
Adjoining figure shows two blocks A and B pushed against the wall with force $F$. The wall is smooth but the surfaces in contact of A and B are rough. Which of the following is true for the blocks to be at rest against the wall ?
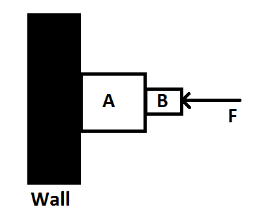
A. $F$ should be more than the weight of A and B.
B. $F$ should be equal to the weight of A and B.
C. $F$ should be less than the weight of A and B.
D. System cannot be in equilibrium.

Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint:In this question, we need to identify the relation between the applied force and total weight of blocks A and B. We also need to focus on the direction of both the force and the weight of the blocks. According to this direction, we will determine the final answer.
Formula used:
$W = mg$
where, $W$is the weight, $m$is the mass and $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first consider the forces in the given system.Let ${m_A}$ be the mass of block A and ${m_B}$ is the mass of block B. We know that weight is given by the formula $W = mg$.Therefore, the weight of block A is ${m_A}g$ and the weight of block A is ${m_B}g$.The total weight of both the books becomes $\left( {{m_A} + {m_B}} \right)g$.Now let us consider the following diagram of the given system and the forces action in the system.
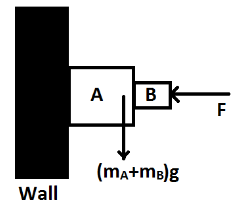
Here, we can see that the force due to mass of the blocks is acting in a vertically downward direction. Whereas, the applied force is in the horizontal direction. Also, it is given that the surface of the wall is smooth. Therefore, there is no frictional force acting in vertically upward direction to balance the weight of the blocks. Thus, the blocks will move down irrespective of the magnitude of the force applied F and they cannot be at rest against the wall.Thus, we can say that the system cannot be in equilibrium.
Thus, option D is the right answer.
Note:In this question, we have applied the concept of the equilibrium condition of the system. The system will be in equilibrium only when the forces action on it are balanced in both horizontal and vertical direction. Here, the forces are not balanced, and therefore the system is not said to be in the equilibrium condition.
Formula used:
$W = mg$
where, $W$is the weight, $m$is the mass and $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first consider the forces in the given system.Let ${m_A}$ be the mass of block A and ${m_B}$ is the mass of block B. We know that weight is given by the formula $W = mg$.Therefore, the weight of block A is ${m_A}g$ and the weight of block A is ${m_B}g$.The total weight of both the books becomes $\left( {{m_A} + {m_B}} \right)g$.Now let us consider the following diagram of the given system and the forces action in the system.

Here, we can see that the force due to mass of the blocks is acting in a vertically downward direction. Whereas, the applied force is in the horizontal direction. Also, it is given that the surface of the wall is smooth. Therefore, there is no frictional force acting in vertically upward direction to balance the weight of the blocks. Thus, the blocks will move down irrespective of the magnitude of the force applied F and they cannot be at rest against the wall.Thus, we can say that the system cannot be in equilibrium.
Thus, option D is the right answer.
Note:In this question, we have applied the concept of the equilibrium condition of the system. The system will be in equilibrium only when the forces action on it are balanced in both horizontal and vertical direction. Here, the forces are not balanced, and therefore the system is not said to be in the equilibrium condition.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




