
How is ammonia manufactured industrially?
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint:Ammonia is a compound composed of one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms held by covalent bonds. It has a lone pair of the electron over the nitrogen atom.
Complete step-by-step answer:
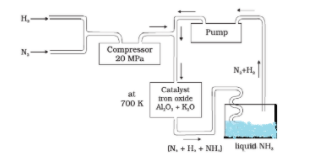
Haber’s process is used for the synthesis of ammonia which is carried out at a high temperature because, at low temperatures, the reaction becomes very slow due to which the rate of formation of ammonia becomes very slow.
To make ammonia, the mixture of ${ N }_{ 2 }$ and ${ H }_{ 2 }$ gases are passed over heated iron. Heated iron acts as a catalyst in the synthesis of ammonia. It accelerates the rate of reaction.\
The following reaction will take place:
${ N }_{ 2 }{ (g)+3H }_{ 2 }{ (g)\rightleftharpoons 2NH }_{ 3 }$
A mixture of dry nitrogen and hydrogen in the ratio of ${ 1:3 }$ by volume is compressed in the presence of pressure approx. ${ 200-300atm }$ and passed over the Fe catalyst at a temperature of approximately ${ 723-773K }$.
Now, the Fe catalyst mixed with aluminium oxide and potassium oxide which acts as promoters.
The ammonia formed is continuously removed by liquefaction.
Additional Information:
Le chatelier's principle is the principle that determines how the equilibrium of a reaction changes by changing various factors on which it depends. According to this principle, change in any of the factors that determine the equilibrium conditions of a system will cause the system to change in such a manner so as to reduce or counteract the effect of the change.
These factors include the concentration of reactant, product, temperature, and catalyst.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may forget that this formation of ammonia by Haber’s process occurs in the presence of a catalyst that acts as a promoter.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Haber’s process is used for the synthesis of ammonia which is carried out at a high temperature because, at low temperatures, the reaction becomes very slow due to which the rate of formation of ammonia becomes very slow.
To make ammonia, the mixture of ${ N }_{ 2 }$ and ${ H }_{ 2 }$ gases are passed over heated iron. Heated iron acts as a catalyst in the synthesis of ammonia. It accelerates the rate of reaction.\
The following reaction will take place:
${ N }_{ 2 }{ (g)+3H }_{ 2 }{ (g)\rightleftharpoons 2NH }_{ 3 }$
A mixture of dry nitrogen and hydrogen in the ratio of ${ 1:3 }$ by volume is compressed in the presence of pressure approx. ${ 200-300atm }$ and passed over the Fe catalyst at a temperature of approximately ${ 723-773K }$.
Now, the Fe catalyst mixed with aluminium oxide and potassium oxide which acts as promoters.
The ammonia formed is continuously removed by liquefaction.

Additional Information:
Le chatelier's principle is the principle that determines how the equilibrium of a reaction changes by changing various factors on which it depends. According to this principle, change in any of the factors that determine the equilibrium conditions of a system will cause the system to change in such a manner so as to reduce or counteract the effect of the change.
These factors include the concentration of reactant, product, temperature, and catalyst.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may forget that this formation of ammonia by Haber’s process occurs in the presence of a catalyst that acts as a promoter.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




