
Adventitious buds at the leaf notches help to propagate the plant of
(a)Potato
(b)Agave
(c) Bryophyllum
(d)Cactus
Answer
604.2k+ views
Hint: Propagation by the leaf is usually not so common. Adventitious buds on leaf notches are observed in a plant also known as air plant or miracle leaf.
Complete step-by-step answer:
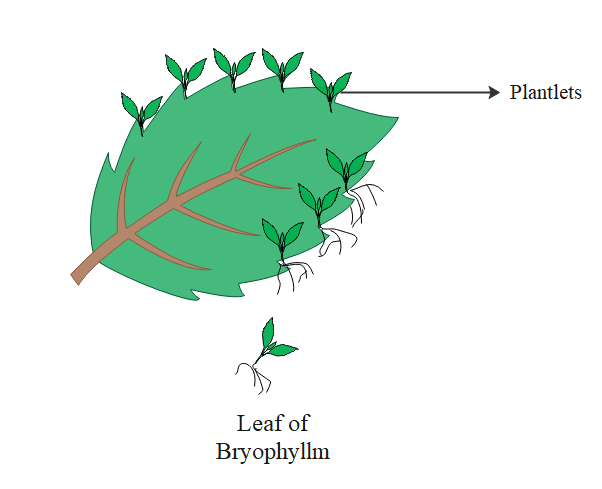
Adventitious buds are produced at the leaf notches of the plant Bryophyllum pinnatum, and these help in vegetative propagation. Propagation by the leaf is also seen in elephant ear plants or Begonia.
In Bryophyllum, plantlets develop from axillary buds on the leaf notches along the leaf margin. These buds are also known as epiphyllous buds.
The development of a fully matured plant from plantlets occurs in the following way:
-The plantlets develop from the epiphyllous buds along the leaf notches.
-After growing for a certain time and developing roots and shoots these plantlets get detached from the leaf margins and fall onto the soil.
-After coming in contact with moist soil these plantlets develop into individual plants and grow independently.
Additional Information: Several other methods of natural vegetative propagation are also seen in plants:
-Vegetative propagation by roots: Roots of plants like Indian redwood, Guava, Murray, etc, have adventitious buds on their roots. Root tubers are seen in sweet potato, Tapioca, Dahlia, which have adventitious buds.
-Vegetative Propagation by underground stems:
-Rhizome: It is an underground stem consisting of nodes and internodes. Possess adventitious buds that form new shoots when conditions are favorable.
-Tuber: It is a terminal part of the underground stem, axillary buds are present in the nodes which form new plants.
-Corm: Short, unbranched, and thick underground stem. Has many buds that sprout under favorable conditions to form new plants.
-Suckers: Grow underground for some time and then grow vertically upwards to give rise to new plants.
So, the correct answer is, "Adventitious buds at the leaf notches help to propagate the plant of Bryophyllum."
Note: Vegetative propagation through leaves is seen in both Bryophyllum and Begonia, but in Begonia adventitious leaf buds are produced from leaf veins and petioles throughout the surface of leaves, whereas in Bryophyllum the buds are produced on leaf margins.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Adventitious buds are produced at the leaf notches of the plant Bryophyllum pinnatum, and these help in vegetative propagation. Propagation by the leaf is also seen in elephant ear plants or Begonia.
In Bryophyllum, plantlets develop from axillary buds on the leaf notches along the leaf margin. These buds are also known as epiphyllous buds.
The development of a fully matured plant from plantlets occurs in the following way:
-The plantlets develop from the epiphyllous buds along the leaf notches.
-After growing for a certain time and developing roots and shoots these plantlets get detached from the leaf margins and fall onto the soil.
-After coming in contact with moist soil these plantlets develop into individual plants and grow independently.

Additional Information: Several other methods of natural vegetative propagation are also seen in plants:
-Vegetative propagation by roots: Roots of plants like Indian redwood, Guava, Murray, etc, have adventitious buds on their roots. Root tubers are seen in sweet potato, Tapioca, Dahlia, which have adventitious buds.
-Vegetative Propagation by underground stems:
-Rhizome: It is an underground stem consisting of nodes and internodes. Possess adventitious buds that form new shoots when conditions are favorable.
-Tuber: It is a terminal part of the underground stem, axillary buds are present in the nodes which form new plants.
-Corm: Short, unbranched, and thick underground stem. Has many buds that sprout under favorable conditions to form new plants.
-Suckers: Grow underground for some time and then grow vertically upwards to give rise to new plants.
So, the correct answer is, "Adventitious buds at the leaf notches help to propagate the plant of Bryophyllum."
Note: Vegetative propagation through leaves is seen in both Bryophyllum and Begonia, but in Begonia adventitious leaf buds are produced from leaf veins and petioles throughout the surface of leaves, whereas in Bryophyllum the buds are produced on leaf margins.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




