
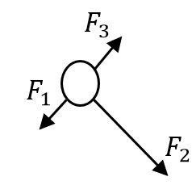
All three forces are in the same plane. Forces are acting on the ball as shown above. Which of the following diagrams but represent the resultant of the forces?
(A)

(B)

(C)

(D)






Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Force is a vector quantity and it can be defined as the rate of change of momentum.Direction of a force plays an important role.
Complete step by step answer:
In the above figure, we observe the forces \[{F_1}\] and \[{F_3}\] are equal in magnitude and opposite to each other. (Since, we can assume that the length of the ray, representing the Force represents the intensity/magnitude of the force)
Since, two equal forces are acting in opposite directions, the net force on the ball due to \[{F_1}\]and \[{F_3}\]will be zero.
Hence, the net resultant force acting on the ball will be because of the force \[{F_2}\]
Thus, the direction of the net force will be same as that of the direction of the force \[{F_2}\]
By observing all the options, we can conclude that (C) represents the direction of the resultant force.
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Additional Information:
If the given forces do not cancel each other. Then we resolve all the forces along X and Y axes and then find the resultant of the resolved vectors to find the resultant vector.
Note:In such examples, observing the diagram is very important. Every minute detail helps. For example, if you don’t observe that the lengths of the rays representing \[{F_1}\]and \[{F_3}\]are nearly similar but the length of the ray representing \[{F_2}\]is longer than the rest of the two. Then you would never have been able to guess that the length of the ray is representing the magnitude of the forces.
Complete step by step answer:
In the above figure, we observe the forces \[{F_1}\] and \[{F_3}\] are equal in magnitude and opposite to each other. (Since, we can assume that the length of the ray, representing the Force represents the intensity/magnitude of the force)
Since, two equal forces are acting in opposite directions, the net force on the ball due to \[{F_1}\]and \[{F_3}\]will be zero.
Hence, the net resultant force acting on the ball will be because of the force \[{F_2}\]
Thus, the direction of the net force will be same as that of the direction of the force \[{F_2}\]
By observing all the options, we can conclude that (C) represents the direction of the resultant force.
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Additional Information:
If the given forces do not cancel each other. Then we resolve all the forces along X and Y axes and then find the resultant of the resolved vectors to find the resultant vector.
Note:In such examples, observing the diagram is very important. Every minute detail helps. For example, if you don’t observe that the lengths of the rays representing \[{F_1}\]and \[{F_3}\]are nearly similar but the length of the ray representing \[{F_2}\]is longer than the rest of the two. Then you would never have been able to guess that the length of the ray is representing the magnitude of the forces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




