
Among i-iii, the boiling point follows the order:
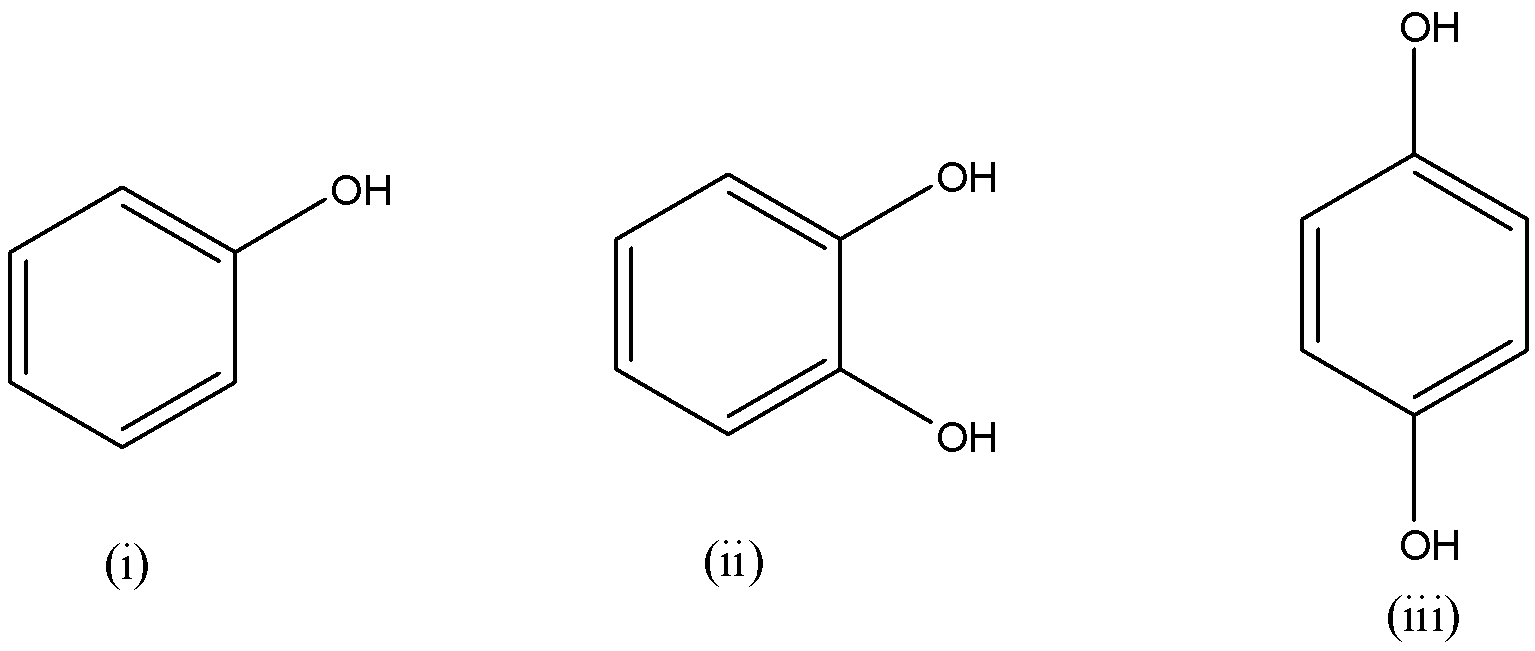
A) ii < i < iii
B) iii < ii < i
C) i < ii < iii
D) ii < iii < i

Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: Some of the given compounds include intermolecular hydrogen bonding and intramolecular hydrogen bonding. They affect the boiling point of a compound significantly.
Complete answer:
- Hydrogen bonding significantly affects the boiling point of a compound. Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules.
It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a $N$ , $O$ , or $F$ atom and another very electronegative atom. Hydrogen bond strengths range from 4 kJ to 50 kJ per mole of hydrogen bonds.
- Because of the difference in electronegativity, the H atom bears a large partial positive charge and the other electronegative atom bears a partial negative charge. So, the $H$ atom is electrostatically attracted to the other electronegative atom.
- Hydrogen bonds have about a tenth of the strength of an average covalent bond, and are being constantly broken and reformed.
If we observe the above compounds, compound (ii) has two $-OH$ atoms very close to each other. So, one of the hydrogens of one $-OH$ is electrostatically attracted to the oxygen of another $-OH$ molecule.
- This type of hydrogen bonding is called intramolecular hydrogen bonding. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding decreases the boiling point of a molecule significantly as the molecule binds strongly to itself and decreases the tendency of intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
If we observe compound (iii), the two $-OH$ atoms are very far from each other and can’t perform intramolecular hydrogen bonding. So, they are involved in intermolecular hydrogen bonding with the adjacent molecules.
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding increases the boiling point significantly as the molecules bind to each other strongly thus increasing boiling point.
Hence, the correct answer is (A) ii < i < iii
Note:
It is important to note that the boiling point of the hydrocarbons also depends on the number of carbon chains. As the number of carbon chains increases, the boiling point also increases and vice-versa. The reason is the force of attraction between molecules increases with the increase in chains.
Complete answer:
- Hydrogen bonding significantly affects the boiling point of a compound. Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules.
It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a $N$ , $O$ , or $F$ atom and another very electronegative atom. Hydrogen bond strengths range from 4 kJ to 50 kJ per mole of hydrogen bonds.
- Because of the difference in electronegativity, the H atom bears a large partial positive charge and the other electronegative atom bears a partial negative charge. So, the $H$ atom is electrostatically attracted to the other electronegative atom.
- Hydrogen bonds have about a tenth of the strength of an average covalent bond, and are being constantly broken and reformed.
If we observe the above compounds, compound (ii) has two $-OH$ atoms very close to each other. So, one of the hydrogens of one $-OH$ is electrostatically attracted to the oxygen of another $-OH$ molecule.
- This type of hydrogen bonding is called intramolecular hydrogen bonding. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding decreases the boiling point of a molecule significantly as the molecule binds strongly to itself and decreases the tendency of intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
If we observe compound (iii), the two $-OH$ atoms are very far from each other and can’t perform intramolecular hydrogen bonding. So, they are involved in intermolecular hydrogen bonding with the adjacent molecules.
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding increases the boiling point significantly as the molecules bind to each other strongly thus increasing boiling point.
Hence, the correct answer is (A) ii < i < iii
Note:
It is important to note that the boiling point of the hydrocarbons also depends on the number of carbon chains. As the number of carbon chains increases, the boiling point also increases and vice-versa. The reason is the force of attraction between molecules increases with the increase in chains.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




