
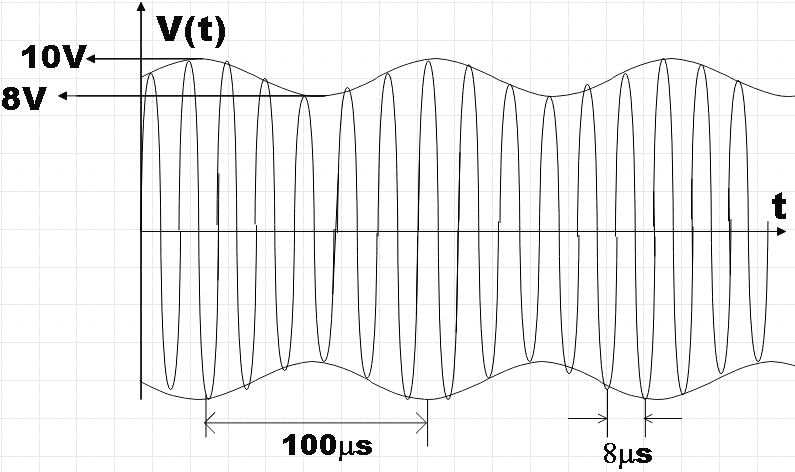
An amplitude modulated signal is plotted below:
Which one of the following best describes the above signal?
A.$\left( 9+\sin \left( 2.5\pi \times {{10}^{5}}t \right) \right)\sin \left( 2\pi \times {{10}^{4}}t \right)V$
B.$\left( 9+\sin \left( 4\pi \times {{10}^{4}}t \right) \right)\sin \left( 5\pi \times {{10}^{5}}t \right)V$
C.$\left( 1+9\sin \left( 2\pi \times {{10}^{4}}t \right) \right)\sin \left( 2.5\pi \times {{10}^{5}}t \right)V$
D.$\left( 9+\sin \left( 2\pi \times {{10}^{4}}t \right) \right)\sin \left( 2.5\pi \times {{10}^{5}}t \right)V$

Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: Firstly find out the voltage of signal wave as well as carrier wave from the given values of maximum and minimum voltages of AM signal. Now, from the given time period of both signal wave and carrier wave, you could find the angular frequencies of both. Then, you could substitute all these in the standard expression to get the required expression.
Formula used:
Equation of AM signal,
${{V}_{AM}}=\left( {{V}_{C}}+{{V}_{S}}\sin {{\omega }_{S}}t \right)\sin {{\omega }_{C}}t$
Complete Step by step solution:
In the given representation of an amplitude modulated wave (AM wave), the maximum and minimum voltage is given and along with that we are also given the time period of both signal waves as well as the time period of the carrier wave.
We know that the maximum voltage of the amplitude modulated signal is the sum of the voltages of carrier wave and signal wave, that is,
${{V}_{\max }}={{V}_{C}}+{{V}_{S}}$
But the maximum voltage for the given signal is 10V, so,
${{V}_{\max }}={{V}_{C}}+{{V}_{S}}=10V$………………………………….. (1)
We also know that the minimum voltage of the amplitude modulated signal is the difference of the voltages of carrier wave and signal wave, that is,
${{V}_{\min }}={{V}_{C}}-{{V}_{S}}$
But the minimum voltage for the given signal is 8V, so,
${{V}_{\min }}={{V}_{C}}-{{V}_{S}}=8V$………………………………….. (2)
Adding equations (1) and (2), we get,
$2{{V}_{C}}=19$
$\therefore {{V}_{C}}=9V$ …………………………. (3)
Substituting in (1),
${{V}_{S}}=10-9=1V$ ………………………. (4)
We have the time period of signal wave as$100\mu s$, so the angular frequency can be given by,
${{\omega }_{S}}=\dfrac{2\pi }{{{T}_{S}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\omega }_{S}}=\dfrac{2\pi }{100\times {{10}^{-6}}s}$
$\therefore {{\omega }_{S}}=2\pi \times {{10}^{4}}{{s}^{-1}}$ ……………………………. (5)
Similarly, we have the time period of carrier wave as$8\mu s$, so the angular frequency can be given by,
${{\omega }_{C}}=\dfrac{2\pi }{{{T}_{C}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\omega }_{C}}=\dfrac{2\pi }{8\times {{10}^{-6}}s}$
$\therefore {{\omega }_{C}}=2.5\pi \times {{10}^{5}}{{s}^{-1}}$ ………………………….. (6)
Now let us recall the equation for voltage of an amplitude modulated wave.
${{V}_{AM}}=\left( {{V}_{C}}+{{V}_{S}}\sin {{\omega }_{S}}t \right)\sin {{\omega }_{C}}t$
Now we could directly substitute (3), (4), (5) and (6) to get,
${{V}_{AM}}=\left( 9+\left( 1 \right)\sin \left( 2\pi \times {{10}^{4}} \right)t \right)\sin \left( 2.5\pi \times {{10}^{5}} \right)t$
So we find that the given signal is best described by,
$\left( 9+\sin \left( 2\pi \times {{10}^{4}}t \right) \right)\sin \left( 2.5\pi \times {{10}^{5}}t \right)V$
Hence, option D is the right answer.
Note:
In the case of the amplitude modulated wave, the amplitude of the carrier signal varies in accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal. In the given diagram the signal wave is represented by dotted lines and the other high frequency wave inside it is the carrier wave. Also, the carrier waves contain no information within it.
Formula used:
Equation of AM signal,
${{V}_{AM}}=\left( {{V}_{C}}+{{V}_{S}}\sin {{\omega }_{S}}t \right)\sin {{\omega }_{C}}t$
Complete Step by step solution:
In the given representation of an amplitude modulated wave (AM wave), the maximum and minimum voltage is given and along with that we are also given the time period of both signal waves as well as the time period of the carrier wave.
We know that the maximum voltage of the amplitude modulated signal is the sum of the voltages of carrier wave and signal wave, that is,
${{V}_{\max }}={{V}_{C}}+{{V}_{S}}$
But the maximum voltage for the given signal is 10V, so,
${{V}_{\max }}={{V}_{C}}+{{V}_{S}}=10V$………………………………….. (1)
We also know that the minimum voltage of the amplitude modulated signal is the difference of the voltages of carrier wave and signal wave, that is,
${{V}_{\min }}={{V}_{C}}-{{V}_{S}}$
But the minimum voltage for the given signal is 8V, so,
${{V}_{\min }}={{V}_{C}}-{{V}_{S}}=8V$………………………………….. (2)
Adding equations (1) and (2), we get,
$2{{V}_{C}}=19$
$\therefore {{V}_{C}}=9V$ …………………………. (3)
Substituting in (1),
${{V}_{S}}=10-9=1V$ ………………………. (4)
We have the time period of signal wave as$100\mu s$, so the angular frequency can be given by,
${{\omega }_{S}}=\dfrac{2\pi }{{{T}_{S}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\omega }_{S}}=\dfrac{2\pi }{100\times {{10}^{-6}}s}$
$\therefore {{\omega }_{S}}=2\pi \times {{10}^{4}}{{s}^{-1}}$ ……………………………. (5)
Similarly, we have the time period of carrier wave as$8\mu s$, so the angular frequency can be given by,
${{\omega }_{C}}=\dfrac{2\pi }{{{T}_{C}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\omega }_{C}}=\dfrac{2\pi }{8\times {{10}^{-6}}s}$
$\therefore {{\omega }_{C}}=2.5\pi \times {{10}^{5}}{{s}^{-1}}$ ………………………….. (6)
Now let us recall the equation for voltage of an amplitude modulated wave.
${{V}_{AM}}=\left( {{V}_{C}}+{{V}_{S}}\sin {{\omega }_{S}}t \right)\sin {{\omega }_{C}}t$
Now we could directly substitute (3), (4), (5) and (6) to get,
${{V}_{AM}}=\left( 9+\left( 1 \right)\sin \left( 2\pi \times {{10}^{4}} \right)t \right)\sin \left( 2.5\pi \times {{10}^{5}} \right)t$
So we find that the given signal is best described by,
$\left( 9+\sin \left( 2\pi \times {{10}^{4}}t \right) \right)\sin \left( 2.5\pi \times {{10}^{5}}t \right)V$
Hence, option D is the right answer.
Note:
In the case of the amplitude modulated wave, the amplitude of the carrier signal varies in accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal. In the given diagram the signal wave is represented by dotted lines and the other high frequency wave inside it is the carrier wave. Also, the carrier waves contain no information within it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




