
All reactions are of $ 1st $ order.
At time $ t = t{}_1(t{}_1 > 0) $
$ \dfrac{{[B]}}{{[C]}} = \alpha . $ Therefore at
Time $ t $ $ = t{}_2 $ (where $ t{}_2 \geqslant t{}_1 $ )
$ \dfrac{{[C]}}{{[D]}} = \beta $ Which of the following is correct?
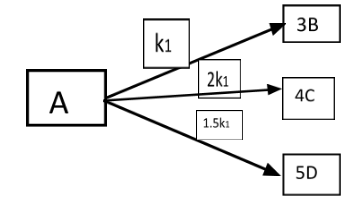
(A) $ \alpha > \beta $
(B) $ \alpha = \beta $
(C) $ \alpha \beta = 0.4 $
(D) $ \alpha + \beta = 0.4 $

Answer
535.8k+ views
Hint: Let us understand what first order reaction is. And step by step see how we can solve this equation. We first will find the relation between alpha and beta at given concentration and given time.
Complete step by step solution:
A first order reaction is a reaction in which the rate of reaction depends on the concentration of one reactant only. In other words, first order reaction is a chemical reaction where the rate varies based on changes in the concentration of one reactant only. Hence the order all these reaction is equal to $ 1 $
$ k = M{}^{(1 - n)}S{}^{ - 1} $
All the given reactions are in first order. At the $ t{}_1 $ the concentration of $ [B] $ and $ [C] $ is given by:
$ \dfrac{{[B]}}{{[C]}} = \alpha . $
All the given reactions are in first order. At the $ t{}_2 $ the concentration of $ [B] $ and $ [D] $ is given by:
$ \dfrac{{[C]}}{{[D]}} = \beta $
Let us now find the relation between $ \alpha $ and $ \beta $
At any time the ,
$ \dfrac{{[B]}}{{[C]}} = \dfrac{{3k{}_1}}{{8k{}_1}} = \dfrac{3}{8} = \alpha $
$ \dfrac{{[C]}}{{[D]}} = \dfrac{{8k{}_1}}{{7.5k{}_1}} = \dfrac{8}{{7.5}} = \beta $
$ \alpha \times \beta = \dfrac{3}{8} \times \dfrac{8}{{7.5}} = 0.4 $
Hence the correct answer is option C.
Additional Information:
A differential rate is used to describe a reaction at a molecular level. The differential rate expression for first order reaction is given by:
Rate= $ - \dfrac{{d[A]}}{{dt}} = k[A]{}^1 = k[A] $
Where,
K is the rate constant
$ [A] $ is the concentration of first order reactant
$ \dfrac{{d[A]}}{{dt}} $ is the change in concentration of the first order reaction A in time interval $ dt $ .
Note:
Here are few examples of first order reaction $ SO{}_2Cl{}_2 \to Cl{}_2 + SO{}_2 $ , $ 2NH{}_2O{}_2 \to O{}_2 + 4NO{}_2 $ , $ 2H{}_2O{}_2 \to 2H{}_2O + O{}_2 $ . The rate constant is expressed in terms of $ s{}^1 $
The units can be determined using the following,
Units of $ k = M{}^{(1 - n)}S{}^{ - 1} $ .
Complete step by step solution:
A first order reaction is a reaction in which the rate of reaction depends on the concentration of one reactant only. In other words, first order reaction is a chemical reaction where the rate varies based on changes in the concentration of one reactant only. Hence the order all these reaction is equal to $ 1 $
$ k = M{}^{(1 - n)}S{}^{ - 1} $
All the given reactions are in first order. At the $ t{}_1 $ the concentration of $ [B] $ and $ [C] $ is given by:
$ \dfrac{{[B]}}{{[C]}} = \alpha . $
All the given reactions are in first order. At the $ t{}_2 $ the concentration of $ [B] $ and $ [D] $ is given by:
$ \dfrac{{[C]}}{{[D]}} = \beta $
Let us now find the relation between $ \alpha $ and $ \beta $
At any time the ,
$ \dfrac{{[B]}}{{[C]}} = \dfrac{{3k{}_1}}{{8k{}_1}} = \dfrac{3}{8} = \alpha $
$ \dfrac{{[C]}}{{[D]}} = \dfrac{{8k{}_1}}{{7.5k{}_1}} = \dfrac{8}{{7.5}} = \beta $
$ \alpha \times \beta = \dfrac{3}{8} \times \dfrac{8}{{7.5}} = 0.4 $
Hence the correct answer is option C.
Additional Information:
A differential rate is used to describe a reaction at a molecular level. The differential rate expression for first order reaction is given by:
Rate= $ - \dfrac{{d[A]}}{{dt}} = k[A]{}^1 = k[A] $
Where,
K is the rate constant
$ [A] $ is the concentration of first order reactant
$ \dfrac{{d[A]}}{{dt}} $ is the change in concentration of the first order reaction A in time interval $ dt $ .
Note:
Here are few examples of first order reaction $ SO{}_2Cl{}_2 \to Cl{}_2 + SO{}_2 $ , $ 2NH{}_2O{}_2 \to O{}_2 + 4NO{}_2 $ , $ 2H{}_2O{}_2 \to 2H{}_2O + O{}_2 $ . The rate constant is expressed in terms of $ s{}^1 $
The units can be determined using the following,
Units of $ k = M{}^{(1 - n)}S{}^{ - 1} $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




