
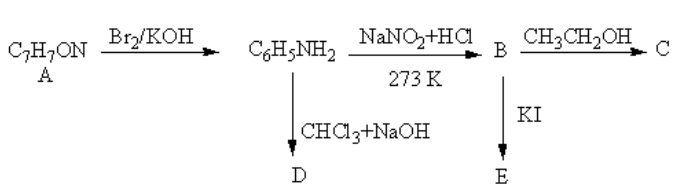
An aromatic compound A of molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{7}}}{\text{ON}} $ undergoes a series of reaction as shown below. Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions.

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint:The reagent ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/KOH}}$ is used to convert the amide functional group into amine. The reagent ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + HCl}}$ is used to convert the amine functional group into diazonium ion. The reagent ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$ adds the proton to cation formed by diazonium ion. The reagent ${\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_3}{\text{ + NaOH}}$ is used to convert the amine functional group into cyanide. The reagent ${\text{KI}}$ is used to add iodine.
Complete answer:
The reagent ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/KOH}}$ converts the amide functional group into amine so, the compound A should be an amide. The structure of A and its reaction is as follows:
The amide reacts with bromine and potassium hydroxide to give amine. The reaction is known as the Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
Initially, the base sodium hydroxide abstract proton form acetamide to generate an anion of amide
The anion of amide now attacks on bromine, so an N-bromoamide generates.
Again the base attacks on N-bromoamide so an anion of bromoamide forms.
Then the methyl group attached with the carbonyl group shifts to the nitrogen atom and bromide ion leaves forming an isocyanate structure.
Nucleophilic attack of water on isocyanate takes place which loses the carbon dioxide and forms a structure in which nitrogen has a negative charge and one hydrogen and one benzene group.
Then the protonation of this nitrogen takes place which gives aniline.
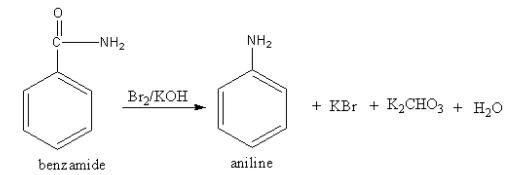
So, A is benzamide.
The reagent ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + HCl}}$converts the amine functional group into diazonium ion. The product of reaction of aniline with${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + HCl}} $ is as follows:
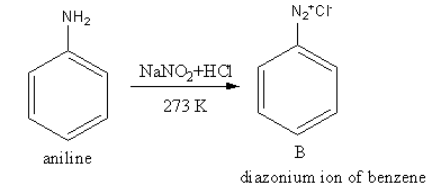
So, B is a diazonium salt of benzene.
The reagent ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$ is used for protonation of benzene cation. The product of reaction of diazonium salt of benzene with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$ is as follows:
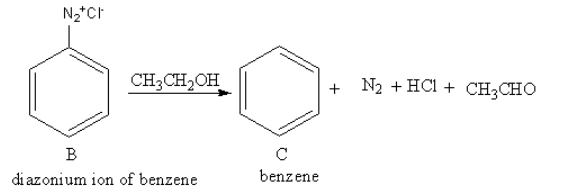
So, C is benzene.
The reagent ${\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_3}{\text{ + NaOH}}$converts the amine functional group into cyanide. The conversion of the amine functional group into the isocyanide functional group by the reaction of primary amine with chloroform and base is known as Carbylamine reaction.
The product of reaction of aniline with${\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_3}{\text{ + NaOH}}$ is as follows:
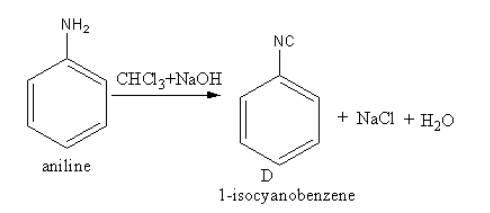
So, D is phenyl isocyanide also known as $1 - $isocyanatobenzene.
The reagent ${\text{KI}}$ is used to add iodine. The reaction of benzene with potassium iodide is a nucleophilic substitution reaction of benzene.
The product of the reaction of benzene with potassium iodide is as follows:
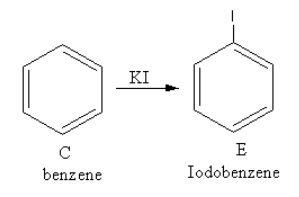
So, E is iodobenzene.
Therefore, A , B ,C, D and E are benzamide, diazonium salt, benzene, phenyl isocyanide and iodobenzene respectively.
Note:
The Reagent used in the Carbylamine reaction is chloroform and a base. The Carbylamine reaction is also known as Hofmann isocyanide synthesis. The reagent used in the Hoffmann bromamide reaction is base.
Complete answer:
The reagent ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/KOH}}$ converts the amide functional group into amine so, the compound A should be an amide. The structure of A and its reaction is as follows:
The amide reacts with bromine and potassium hydroxide to give amine. The reaction is known as the Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
Initially, the base sodium hydroxide abstract proton form acetamide to generate an anion of amide
The anion of amide now attacks on bromine, so an N-bromoamide generates.
Again the base attacks on N-bromoamide so an anion of bromoamide forms.
Then the methyl group attached with the carbonyl group shifts to the nitrogen atom and bromide ion leaves forming an isocyanate structure.
Nucleophilic attack of water on isocyanate takes place which loses the carbon dioxide and forms a structure in which nitrogen has a negative charge and one hydrogen and one benzene group.
Then the protonation of this nitrogen takes place which gives aniline.

So, A is benzamide.
The reagent ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + HCl}}$converts the amine functional group into diazonium ion. The product of reaction of aniline with${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + HCl}} $ is as follows:

So, B is a diazonium salt of benzene.
The reagent ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$ is used for protonation of benzene cation. The product of reaction of diazonium salt of benzene with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$ is as follows:

So, C is benzene.
The reagent ${\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_3}{\text{ + NaOH}}$converts the amine functional group into cyanide. The conversion of the amine functional group into the isocyanide functional group by the reaction of primary amine with chloroform and base is known as Carbylamine reaction.
The product of reaction of aniline with${\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_3}{\text{ + NaOH}}$ is as follows:

So, D is phenyl isocyanide also known as $1 - $isocyanatobenzene.
The reagent ${\text{KI}}$ is used to add iodine. The reaction of benzene with potassium iodide is a nucleophilic substitution reaction of benzene.
The product of the reaction of benzene with potassium iodide is as follows:

So, E is iodobenzene.
Therefore, A , B ,C, D and E are benzamide, diazonium salt, benzene, phenyl isocyanide and iodobenzene respectively.
Note:
The Reagent used in the Carbylamine reaction is chloroform and a base. The Carbylamine reaction is also known as Hofmann isocyanide synthesis. The reagent used in the Hoffmann bromamide reaction is base.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




