
An automobile dealer provides motorcycles and scooters in three body patterns and 4 different colours each. The number of choices open to a customer is
$\begin{align}
& {{(i)}^{5}}{{C}_{3}} \\
& {{(ii)}^{4}}{{C}_{3}} \\
& (iii)4\times 3 \\
& (iv)4\times 3\times 2 \\
\end{align}$
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: The question is based on the multiplication theorem of combination. According to it, if an event ${{E}_{1}}$ can occur in ${{n}_{1}}$ different ways, then the number of ways of simultaneous occurrence of both the events in a definite order is ${{n}_{1}}\times {{n}_{2}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, we have ${{n}_{1}}=2,{{n}_{2}}=3$ and ${{n}_{3}}=4$. So, on multiplying these values we will get the answer.
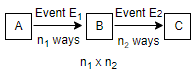
Now, in the question, the customer has to choose motorcycles or scooter, then the body patterns and then the colour.
So, let ${{E}_{1}}$ be the event to choose a motorcycle or scooter. So ${{n}_{1}}=2$.
Then, let ${{E}_{2}}$ be the event to choose body patterns among the 3 patterns. So, ${{n}_{2}}=3$.
And, let ${{E}_{3}}$ be the event to choose colour among 4 different colours. So, ${{n}_{3}}=4$.
So, number of choices open to the customer is equal to the number of ways simultaneous occurrence of all the events in order,
$\underset{\left( {{n}_{1}} \right)}{\mathop{{{E}_{1}}}}\,\to \underset{\left( {{n}_{2}} \right)}{\mathop{{{E}_{2}}}}\,\to \underset{\left( {{n}_{3}} \right)}{\mathop{{{E}_{3}}}}\,$
Hence, the number of ways = ${{n}_{1}}\times {{n}_{2}}\times {{n}_{3}}$.
On substituting the value of ${{n}_{1}}=2,{{n}_{2}}=3$ and ${{n}_{3}}=4$, we will get as follows.
$\begin{align}
& =2\times 3\times 4 \\
& =24 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we get that the number of choices open to the customer is equal to 24.
Hence, option (d), that is, $4\times 3\times 2$ is the correct answer.
Note: In this question, all the motorcycles and scooters are unique, different from each other. We can directly multiply all the ways, but if two or more things or ways are identical then we can’t multiply directly, as there will be repetition and we have to divide it by the number of identical ways in any event.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, we have ${{n}_{1}}=2,{{n}_{2}}=3$ and ${{n}_{3}}=4$. So, on multiplying these values we will get the answer.
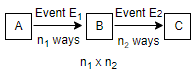
Now, in the question, the customer has to choose motorcycles or scooter, then the body patterns and then the colour.
So, let ${{E}_{1}}$ be the event to choose a motorcycle or scooter. So ${{n}_{1}}=2$.
Then, let ${{E}_{2}}$ be the event to choose body patterns among the 3 patterns. So, ${{n}_{2}}=3$.
And, let ${{E}_{3}}$ be the event to choose colour among 4 different colours. So, ${{n}_{3}}=4$.
So, number of choices open to the customer is equal to the number of ways simultaneous occurrence of all the events in order,
$\underset{\left( {{n}_{1}} \right)}{\mathop{{{E}_{1}}}}\,\to \underset{\left( {{n}_{2}} \right)}{\mathop{{{E}_{2}}}}\,\to \underset{\left( {{n}_{3}} \right)}{\mathop{{{E}_{3}}}}\,$
Hence, the number of ways = ${{n}_{1}}\times {{n}_{2}}\times {{n}_{3}}$.
On substituting the value of ${{n}_{1}}=2,{{n}_{2}}=3$ and ${{n}_{3}}=4$, we will get as follows.
$\begin{align}
& =2\times 3\times 4 \\
& =24 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we get that the number of choices open to the customer is equal to 24.
Hence, option (d), that is, $4\times 3\times 2$ is the correct answer.
Note: In this question, all the motorcycles and scooters are unique, different from each other. We can directly multiply all the ways, but if two or more things or ways are identical then we can’t multiply directly, as there will be repetition and we have to divide it by the number of identical ways in any event.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




