
An alkene given two molecules of $HCHO$, one mole of $C{{O}_{2}}$ and one mole of $C{{H}_{3}}COCHO$ on ozonolysis. What is its structure
A.
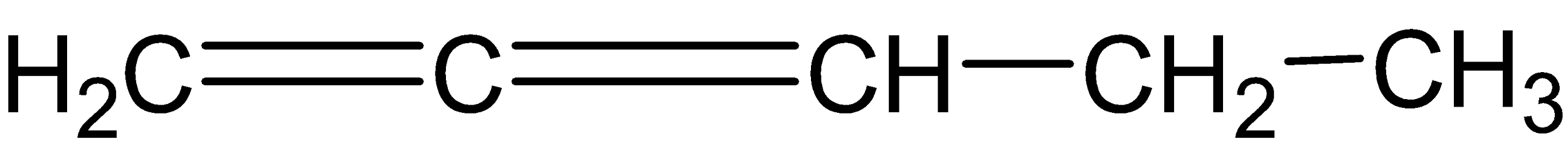
B.
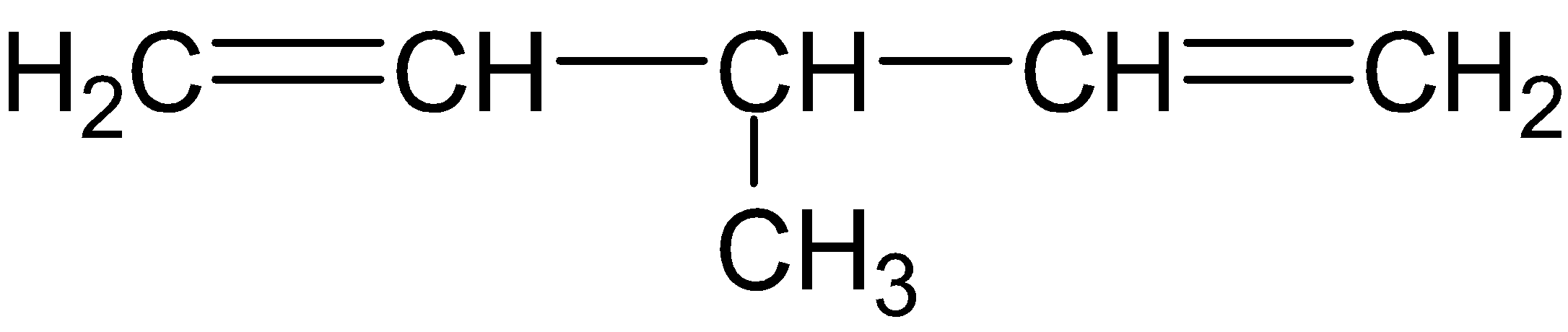
C.
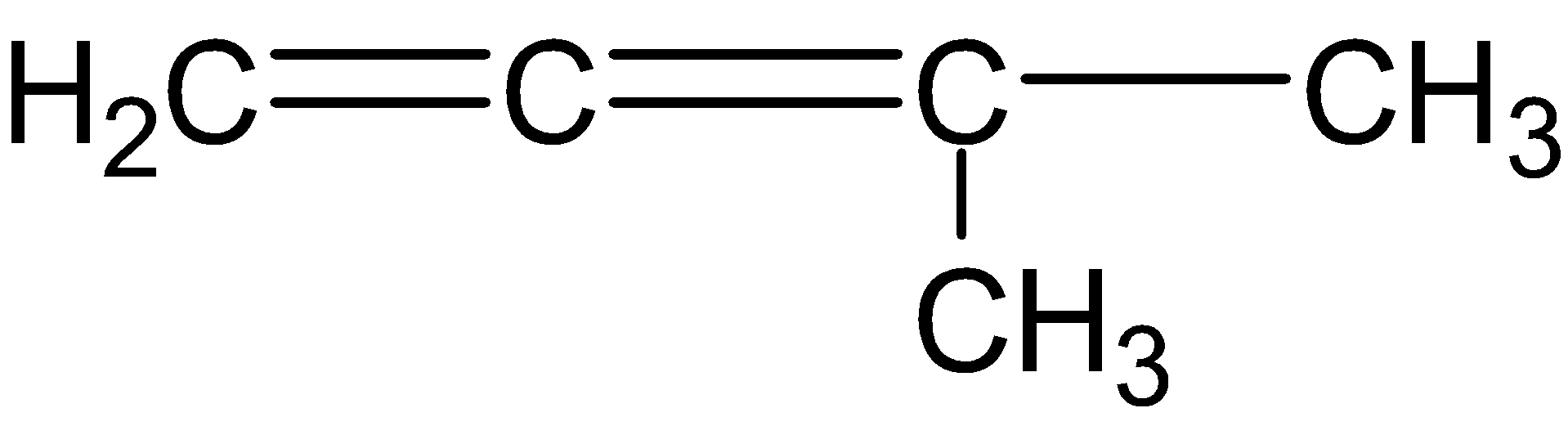
D.

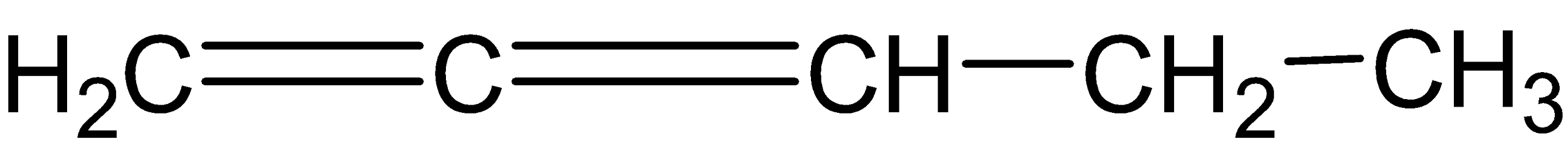



Answer
357k+ views
Hint: The ozonolysis of alkenes is a method of oxidatively cleaving alkenes or alkynes using ozone, ${{O}_{3}}$. By this method, carbon-carbon double bonds or triple bonds are replaced by double bonds with oxygen. Here we have to check whether the given substrates are alkenes or alkynes to produce the desired product.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Ozonolysis is a method in which ozone cleaves the unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes, or azo compounds. Thereby cleaving the double-bonded oxygen of alkene and alkynes produce carbonyl compounds. Also by ozonolysis, azo compounds produce nitrosamines. Through this oxidising method alcohols, ketones, aldehydes as well as carboxylic acids can be formed.
The intermediate ozonide further converts to a carbonyl derivative after completion of the workup. Here the workup may be reductive or oxidative. Carboxylic acids are produced by oxidative workup and aldehydes or ketones are formed by a reductive workup of ozonide.
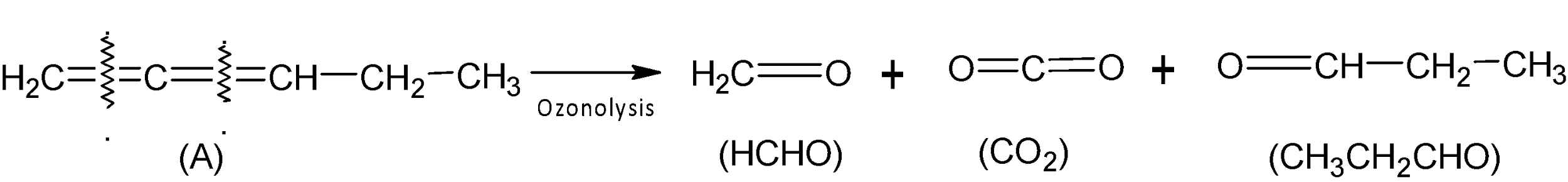
When compound (A) undergoes ozonolysis, one molecule of $HCHO$, $C{{O}_{2}}$and $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CHO$are formed after reductive work up.
By ozonolysis of compound (B), we get two molecules $HCHO$and one molecule ${{(CHO)}_{2}}CH(C{{H}_{3}})$ after reductive workup.
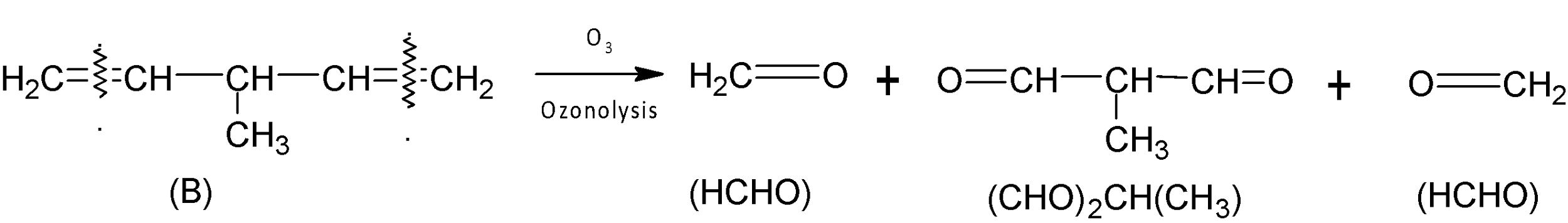
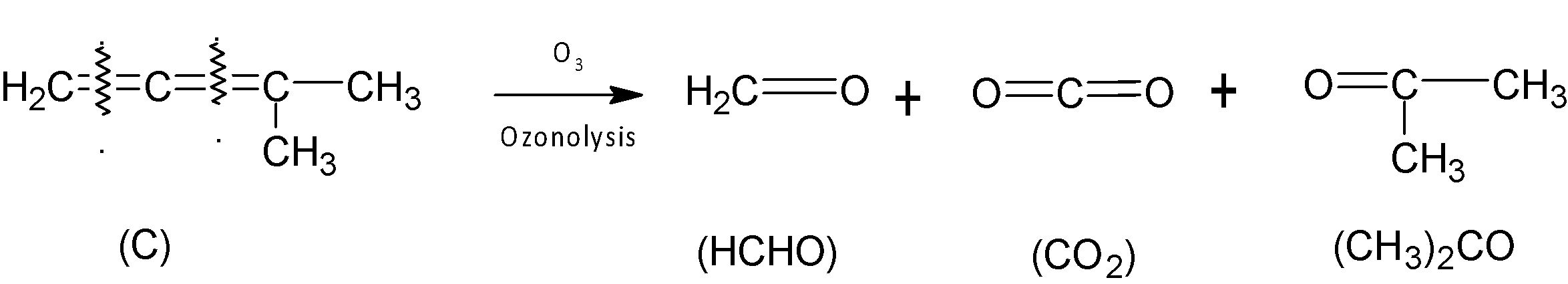
By ozonolysis of compound (C), we get one molecule of $HCHO,C{{O}_{2}}$and ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}C=O$ after work up.
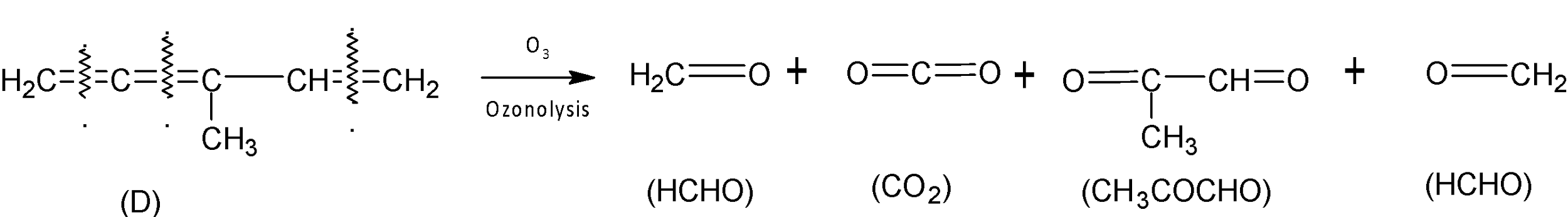
When compound (D) undergoes ozonolysis, two molecules of $HCHO$ and one molecule of $C{{O}_{2}}$and $C{{H}_{3}}COCHO$are produced after work up.
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note: To approach the question we must take care about the product, which is being asked. Here in this question, the final product is a carbonyl compound, formed by reductive work but if the final product is carboxylic acid then the reaction follows a way of oxidative work up.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Ozonolysis is a method in which ozone cleaves the unsaturated bonds of alkenes, alkynes, or azo compounds. Thereby cleaving the double-bonded oxygen of alkene and alkynes produce carbonyl compounds. Also by ozonolysis, azo compounds produce nitrosamines. Through this oxidising method alcohols, ketones, aldehydes as well as carboxylic acids can be formed.
The intermediate ozonide further converts to a carbonyl derivative after completion of the workup. Here the workup may be reductive or oxidative. Carboxylic acids are produced by oxidative workup and aldehydes or ketones are formed by a reductive workup of ozonide.
When compound (A) undergoes ozonolysis, one molecule of $HCHO$, $C{{O}_{2}}$and $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CHO$are formed after reductive work up.

By ozonolysis of compound (B), we get two molecules $HCHO$and one molecule ${{(CHO)}_{2}}CH(C{{H}_{3}})$ after reductive workup.
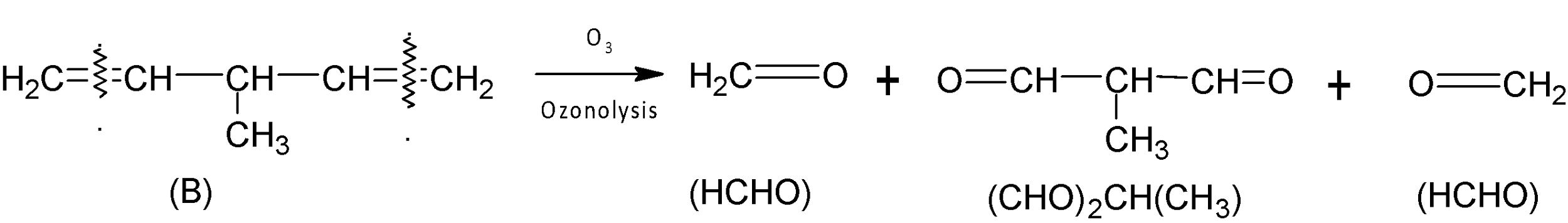
By ozonolysis of compound (C), we get one molecule of $HCHO,C{{O}_{2}}$and ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}C=O$ after work up.

When compound (D) undergoes ozonolysis, two molecules of $HCHO$ and one molecule of $C{{O}_{2}}$and $C{{H}_{3}}COCHO$are produced after work up.

Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note: To approach the question we must take care about the product, which is being asked. Here in this question, the final product is a carbonyl compound, formed by reductive work but if the final product is carboxylic acid then the reaction follows a way of oxidative work up.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




