
$AlC{{l}_{3}}$achieves stability by forming a dimer. In the trivalent state, the compound is hydrolysed in water. $AlC{{l}_{3}}$ in acidified aqueous solutions forms:
(A)- $Al{{(OH)}_{3}}+HCl$
(B)- ${{[Al{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}]}^{3+}}+3C{{l}^{-}}$
(C)- $AlC{{l}_{3}}.2{{H}_{2}}O$
(D)- $A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}+HCl$
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: The coordination number of Al metal is 6. There are two different types of bonds formed of which one gets ionized in aqueous solution.
Complete step by step answer:
-Aluminium trichloride or aluminium chloride is a chemical compound with aluminium and chloride atoms in a ratio 1:3. Another form which contains six waters of hydration is also available.
-The trifluorides of Al, Ga, In and Tl are ionic while the chlorides, bromides and iodides are largely covalent in the anhydrous state. The covalent nature decreases down the group. Trihalides fume in air and undergo hydrolysis.
-The tendency of accepting an electron pair is observed in this case. The tendency decreases as the size of the cation increases.
-They form complex halides like ${{[M{{X}_{6}}]}^{3-}}$ where a metal atom has the coordination number equal to 6 by the use of d- orbitals. There is no back bonding due to an increase in the size of the element.
They use vacant p – orbitals to form coordinate bonds to complete their octets thus forming dimers.
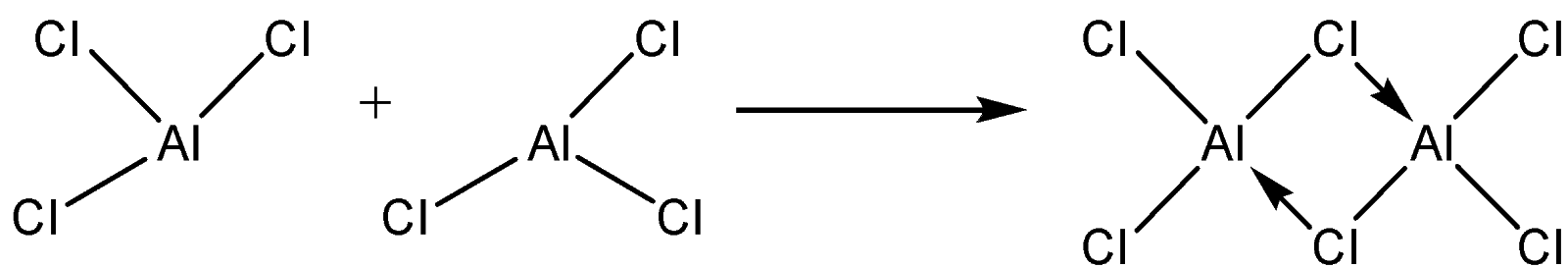
-Dimers formed exist in a vapour state and in non-polar solvents.
-Dimers disappear when the halides are dissolved in water. This is due to high hydration energy.
$AlC{{l}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to {{[Al{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}]}^{3+}}+3C{{l}^{3-}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The halides have a planar $s{{p}^{2}} $hybrid structure. The $AlC{{l}_{3}}$ behaves as a Lewis acid. It is borderline for being ionic or covalent. $AlC{{l}_{3}}$ when solid is usually ionic and when in the vapour is covalent. Aluminium chloride in its +3 oxidation state makes six electrons ( 3 electrons from Al and 3 electrons from Cl) to get the most favourable 8 electron octet and thus forms dimmers by extra sharing of electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
-Aluminium trichloride or aluminium chloride is a chemical compound with aluminium and chloride atoms in a ratio 1:3. Another form which contains six waters of hydration is also available.
-The trifluorides of Al, Ga, In and Tl are ionic while the chlorides, bromides and iodides are largely covalent in the anhydrous state. The covalent nature decreases down the group. Trihalides fume in air and undergo hydrolysis.
-The tendency of accepting an electron pair is observed in this case. The tendency decreases as the size of the cation increases.
-They form complex halides like ${{[M{{X}_{6}}]}^{3-}}$ where a metal atom has the coordination number equal to 6 by the use of d- orbitals. There is no back bonding due to an increase in the size of the element.
They use vacant p – orbitals to form coordinate bonds to complete their octets thus forming dimers.

-Dimers formed exist in a vapour state and in non-polar solvents.
-Dimers disappear when the halides are dissolved in water. This is due to high hydration energy.
$AlC{{l}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to {{[Al{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}]}^{3+}}+3C{{l}^{3-}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The halides have a planar $s{{p}^{2}} $hybrid structure. The $AlC{{l}_{3}}$ behaves as a Lewis acid. It is borderline for being ionic or covalent. $AlC{{l}_{3}}$ when solid is usually ionic and when in the vapour is covalent. Aluminium chloride in its +3 oxidation state makes six electrons ( 3 electrons from Al and 3 electrons from Cl) to get the most favourable 8 electron octet and thus forms dimmers by extra sharing of electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




