
An airplane is flying in a horizontal direction with a velocity of $600km/h$ at height of \[1960m\]. When it is vertically above the point $A$ on the ground, a body is dropped from it. The body strikes the ground at point $B$. Calculate the distance \[AB\]
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: We know that a projectile motion has two components, namely the x and y component. To find the distance along the x-component, the velocity along the x-component is given, so we need the time taken. Since the time taken by the aeroplane along the y-component is equal to the x-component, we can find the time using the height of the aeroplane.
Formula used:
$H=u_{y}t+\dfrac{1}{2}a_{y}t^{2}$ and $x=vt$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that the aeroplane is flying at a height $H=1960m$ from $A$, with an initial velocity of $v=600km/h$.
Then, we know that $v=\dfrac{x}{t}$, where $x$ is the distance covered by the body from $A$ to $B$, and $t$ is the time taken to cover the distance $x$. Since the body is dropped from the aeroplane moving with velocity $v=600km/h$, then the body when dropped from the moving aeroplane, will also have a velocity $v=600km/h$.
Given that the aeroplane is flying at a height $H=1960m$ above $A$ and drops a body.
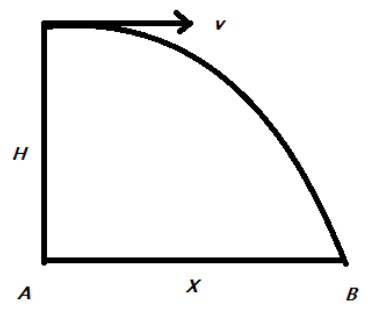
Clearly, here $u_{y}=0$ and $a_{y}=g=10m/s$ where $g$ is the acceleration due to gravitation.
Then, we can say that
$H=u_{y}t+\dfrac{1}{2}a_{y}t^{2}$
Substituting the values we get,$1960=\dfrac{1}{2}10\times t^{2}$
We can find the unknown $t$,
Or $t=\sqrt{\dfrac{1960}{5}}$
Or, $t=\sqrt{ 392}=19.79 sec$
Then, we can say from projectile motion that the distance covered by the body from $A$ to $B$ as $x$, then,
$x=vt$
$x=600\times\dfrac{5}{18}\times19.79=3296.6m=3.29km$
Thus, the distance covered by the body from $A$ to $B$ is \[3.29km\]
Note: We are converting the speed from $km/h$ to $m/s$ by multiplying the speed in $km/h$ to $\dfrac{5}{18}$ for maintaining the units and easy calculations. However, one can convert the time from seconds to hours by dividing the time in a sec by \[3600\]. And it is suggested that the child knows the conversions beforehand.
Formula used:
$H=u_{y}t+\dfrac{1}{2}a_{y}t^{2}$ and $x=vt$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that the aeroplane is flying at a height $H=1960m$ from $A$, with an initial velocity of $v=600km/h$.
Then, we know that $v=\dfrac{x}{t}$, where $x$ is the distance covered by the body from $A$ to $B$, and $t$ is the time taken to cover the distance $x$. Since the body is dropped from the aeroplane moving with velocity $v=600km/h$, then the body when dropped from the moving aeroplane, will also have a velocity $v=600km/h$.
Given that the aeroplane is flying at a height $H=1960m$ above $A$ and drops a body.

Clearly, here $u_{y}=0$ and $a_{y}=g=10m/s$ where $g$ is the acceleration due to gravitation.
Then, we can say that
$H=u_{y}t+\dfrac{1}{2}a_{y}t^{2}$
Substituting the values we get,$1960=\dfrac{1}{2}10\times t^{2}$
We can find the unknown $t$,
Or $t=\sqrt{\dfrac{1960}{5}}$
Or, $t=\sqrt{ 392}=19.79 sec$
Then, we can say from projectile motion that the distance covered by the body from $A$ to $B$ as $x$, then,
$x=vt$
$x=600\times\dfrac{5}{18}\times19.79=3296.6m=3.29km$
Thus, the distance covered by the body from $A$ to $B$ is \[3.29km\]
Note: We are converting the speed from $km/h$ to $m/s$ by multiplying the speed in $km/h$ to $\dfrac{5}{18}$ for maintaining the units and easy calculations. However, one can convert the time from seconds to hours by dividing the time in a sec by \[3600\]. And it is suggested that the child knows the conversions beforehand.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




