the primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers and top carnivores. The ecological pyramids have a disadvantage that they do not provide appropriate representation of decomposers.
Now, there are following types of ecological pyramids:
1) Pyramid of energy that shows the flow of energy in an ecosystem. It is always upright because energy is lost at each trophic level in the form of heat and respiratory losses.
2) Pyramid of numbers that depicts the number of organisms at each trophic level. Generally, the producers are the largest in numbers, followed by a gradual decrease in number of consumer organisms. So, it is upright. A somewhat inverted pyramid of numbers is seen when a tree is a producer and is supporting a number of organisms.
3) Pyramid of biomass shows the relation between organisms occupying the different trophic levels based on their biomass. So, if in a given ecosystem, the producers are bulky, the pyramid of biomass will be upright and if the producers have low biomass, it becomes inverted.
An inverted pyramid of biomass is seen in oceans or aquatic ecosystems where the producers are phytoplanktons. Their number is quite large but their biomass is less than zooplanktons and so on.
An inverted pyramid of biomass in ocean is shown below:

Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note: The biomass of producers in desert and rainforest is way too more than the consumers, so they show an upright pyramid of biomass.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




