
Among the three molecules, $Xe{F_4}$, $S{F_4}$and $Si{F_4}$, which has/ have tetrahedral structure?
A) All three
B) $Si{F_4}$ and $S{F_4}$
C) Only $Si{F_4}$
D) Only $S{F_4}$
Answer
546.6k+ views
Hint:
To answer this question you must recall the VSEPR theory. The Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory proposes that the hybridized orbitals in an atom arrange themselves in such a way so as to minimize the repulsion between them, hence determining the geometry of a molecule on the basis of its hybridization.
Complete step by step solution:
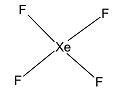
First we consider, $Xe{F_4}$.
We know that Xenon has 8 valence electrons. Since it forms four bonds with fluorine, thus, we can conclude that 2 electrons from the $5p$ orbital are excited to the empty $5d$ orbital. The atom undergoes an $s{p^3}{d^2}$ hybridisation. The geometry of the molecule is octahedral. The hybrid orbitals form four bond pairs and two lone pairs. Thus, the structure is square planar.
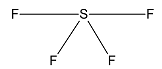
Now, we consider $S{F_4}$.
Sulphur has 6 valence electrons out of which 2 are unpaired. One electron from the $3p$ orbital is excited to $3d$ orbital and the atom undergoes $s{p^3}d$ hybridization. Geometry of molecules is trigonal bipyramidal but due to the presence of a lone pair the structure is see-saw shaped.
Considering $Si{F_4}$
Silicon has 4 valence electrons. One valence electron from $3s$ is excited to $3p$. The atom undergoes $s{p^3}$ hybridisation. All four hybrid orbitals form bond pairs and the structure is tetrahedral.

Thus, the correct answer is C.
Note:
The concept of mixing of atomic orbitals in order to form new hybrid orbitals that possess different shapes and energies as compared to the original parent atomic orbitals is known as hybridisation. Hybrid orbitals are suitable to form chemical bonds of equal energies. Also hybridization of orbitals leads to the formation of more stable compounds because hybrid orbitals have lower energy than the unhybrid orbitals.
To answer this question you must recall the VSEPR theory. The Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory proposes that the hybridized orbitals in an atom arrange themselves in such a way so as to minimize the repulsion between them, hence determining the geometry of a molecule on the basis of its hybridization.
Complete step by step solution:
First we consider, $Xe{F_4}$.
We know that Xenon has 8 valence electrons. Since it forms four bonds with fluorine, thus, we can conclude that 2 electrons from the $5p$ orbital are excited to the empty $5d$ orbital. The atom undergoes an $s{p^3}{d^2}$ hybridisation. The geometry of the molecule is octahedral. The hybrid orbitals form four bond pairs and two lone pairs. Thus, the structure is square planar.

Now, we consider $S{F_4}$.
Sulphur has 6 valence electrons out of which 2 are unpaired. One electron from the $3p$ orbital is excited to $3d$ orbital and the atom undergoes $s{p^3}d$ hybridization. Geometry of molecules is trigonal bipyramidal but due to the presence of a lone pair the structure is see-saw shaped.

Considering $Si{F_4}$
Silicon has 4 valence electrons. One valence electron from $3s$ is excited to $3p$. The atom undergoes $s{p^3}$ hybridisation. All four hybrid orbitals form bond pairs and the structure is tetrahedral.

Thus, the correct answer is C.
Note:
The concept of mixing of atomic orbitals in order to form new hybrid orbitals that possess different shapes and energies as compared to the original parent atomic orbitals is known as hybridisation. Hybrid orbitals are suitable to form chemical bonds of equal energies. Also hybridization of orbitals leads to the formation of more stable compounds because hybrid orbitals have lower energy than the unhybrid orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




