
Among the following substituted pyridines, the most basic compound is:
A)
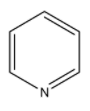
B)
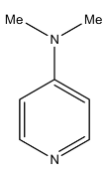
C)
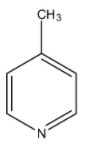
D)
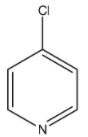




Answer
599.7k+ views
Hint: The compound which donates its electrons very easily to electron deficient atoms or molecules is called basic compounds. The electron deficient atom or molecules is called acidic compounds. The strength of a basic compound is going to depend on the strength of its donating capability of electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find the most basic pyridine compound among the given options.
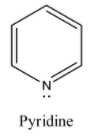
> Coming to given options, option A, pyridine. Pyridine itself is a basic compound because the nitrogen atom in the pyridine ring contains a lone pair of electrons. The lone pair of electrons does not involve in the conjugation of the benzene ring. So, nitrogen atoms in pyridine donate electrons very easily. So, pyridine is a basic compound.
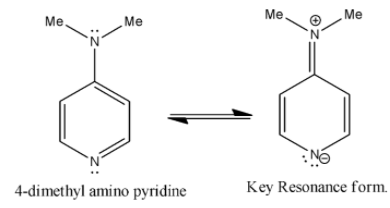
> Coming to option B, 4-dimethylamino pyridine. We know that ring activating groups increase the basicity of the pyridine compounds as in the option B, 4-dimethylamino pyridine has two ring activation groups so it has more basicity.
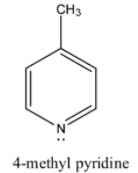
> Coming to option C, 4-methyl pyridine. Due to +I effect due to methyl group it is also a basic compound. But less basic than 4-dimethylamino pyridine.
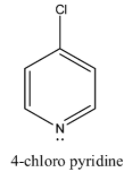
> Coming to option D, 4-chloro pyridine. Due to –I effect of chlorine, 4-chloro pyridine does not donate electrons easily.
Therefore among the given pyridine compounds, the highly basic compound is B, 4-dimethylamino pyridine.
So, the correct option is B.
Note: Don’t be confused with +I effect and –I effect.
+I effect: When a chemical species or substance which has a tendency to release or donate electrons, like an alkyl group is called positive inductive effect (+I effect).
-I effect: When a chemical species or substance which has a tendency to take or withdraw electrons, like halogens is called negative inductive effect (-I effect).
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find the most basic pyridine compound among the given options.
> Coming to given options, option A, pyridine. Pyridine itself is a basic compound because the nitrogen atom in the pyridine ring contains a lone pair of electrons. The lone pair of electrons does not involve in the conjugation of the benzene ring. So, nitrogen atoms in pyridine donate electrons very easily. So, pyridine is a basic compound.

> Coming to option B, 4-dimethylamino pyridine. We know that ring activating groups increase the basicity of the pyridine compounds as in the option B, 4-dimethylamino pyridine has two ring activation groups so it has more basicity.

> Coming to option C, 4-methyl pyridine. Due to +I effect due to methyl group it is also a basic compound. But less basic than 4-dimethylamino pyridine.

> Coming to option D, 4-chloro pyridine. Due to –I effect of chlorine, 4-chloro pyridine does not donate electrons easily.

Therefore among the given pyridine compounds, the highly basic compound is B, 4-dimethylamino pyridine.
So, the correct option is B.
Note: Don’t be confused with +I effect and –I effect.
+I effect: When a chemical species or substance which has a tendency to release or donate electrons, like an alkyl group is called positive inductive effect (+I effect).
-I effect: When a chemical species or substance which has a tendency to take or withdraw electrons, like halogens is called negative inductive effect (-I effect).
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




