
A.In a right-angled triangle, the sides forming the right angle measure 15 cm and 20 cm. Find its (i) area, (ii) hypotenuse, (iii) perimeter, and (iv) the length of the perpendicular from the vertex of the right angle to the hypotenuse.
B.If the ratio of the shortest and longest sides of a right-angled triangle be 3:5 and its perimeter is 36 cm then find the area of the triangle.
C.In a right-angled triangle the smaller sides are (x+9) cm and (2x + 3) cm. Find its perimeter if its area is $ 54\;c{m^2} $
Answer
561.9k+ views
Hint: Any side of a right-angle triangle can be found out by Pythagoras theorem if the other two sides are known. Perimeter is the sum of all the sides present in the figure and area is half of the product of the base and height, so perimeter and area can be calculated after finding the length of all sides. Length of the perpendicular from vertex to the opposite side can be calculated by proving two triangles similar.
Complete step-by-step answer:
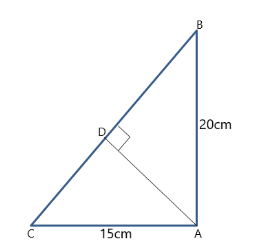
Area of a triangle, $ Area = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height $
We are given that $ base = 15\;cm $ and $ height = 20\;cm $ , so $ area = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 15 \times 20 = 150\;c{m^2} $
From Pythagoras theorem, we know that
$
hypotenus{e^2} = bas{e^2} + heigh{t^2} \\
\Rightarrow hypotenuse = \sqrt {{{(15)}^2} + {{(20)}^2}} = \sqrt {625} = 25\;cm \;
$
Perimeter of a figure is the sum of the length of all its sides, so
$ perimeter = 15 + 20 + 25 = 50\;cm $
In the figure, a perpendicular from A to BC is shown.
We see that,
$
\angle ADB = \angle BAC = 90^\circ \\
\angle CBA = \angle DBA\,(common) \;
$
By AA similarity criterion,
$
\vartriangle CAB \sim \vartriangle ADB \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{CA}}{{AD}} = \dfrac{{CB}}{{AB}} \\
AD = \dfrac{{CA \times AB}}{{CB}} \\
AD = \dfrac{{15 \times 20}}{{25}} = 12\;cm \;
$
B.Hypotenuse is the longest side of a triangle and shortest side can be either one of the base and the height. Ratio of longest and shortest side is $ 3:5 $ . Removing the ratio, the longest side will be 5x and the shortest side is 3x.
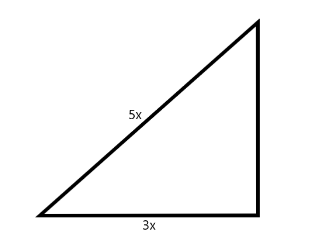
Applying Pythagoras theorem, we get other side $ = \sqrt {{{(5x)}^2} - {{(3x)}^2}} = \sqrt {16{x^2}} = 4x $
Perimeter of the triangle is 36cm, that is
$
4x + 5x + 3x = 36 \\
12x = 36 \\
x = 3\;cm \;
$
We get – Hypotenuse $ = 15\;cm $ and other sides $ 9\;cm $ and $ 12\;cm $ .
So the area of the triangle is $ A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 9 \times 12 = 54\;c{m^2} $ .
C.The smaller sides of the triangle are (x+9) cm and (2x + 3) cm.
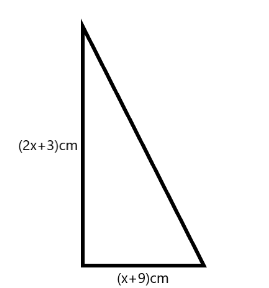
Its area is $ 54\;c{m^2} $ so we have,
$
54 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times (x + 9) \times (2x + 3) \\
108 = 2{x^2} + 21x + 27 \\
2{x^2} + 21x - 81 = 0 \;
$
Solving the above quadratic equation, we get
$ x = 3\,or\,x = \dfrac{{ - 27}}{2} $ , as the side cannot be negative so $ x = 3 $ is the only possible value.
Shorter sides of the triangle are $ 12\;cm $ and $ 9\;cm $ .
Hypotenuse is $ H = \sqrt {{{(12)}^2} + {{(9)}^2}} = \sqrt {225} = 15\;cm $
Perimeter, $ P = 12 + 9 + 15 = 36\;cm $
So the perimeter of the triangle is $ 36\;cm $ .
Note: In a right-angled triangle, the hypotenuse is the longest side as it is the square root of the sum of the square of both sides. Two triangles are similar if their shape is same but only size or orientation is different. There are certain methods to prove two triangles similar. For example, AA similarity criterion, SAS similarity criterion, SSS similarity criterion.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Area of a triangle, $ Area = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height $
We are given that $ base = 15\;cm $ and $ height = 20\;cm $ , so $ area = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 15 \times 20 = 150\;c{m^2} $
From Pythagoras theorem, we know that
$
hypotenus{e^2} = bas{e^2} + heigh{t^2} \\
\Rightarrow hypotenuse = \sqrt {{{(15)}^2} + {{(20)}^2}} = \sqrt {625} = 25\;cm \;
$
Perimeter of a figure is the sum of the length of all its sides, so
$ perimeter = 15 + 20 + 25 = 50\;cm $
In the figure, a perpendicular from A to BC is shown.
We see that,
$
\angle ADB = \angle BAC = 90^\circ \\
\angle CBA = \angle DBA\,(common) \;
$
By AA similarity criterion,
$
\vartriangle CAB \sim \vartriangle ADB \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{CA}}{{AD}} = \dfrac{{CB}}{{AB}} \\
AD = \dfrac{{CA \times AB}}{{CB}} \\
AD = \dfrac{{15 \times 20}}{{25}} = 12\;cm \;
$
B.Hypotenuse is the longest side of a triangle and shortest side can be either one of the base and the height. Ratio of longest and shortest side is $ 3:5 $ . Removing the ratio, the longest side will be 5x and the shortest side is 3x.

Applying Pythagoras theorem, we get other side $ = \sqrt {{{(5x)}^2} - {{(3x)}^2}} = \sqrt {16{x^2}} = 4x $
Perimeter of the triangle is 36cm, that is
$
4x + 5x + 3x = 36 \\
12x = 36 \\
x = 3\;cm \;
$
We get – Hypotenuse $ = 15\;cm $ and other sides $ 9\;cm $ and $ 12\;cm $ .
So the area of the triangle is $ A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 9 \times 12 = 54\;c{m^2} $ .
C.The smaller sides of the triangle are (x+9) cm and (2x + 3) cm.

Its area is $ 54\;c{m^2} $ so we have,
$
54 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times (x + 9) \times (2x + 3) \\
108 = 2{x^2} + 21x + 27 \\
2{x^2} + 21x - 81 = 0 \;
$
Solving the above quadratic equation, we get
$ x = 3\,or\,x = \dfrac{{ - 27}}{2} $ , as the side cannot be negative so $ x = 3 $ is the only possible value.
Shorter sides of the triangle are $ 12\;cm $ and $ 9\;cm $ .
Hypotenuse is $ H = \sqrt {{{(12)}^2} + {{(9)}^2}} = \sqrt {225} = 15\;cm $
Perimeter, $ P = 12 + 9 + 15 = 36\;cm $
So the perimeter of the triangle is $ 36\;cm $ .
Note: In a right-angled triangle, the hypotenuse is the longest side as it is the square root of the sum of the square of both sides. Two triangles are similar if their shape is same but only size or orientation is different. There are certain methods to prove two triangles similar. For example, AA similarity criterion, SAS similarity criterion, SSS similarity criterion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




