
How is the amplification of genes done using the technique of PCR? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint: The gene is the fundamental physical inheritance unit. Genes are passed from parents to offspring and provide the data required to determine characteristics.
Complete answer:
Gene amplification is an increase in the number of copies of the gene without a corresponding increase in other genes. This can result from duplication of a DNA region containing a gene through errors in the machinery of DNA replication and repair, as well as by fortuitous capture by selfish genetic elements.
A relatively simple technique that amplifies a DNA template to produce specific DNA fragments in vitro is polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Traditional methods often require days or weeks of work to clone a DNA sequence into a vector and replicate it in a living cell, but amplification of DNA sequences by PCR requires only hours.
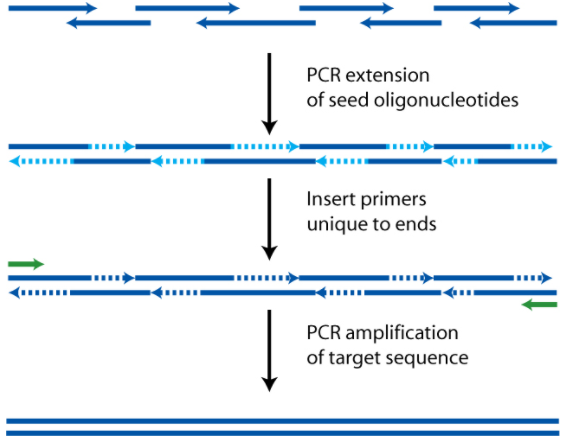
Each PCR cycle includes steps for denaturation of templates, annealing of the primer and extension of the primer.
Denaturation: By heating it to 94°C or higher for 15 seconds to 2 minutes, the initial step denatures the target DNA. The two intertwined strands of DNA separate from each other in the denaturation process, producing the required single-stranded DNA template for thermostable DNA polymerase replication.
Annealing: The temperature is reduced to about 40-60 ° C in the next phase of the cycle. The oligonucleotide primers can form stable associations with the denatured target DNA at this temperature and serve as DNA polymerase primers. This step is roughly 15-60 seconds long. Finally, as the reaction temperature is raised to the optimum for the DNA polymerase, the synthesis of new DNA begins. This temperature is in the range of 70-74°C for most thermostable DNA polymerases. The step of extension lasts for approximately 1-2 minutes. With a return to 94 ° C for denaturation, the next cycle begins. For each template and primer pair combination, each phase of the cycle should be optimised.
Extension: If the temperature is similar during the steps of annealing and extension, these two steps can be combined into a single step in which both the annealing of the primer and the extension take place. The amplified product may be analysed for size, quantity, sequence, etc. after 20-40 cycles or used in further experimental procedures.
Note: PCR technique is useful not only in basic research, but also in commercial applications, such as genetic identity testing, forensics, in vitro diagnostics, and industrial quality control.
Complete answer:
Gene amplification is an increase in the number of copies of the gene without a corresponding increase in other genes. This can result from duplication of a DNA region containing a gene through errors in the machinery of DNA replication and repair, as well as by fortuitous capture by selfish genetic elements.
A relatively simple technique that amplifies a DNA template to produce specific DNA fragments in vitro is polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Traditional methods often require days or weeks of work to clone a DNA sequence into a vector and replicate it in a living cell, but amplification of DNA sequences by PCR requires only hours.

Each PCR cycle includes steps for denaturation of templates, annealing of the primer and extension of the primer.
Denaturation: By heating it to 94°C or higher for 15 seconds to 2 minutes, the initial step denatures the target DNA. The two intertwined strands of DNA separate from each other in the denaturation process, producing the required single-stranded DNA template for thermostable DNA polymerase replication.
Annealing: The temperature is reduced to about 40-60 ° C in the next phase of the cycle. The oligonucleotide primers can form stable associations with the denatured target DNA at this temperature and serve as DNA polymerase primers. This step is roughly 15-60 seconds long. Finally, as the reaction temperature is raised to the optimum for the DNA polymerase, the synthesis of new DNA begins. This temperature is in the range of 70-74°C for most thermostable DNA polymerases. The step of extension lasts for approximately 1-2 minutes. With a return to 94 ° C for denaturation, the next cycle begins. For each template and primer pair combination, each phase of the cycle should be optimised.
Extension: If the temperature is similar during the steps of annealing and extension, these two steps can be combined into a single step in which both the annealing of the primer and the extension take place. The amplified product may be analysed for size, quantity, sequence, etc. after 20-40 cycles or used in further experimental procedures.
Note: PCR technique is useful not only in basic research, but also in commercial applications, such as genetic identity testing, forensics, in vitro diagnostics, and industrial quality control.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




