
Aerenchyma provides
A. Flexibility to plants
B. Mechanical strength to plants
C. Buoyancy to hydrophytic plants
D. None of the above
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: Aerenchyma cells are circular and contain air chambers which are filled with oxygen that is released during photosynthesis. They have a function similar to that of floating tubes used by swimmers.
Complete answer:
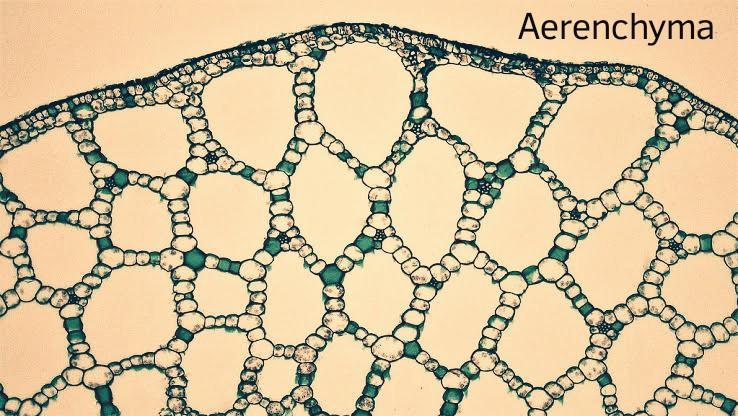
Aerenchyma is a type of simple parenchymatous tissue, it consists of air chambers of lysogenic origin and it provides buoyancy to hydrophytic plants.
Additional Information:
Parenchymatous tissue has the following features:
- These are living simple and permanent tissues. The cells are thin-walled and isodiametric in shape.
- The most abundantly found a tissue in plants is parenchymatous tissue
- The shape of the cells can vary between oval, polygonal and rounded types.
- The cell wall is cellulosic and it lacks a secondary cell wall.
The different types of parenchymatous cells are as follows:
- Prosenchyma: In this type of parenchymatous tissue long and elongated cells with pointed ends are found.
- Stellate Parenchyma: The cells are branched and stellate and air spaces are not well developed. They provide mechanical support to plants.
- Chlorenchyma: This type of parenchymatous tissue contains chloroplast. Chlorenchymatous tissue is of two types as found in dorsiventral leaves. Palisade chlorenchymatous tissue and spongy chlorenchymatous tissue.
- Mucilage Parenchyma: The cells of this type of tissue contain large vacuoles and mucilage. This type of tissue is seen in succulent xerophytic plants, for example in aloe vera.
- Idioblast cells: The cells are specialized for the storage of waste materials such as oils, tannins, and crystals of calcium carbonate.
So, the correct answer is,” Aerenchyma provides buoyancy to hydrophytic plants.”
Note:
The term parenchyma was coined by a scientist named Grew. The aerenchymatous cells provide buoyancy to cells but the other parenchymatous cells perform several other functions which include:
> Storage of food substances and water
> Performing gaseous exchange
> Rigidity and support
> Maintaining of plant shape
> Photosynthesis
Complete answer:
Aerenchyma is a type of simple parenchymatous tissue, it consists of air chambers of lysogenic origin and it provides buoyancy to hydrophytic plants.
Additional Information:
Parenchymatous tissue has the following features:
- These are living simple and permanent tissues. The cells are thin-walled and isodiametric in shape.
- The most abundantly found a tissue in plants is parenchymatous tissue
- The shape of the cells can vary between oval, polygonal and rounded types.
- The cell wall is cellulosic and it lacks a secondary cell wall.
The different types of parenchymatous cells are as follows:
- Prosenchyma: In this type of parenchymatous tissue long and elongated cells with pointed ends are found.
- Stellate Parenchyma: The cells are branched and stellate and air spaces are not well developed. They provide mechanical support to plants.
- Chlorenchyma: This type of parenchymatous tissue contains chloroplast. Chlorenchymatous tissue is of two types as found in dorsiventral leaves. Palisade chlorenchymatous tissue and spongy chlorenchymatous tissue.
- Mucilage Parenchyma: The cells of this type of tissue contain large vacuoles and mucilage. This type of tissue is seen in succulent xerophytic plants, for example in aloe vera.
- Idioblast cells: The cells are specialized for the storage of waste materials such as oils, tannins, and crystals of calcium carbonate.
So, the correct answer is,” Aerenchyma provides buoyancy to hydrophytic plants.”

Note:
The term parenchyma was coined by a scientist named Grew. The aerenchymatous cells provide buoyancy to cells but the other parenchymatous cells perform several other functions which include:
> Storage of food substances and water
> Performing gaseous exchange
> Rigidity and support
> Maintaining of plant shape
> Photosynthesis
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




