
An alternating current is converted to direct current by
A. Rectifier
B. Dynamo
C. Transformer
D. Motor
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Alternating current is a current in which the current reverses the direction and the magnitude of current changes continuously with respect to time. In alternating current changes its magnitude from maximum to minimum through zero with the time .But in the case of direct current, the current does not change with time and flows in only one direction. A diode is a device which converts the positive half of alternating current to direct current. But in the negative half of the alternating current the output of the diode is zero. So the output during the positive half cycle of alternating current of a diode is maximum and during the negative half cycle, the output is zero.
Complete answer:
A diode acts as a switch, during the forward bias of the diode it allows the current to pass through it and during reversed bias it acts as an open switch. A rectifier uses diodes as its elements. There are two types of rectifier: half-wave and full-wave rectifier. A half-wave rectifier uses one diode and converts half of the input alternating current to direct current and the full wave rectifier consists of two diodes in the two branches and converts the both positive-half cycle as well as negative-half cycle of the input alternating current to direct current.
So the rectifier is a device which converts the input alternating current to the output direct current.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
In half-wave rectification the rectifier conducts current only during the positive half-cycles of input a.c supply.The negative half-cycles of ac. supplies are suppressed i.e. during negative half-cycles, no current is conducted and no voltage appears across the load. Therefore, current always flows in one direction (i.e. dc) through the load though after every half-cycle.
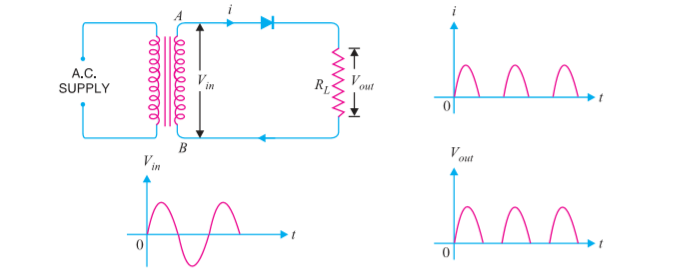
Circuit details: Figure shows the circuit where a single crystal diode acts as a half-wave rectifier. The a.c supply to be rectified is applied in series with the lode and load resistance ${{R}_{L}}$ Generally, a c supply Is given through a transformer.
Operation: The alternating voltage across the secondary winding changes polarities after every half-cycle. During the positive half-cycle of input voltage, end A becomes positive with respect to end B. Due to this the diode forward biased and hence it will conduct current. During the negative half-cycle, end A is negative with respect and B. So the diode is reverse biased and it conducts no current. Therefore, current flows through the diode during positive half-cycles of input alternating voltage only and it is blocked during the negative half-cycles. In this way, current flows through load always in the same direction. Hence d.c output is obtained across the load.
Note:
Disadvantages: The main disadvantages of a half-wave rectifier are
(i)The output is in the form of pulsating current.
(ii) This pulsating current in the load contains alternating components whose basic frequency is equal to the supply frequency.
(iii) The a c. supply delivers power only half the time. Therefore, the output is low.
Complete answer:
A diode acts as a switch, during the forward bias of the diode it allows the current to pass through it and during reversed bias it acts as an open switch. A rectifier uses diodes as its elements. There are two types of rectifier: half-wave and full-wave rectifier. A half-wave rectifier uses one diode and converts half of the input alternating current to direct current and the full wave rectifier consists of two diodes in the two branches and converts the both positive-half cycle as well as negative-half cycle of the input alternating current to direct current.
So the rectifier is a device which converts the input alternating current to the output direct current.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
In half-wave rectification the rectifier conducts current only during the positive half-cycles of input a.c supply.The negative half-cycles of ac. supplies are suppressed i.e. during negative half-cycles, no current is conducted and no voltage appears across the load. Therefore, current always flows in one direction (i.e. dc) through the load though after every half-cycle.

Circuit details: Figure shows the circuit where a single crystal diode acts as a half-wave rectifier. The a.c supply to be rectified is applied in series with the lode and load resistance ${{R}_{L}}$ Generally, a c supply Is given through a transformer.
Operation: The alternating voltage across the secondary winding changes polarities after every half-cycle. During the positive half-cycle of input voltage, end A becomes positive with respect to end B. Due to this the diode forward biased and hence it will conduct current. During the negative half-cycle, end A is negative with respect and B. So the diode is reverse biased and it conducts no current. Therefore, current flows through the diode during positive half-cycles of input alternating voltage only and it is blocked during the negative half-cycles. In this way, current flows through load always in the same direction. Hence d.c output is obtained across the load.
Note:
Disadvantages: The main disadvantages of a half-wave rectifier are
(i)The output is in the form of pulsating current.
(ii) This pulsating current in the load contains alternating components whose basic frequency is equal to the supply frequency.
(iii) The a c. supply delivers power only half the time. Therefore, the output is low.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




