
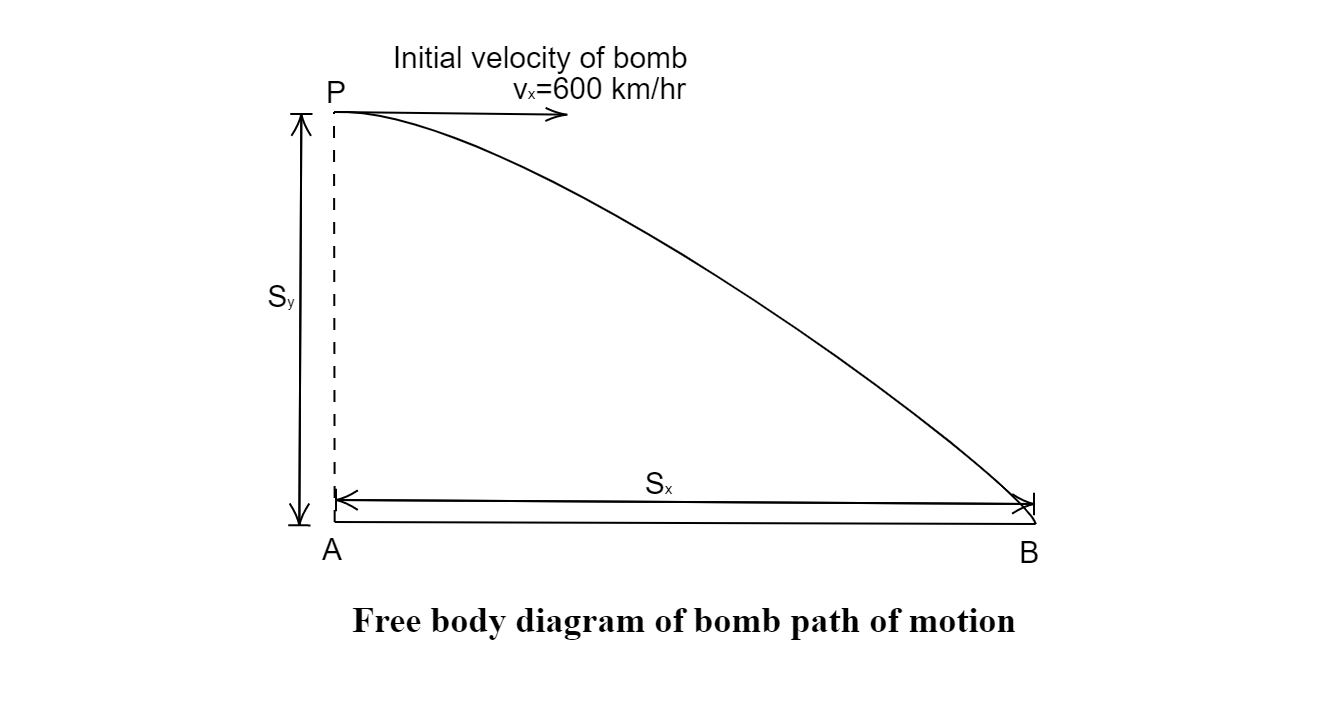
An airplane is flying horizontally with a velocity of $600\;km{h^{ - 1}}$ and at a height of $1960\;m$. When it is vertically at a point A on the ground a bomb is released from it. The bomb strikes the ground at point B. What is the distance between AB?
A. $1200\;m$
B. $0.33\;km$
C. $3.33\;km$
D. $33\;km$
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: When a plane flying in horizontal direction drops a bomb towards the ground, the bomb follows a path as projectile motion. Since the plane moves in a horizontal direction, then the velocity of the bomb in vertical direction would be zero, and also the acceleration in the horizontal direction is zero, it is due to the vertical motion of the bomb due to gravity. By using the equation of motion formula the distance AB can be calculated.
Formula used:
The second equation of motion,
${S_y} = {u_y}t + \dfrac{1}{2}{a_y}{t^2}$
Where, ${S_y}$ is the vertical distance travelled by bomb, ${u_y}$ is the velocity in vertical direction, ${a_y}$ is the acceleration in vertical direction and $t$ is the time taken.
The relation between velocity and distance,
$S = vt$
Where $S$ is the distance traveled by the object, $v$ is the velocity of the object and $t$ is the time taken to travel.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, The horizontal velocity, ${v_x} = 600\;km{h^{ - 1}} = 166.666\;m{s^{ - 1}}$
The vertical distance, ${S_y} = 1960\;m$
The second equation of motion,
${S_y} = {u_y}t + \dfrac{1}{2}{a_y}{t^2}$
Since, the bomb has the horizontal velocity and there will not be any vertical velocity. So, ${u_y} = 0$ and the vertical acceleration is due to gravity. So, ${a_y} = g$
Hence,
${S_y} = \left( 0 \right)t + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( g \right){t^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
By substituting the values of ${S_y}$ and $g = 9.81\;m{s^{ - 2}}$ in above relation, we get
$1960\;m = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {9.81\;m{s^{ - 2}}} \right){t^2}$
By rearranging, we get
$\dfrac{{2 \times 1960}}{{9.81}} = {t^2}$
Taking square on both sides,
$
t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2 \times 1960}}{{9.81}}} \\
t = \sqrt {399.59} \\
t = 19.98\;s \\
$
The relation between velocity and distance in horizontal direction,
${S_x} = {v_x}t$
Where, ${S_x}$ is the horizontal distance equal to AB, and ${v_x}$ is the horizontal velocity of the bomb.
By substituting the given values, we get
$
{S_x} = 166.666\;m{s^{ - 1}} \times 19.98\;s \\
{S_x} = 3316.65\;m \\
$
In SI unit, ${S_x} = 3.316\;km$
$\therefore$ The horizontal distance between points A and B is ${S_x} \simeq 3.33\;km$. Hence the option (C) is correct.
Note:
The airplane and the bomb have the same velocity in the horizontal direction, and vertically the bomb doesn’t have any velocity. The bomb moves vertically due to the acceleration due to gravity. So, the only factor that tends the bomb to move in a vertical direction is gravity. Hence, due to the combined factor of kinetic energy in a horizontal direction and gravity in the vertical direction, the bomb moves in a projectile path.
Formula used:
The second equation of motion,
${S_y} = {u_y}t + \dfrac{1}{2}{a_y}{t^2}$
Where, ${S_y}$ is the vertical distance travelled by bomb, ${u_y}$ is the velocity in vertical direction, ${a_y}$ is the acceleration in vertical direction and $t$ is the time taken.
The relation between velocity and distance,
$S = vt$
Where $S$ is the distance traveled by the object, $v$ is the velocity of the object and $t$ is the time taken to travel.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, The horizontal velocity, ${v_x} = 600\;km{h^{ - 1}} = 166.666\;m{s^{ - 1}}$
The vertical distance, ${S_y} = 1960\;m$

The second equation of motion,
${S_y} = {u_y}t + \dfrac{1}{2}{a_y}{t^2}$
Since, the bomb has the horizontal velocity and there will not be any vertical velocity. So, ${u_y} = 0$ and the vertical acceleration is due to gravity. So, ${a_y} = g$
Hence,
${S_y} = \left( 0 \right)t + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( g \right){t^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
By substituting the values of ${S_y}$ and $g = 9.81\;m{s^{ - 2}}$ in above relation, we get
$1960\;m = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {9.81\;m{s^{ - 2}}} \right){t^2}$
By rearranging, we get
$\dfrac{{2 \times 1960}}{{9.81}} = {t^2}$
Taking square on both sides,
$
t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2 \times 1960}}{{9.81}}} \\
t = \sqrt {399.59} \\
t = 19.98\;s \\
$
The relation between velocity and distance in horizontal direction,
${S_x} = {v_x}t$
Where, ${S_x}$ is the horizontal distance equal to AB, and ${v_x}$ is the horizontal velocity of the bomb.
By substituting the given values, we get
$
{S_x} = 166.666\;m{s^{ - 1}} \times 19.98\;s \\
{S_x} = 3316.65\;m \\
$
In SI unit, ${S_x} = 3.316\;km$
$\therefore$ The horizontal distance between points A and B is ${S_x} \simeq 3.33\;km$. Hence the option (C) is correct.
Note:
The airplane and the bomb have the same velocity in the horizontal direction, and vertically the bomb doesn’t have any velocity. The bomb moves vertically due to the acceleration due to gravity. So, the only factor that tends the bomb to move in a vertical direction is gravity. Hence, due to the combined factor of kinetic energy in a horizontal direction and gravity in the vertical direction, the bomb moves in a projectile path.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




