
An alcohol A $({C_{10}}{H_{18}}O)$ is converted into a mixture of alkenes B and C on being heated with potassium hydrogen sulphate $(KHS{O_4})$ . Catalytic hydrogenation of B and C yield the same product. Assuming the dehydration of alcohol proceeds without rearrangement, deduce the structure of alcohol A and alkenes C .
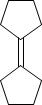
COMPOUND-B

Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint:Potassium hydrogen sulphate is used as a dehydrating agent. Dehydration means removal of water. Hydrogenation is the addition of hydrogen molecules. Such processes generally require catalysts.
Complete step by step answer:
Potassium hydrogen sulphate is a dehydrating agent. The elimination of water molecules from a compound is called dehydration. When alcohols are treated with dehydrating agents, they give alkene as a product. This reaction is also called as $beta - $ elimination of alcohols.
In the dehydration reaction of alcohol, the $ - OH$ group from the $alpha $ carbon and hydrogen from the $beta $ carbon is lost as the water molecule. If there are more than one type of $beta $ hydrogen , then more than one type of product is possible.
The major product of dehydration of alcohol is given by Saytzeff’s rule. In the elimination reaction of alcohols, the more substituted alkene is formed as the major product. The other minor product is the less substituted alkene.
Now alcohol A gives alkene B and C. The structure of B is given . Now we can predict the structure of C. it might be-
COMPOUND-C
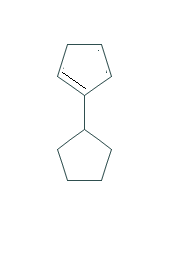
As we can see that the only possible alkene could be the above alkene. So we can say that compound B is major alkene and compound C is minor alkene.
Catalytic hydrogenation is the addition of hydrogen across the unsaturated site in the presence of a catalyst. The catalysts used are nickel, palladium or platinum.
Compound B and Compound C on catalytic hydrogenation will give the same product.
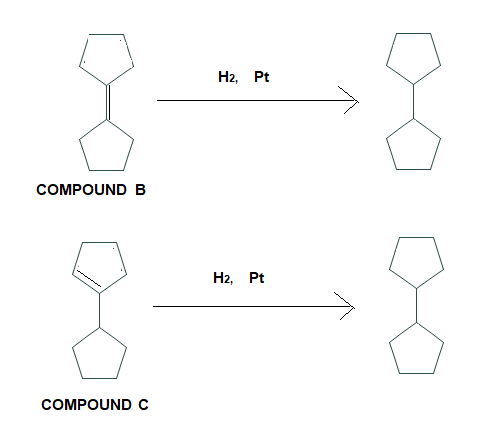
Complete step by step answer:
Potassium hydrogen sulphate is a dehydrating agent. The elimination of water molecules from a compound is called dehydration. When alcohols are treated with dehydrating agents, they give alkene as a product. This reaction is also called as $beta - $ elimination of alcohols.
In the dehydration reaction of alcohol, the $ - OH$ group from the $alpha $ carbon and hydrogen from the $beta $ carbon is lost as the water molecule. If there are more than one type of $beta $ hydrogen , then more than one type of product is possible.
The major product of dehydration of alcohol is given by Saytzeff’s rule. In the elimination reaction of alcohols, the more substituted alkene is formed as the major product. The other minor product is the less substituted alkene.
Now alcohol A gives alkene B and C. The structure of B is given . Now we can predict the structure of C. it might be-
COMPOUND-C

As we can see that the only possible alkene could be the above alkene. So we can say that compound B is major alkene and compound C is minor alkene.
Catalytic hydrogenation is the addition of hydrogen across the unsaturated site in the presence of a catalyst. The catalysts used are nickel, palladium or platinum.
Compound B and Compound C on catalytic hydrogenation will give the same product.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




