
Alkali metals are not found in free state due to their highly reactive nature. This is due to:
A.Their large size and low ionization enthalpy
B.Their large size and high ionization enthalpy
C.Their low ionization enthalpy and high electron gain enthalpy
D.Their tendency to impart colour to the flame.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: The size of the element increases through the group going down and through the period it also increases. When the size increases ionization enthalpy decreases. As ionization enthalpy is the minimum amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from valence electron.
Complete answer:
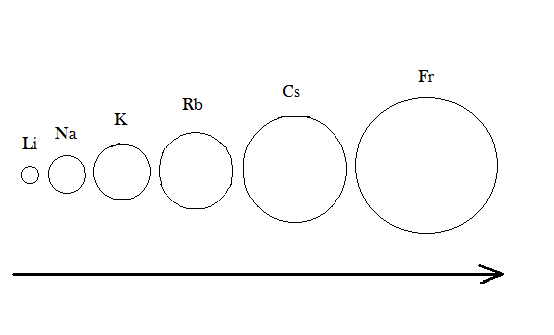
In our periodic table alkali metals, they are called as such because they do reactions with water from alkali’s which are strong bases capable of neutralizing acids. Alkali metals are present in periodic table as group$1$consist of six elements which are as follows: lithium $Li$, sodium $Na$, potassium $K$, rubidium $Rb$, caesium $Cs$, francium $Fr$ .They are not found in free state as they are found in metal oxides, metal carbonates etc.
Now when we talk about their chemical properties as they are first group elements so they have one valence electron $n{{s}^{1}}$ so their reactivity depends upon that how easily the element can lose the electron to achieve the nearest noble gas configuration so they lose electron to give monovalent ${{M}^{+}}$ ions.
In periodic table when we go down the group the atomic size increases and the number of shells increases due to which the force of attraction between the nucleus and the electrons of the valence shell decreases, which help it to lose electron easily when we give them heat and light, so we can conclude that they have low ionization enthalpy.
Hence, the correct answer is Option A.
Note:
-In alkali metals the loosely held s-electron in the outermost valence shell of these elements makes them the most electropositive metals.
-One more important point is that the size of elements increases going left to right in periodic tables due to which first group has the largest size.
- Whenever an electron is withdrawn from a molecule, it takes a particular amount of energy to detach it, so the enthalpies of chemical elements are always positive for ionisation.
Complete answer:
In our periodic table alkali metals, they are called as such because they do reactions with water from alkali’s which are strong bases capable of neutralizing acids. Alkali metals are present in periodic table as group$1$consist of six elements which are as follows: lithium $Li$, sodium $Na$, potassium $K$, rubidium $Rb$, caesium $Cs$, francium $Fr$ .They are not found in free state as they are found in metal oxides, metal carbonates etc.

Now when we talk about their chemical properties as they are first group elements so they have one valence electron $n{{s}^{1}}$ so their reactivity depends upon that how easily the element can lose the electron to achieve the nearest noble gas configuration so they lose electron to give monovalent ${{M}^{+}}$ ions.
In periodic table when we go down the group the atomic size increases and the number of shells increases due to which the force of attraction between the nucleus and the electrons of the valence shell decreases, which help it to lose electron easily when we give them heat and light, so we can conclude that they have low ionization enthalpy.
Hence, the correct answer is Option A.
Note:
-In alkali metals the loosely held s-electron in the outermost valence shell of these elements makes them the most electropositive metals.
-One more important point is that the size of elements increases going left to right in periodic tables due to which first group has the largest size.
- Whenever an electron is withdrawn from a molecule, it takes a particular amount of energy to detach it, so the enthalpies of chemical elements are always positive for ionisation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




