
Who am I? I am a chemical factory of the cell.
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint: It is one of the cell organelles. It is also known as the powerhouse of the cell. It is a double-membrane structure that plays an important role in the production of the energy currency of the cell.
Complete answer: It refers to mitochondria. It is also known as the powerhouse of the cell. It synthesizes ATP molecules. ATP refers to Adenosine triphosphate. It becomes adenosine triphosphate when a phosphate molecule is introduced to the adenosine diphosphate. The whole process is called oxidative phosphorylation if it occurs in the presence of oxygen. Much of the ATP is synthesized in the mitochondria through oxidative phosphorylation. Two main membranes constitute the mitochondria. The mitochondrial outer membrane and the mitochondrial inner membrane. The intermembrane space between the membranes is small. There are several protein-based pores on the outer membrane that are wide enough to allow ions and molecules that are almost the size of small proteins to move through.
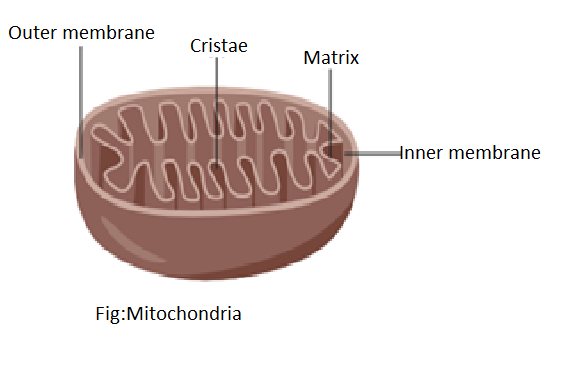
Like a cell's plasma membrane, the inner membrane has little permeability. The inner membrane is also filled with proteins involved in electron transport and ATP synthesis. The inner membrane surrounds the mitochondrial matrix, where electrons are released by the citric acid cycle. They move within the inner membrane from one protein complex to the next. The final electron acceptor at the end of this electron transport chain is oxygen, which eventually forms water. The electron transport chain creates ATP at the same time. (This technique is therefore referred to as oxidative phosphorylation)
Note: Mitochondria can differentiate by simple fission independently of the cell cycle. The mitochondrial genome is identical to its prokaryotic ancestor and its RNA is closely related to bacterial RNA as well as to eukaryotic RNA.
Complete answer: It refers to mitochondria. It is also known as the powerhouse of the cell. It synthesizes ATP molecules. ATP refers to Adenosine triphosphate. It becomes adenosine triphosphate when a phosphate molecule is introduced to the adenosine diphosphate. The whole process is called oxidative phosphorylation if it occurs in the presence of oxygen. Much of the ATP is synthesized in the mitochondria through oxidative phosphorylation. Two main membranes constitute the mitochondria. The mitochondrial outer membrane and the mitochondrial inner membrane. The intermembrane space between the membranes is small. There are several protein-based pores on the outer membrane that are wide enough to allow ions and molecules that are almost the size of small proteins to move through.

Like a cell's plasma membrane, the inner membrane has little permeability. The inner membrane is also filled with proteins involved in electron transport and ATP synthesis. The inner membrane surrounds the mitochondrial matrix, where electrons are released by the citric acid cycle. They move within the inner membrane from one protein complex to the next. The final electron acceptor at the end of this electron transport chain is oxygen, which eventually forms water. The electron transport chain creates ATP at the same time. (This technique is therefore referred to as oxidative phosphorylation)
Note: Mitochondria can differentiate by simple fission independently of the cell cycle. The mitochondrial genome is identical to its prokaryotic ancestor and its RNA is closely related to bacterial RNA as well as to eukaryotic RNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




