
Ammonia is used as a refrigerating agent. Why?
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint:We know that ammonia is gas of no colour and pungent odour. Its chemical formula is ${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$ and it is an inorganic compound. When it is dissolved in water, it forms ammonium hydroxide. It is very dangerous in its concentrated form.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s understand the use of ammonia as a refrigerating agent. Ammonia in anhydrous form is a clear liquid which boils at $ - 28^\circ {\rm{F}}$. In the process of refrigeration, in closed containers a liquid is stored under high pressure. The releasing of pressure causes rapid evaporation of liquid forming an invisible gas or vapor. This rapid evaporation results in the drop down of temperature of the liquid until the reaching the normal boiling point of $ - 28^\circ {\rm{F}}$. This effect is also observed in evaporation of water from the skin and which causes a cooling effect. This is the reason for using ammonia as a refrigerating agent.
Additional Information:
The structure of ammonia is,
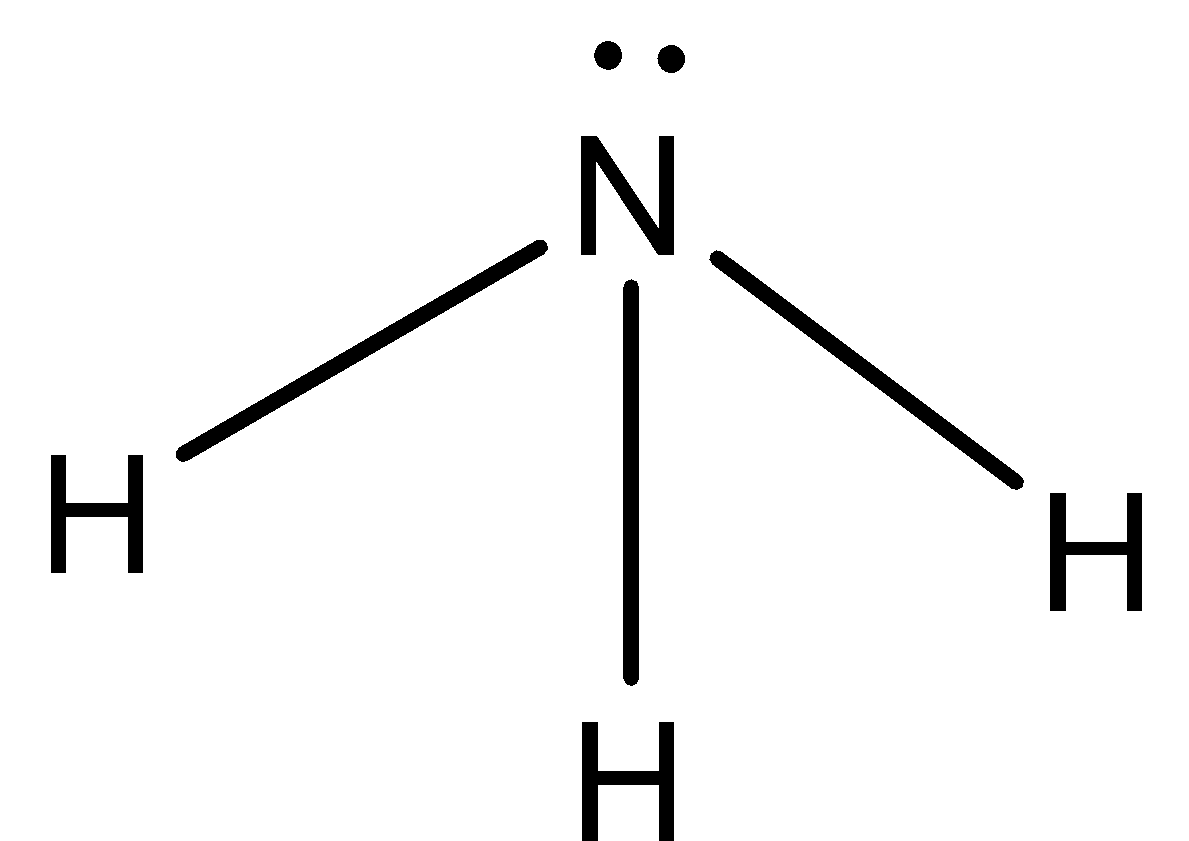
As two lone pairs are present on the nitrogen atom, it can donate its lone pair to form chemical bonds so it acts as a base.
The ammonia is produced in laboratory by heating salt of ammonia such as ${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{Cl}}$ in presence of strong alkali such as ${\rm{Ca}}{\left( {{\rm{OH}}} \right)_2}$.
$2{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{Cl}} + {\rm{Ca}}{\left( {{\rm{OH}}} \right)_2} \to {\rm{CaC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{2}}} + 2{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}} \to {\rm{2N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}$
Another important process is Haber’s process. In this process, hydrogen is reacted with nitrogen to form ammonia.
${{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ + 3}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} \to 2{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$
Note:
There are many uses of ammonia in different fields, such as manufacturing of fertilizers, fermentation industry, and textile industries etc. It is also used as an antimicrobial agent in food products. It is also used in manufacturing of synthetic fibres like nylon and rayon.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s understand the use of ammonia as a refrigerating agent. Ammonia in anhydrous form is a clear liquid which boils at $ - 28^\circ {\rm{F}}$. In the process of refrigeration, in closed containers a liquid is stored under high pressure. The releasing of pressure causes rapid evaporation of liquid forming an invisible gas or vapor. This rapid evaporation results in the drop down of temperature of the liquid until the reaching the normal boiling point of $ - 28^\circ {\rm{F}}$. This effect is also observed in evaporation of water from the skin and which causes a cooling effect. This is the reason for using ammonia as a refrigerating agent.
Additional Information:
The structure of ammonia is,

As two lone pairs are present on the nitrogen atom, it can donate its lone pair to form chemical bonds so it acts as a base.
The ammonia is produced in laboratory by heating salt of ammonia such as ${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{Cl}}$ in presence of strong alkali such as ${\rm{Ca}}{\left( {{\rm{OH}}} \right)_2}$.
$2{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{Cl}} + {\rm{Ca}}{\left( {{\rm{OH}}} \right)_2} \to {\rm{CaC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{2}}} + 2{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}} \to {\rm{2N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}$
Another important process is Haber’s process. In this process, hydrogen is reacted with nitrogen to form ammonia.
${{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ + 3}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} \to 2{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$
Note:
There are many uses of ammonia in different fields, such as manufacturing of fertilizers, fermentation industry, and textile industries etc. It is also used as an antimicrobial agent in food products. It is also used in manufacturing of synthetic fibres like nylon and rayon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




