
Among the above given pair, identify one which gives higher heat of hydrogenation?
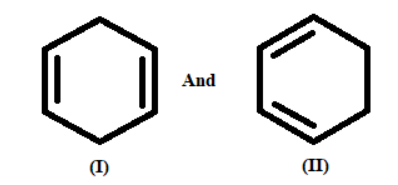
A. I
B. II
C. Both are equal
D. Cannot be determined

Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Heat of hydrogenation of an alkene is the standard enthalpy of reactant hydrogenation of an alkene. Synergist hydrogenation of an alkene is consistently exothermic. Accordingly, the warmth of hydrogenation of alkenes is consistently negative.
Heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is additive, provided that the double bonds are not conjugated.
Heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is a measure of the stability of carbon-carbon double bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
Heat of hydrogenation of an alkene is the standard enthalpy of reactant hydrogenation of an alkene. Synergist hydrogenation of an alkene is consistently exothermic. Accordingly, the warmth of hydrogenation of alkenes is consistently negative.
Heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is a measure of the stability of carbon-carbon double bonds.
Heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is additive, provided that the double bonds are not conjugated.
So, In compound (I), the two fold bonds are not formed.
And In compound (II), the two fold bonds are formed. This results in delocalization of the electron thickness, which gives more noteworthy strength to form diene.
More steady formed dienes have lower warms of hydrogenation than less steady non formed dienes.
Henceforth, compound (I) has higher warmth of hydrogenation than non-formed diene.
Hence, Option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:
Heat of hydrogenation of an alkene is the standard enthalpy of reactant hydrogenation of an alkene. Synergist hydrogenation of an alkene is consistently exothermic. Accordingly, the warmth of hydrogenation of alkenes is consistently negative. Heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is additive, provided that the double bonds are not conjugated.
Heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is additive, provided that the double bonds are not conjugated.
Heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is a measure of the stability of carbon-carbon double bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
Heat of hydrogenation of an alkene is the standard enthalpy of reactant hydrogenation of an alkene. Synergist hydrogenation of an alkene is consistently exothermic. Accordingly, the warmth of hydrogenation of alkenes is consistently negative.
Heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is a measure of the stability of carbon-carbon double bonds.
Heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is additive, provided that the double bonds are not conjugated.
So, In compound (I), the two fold bonds are not formed.
And In compound (II), the two fold bonds are formed. This results in delocalization of the electron thickness, which gives more noteworthy strength to form diene.
More steady formed dienes have lower warms of hydrogenation than less steady non formed dienes.
Henceforth, compound (I) has higher warmth of hydrogenation than non-formed diene.
Hence, Option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:
Heat of hydrogenation of an alkene is the standard enthalpy of reactant hydrogenation of an alkene. Synergist hydrogenation of an alkene is consistently exothermic. Accordingly, the warmth of hydrogenation of alkenes is consistently negative. Heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is additive, provided that the double bonds are not conjugated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




