
An alcohol of formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{9}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}{\text{O}}$ reacts with ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$ to form a compound having a formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{9}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\text{O}}$. The original alcohol might be:
A.
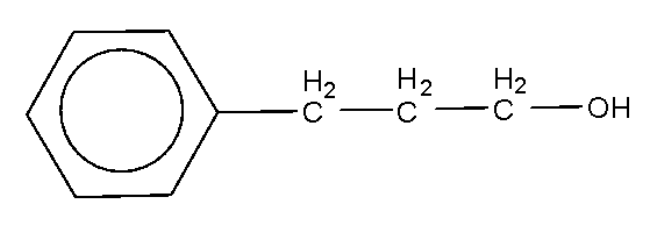
B.
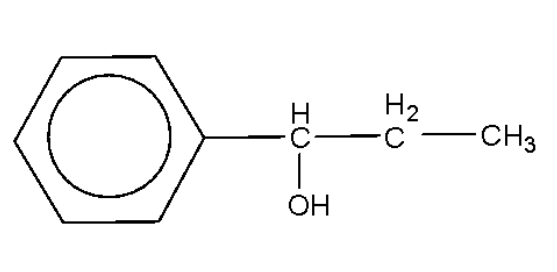
C.
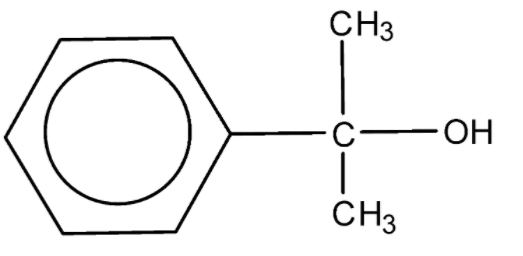
D.
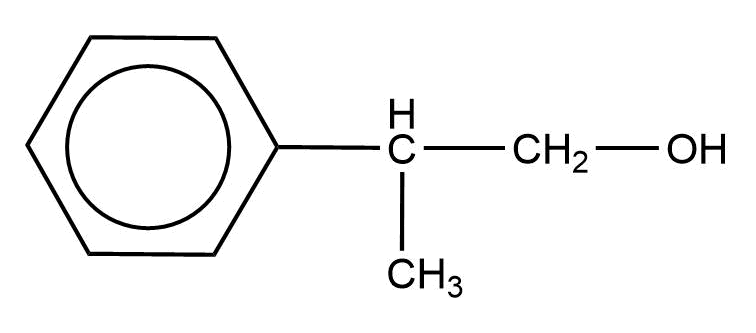




Answer
557.4k+ views
Hint: Sodium Dichromate oxidises different organic compounds, under different acidic conditions as it is a strong oxidising agent. Alcohol can oxidise to carbonyl compounds or carboxylic acid.
Complete Step by step solution:
Alcohols are oxidized by oxidising agents like sodium dichromate and potassium permanganate under highly acidic conditions to form aldehydes or ketones. This may be further oxidized to form carboxylic acids. The empirical formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{9}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\text{O}}$ has six carbon atoms and 5 hydrogen atoms for the phenyl ring, which leaves us with three carbon atoms, 5 hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom. In the above options all the options have the said number of carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and oxygen atoms.
Among the given options only option B will be oxidized by the sodium dichromate to form the compound with the empirical formula as given.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Notes: Sodium and potassium dichromate are strong oxidising agents that can oxidise alcohols into aldehydes and ketones. Due to the oxidation, the orange oxidising agent turns green due to the formation of the chromic salt. The type of products depends on the type of the alcohol. Primary alcohols give either aldehydes or ketones depending on the reaction conditions. Secondary alcohols are always converted to form ketones by the action of Sodium and potassium dichromate under acidic conditions. While tertiary alcohols are not converted into either alcohols or ketones due to their inability to react.
Complete Step by step solution:
Alcohols are oxidized by oxidising agents like sodium dichromate and potassium permanganate under highly acidic conditions to form aldehydes or ketones. This may be further oxidized to form carboxylic acids. The empirical formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{9}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\text{O}}$ has six carbon atoms and 5 hydrogen atoms for the phenyl ring, which leaves us with three carbon atoms, 5 hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom. In the above options all the options have the said number of carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and oxygen atoms.
Among the given options only option B will be oxidized by the sodium dichromate to form the compound with the empirical formula as given.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Notes: Sodium and potassium dichromate are strong oxidising agents that can oxidise alcohols into aldehydes and ketones. Due to the oxidation, the orange oxidising agent turns green due to the formation of the chromic salt. The type of products depends on the type of the alcohol. Primary alcohols give either aldehydes or ketones depending on the reaction conditions. Secondary alcohols are always converted to form ketones by the action of Sodium and potassium dichromate under acidic conditions. While tertiary alcohols are not converted into either alcohols or ketones due to their inability to react.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




