
Addition of excess potassium iodide solution to a solution of mercuric chloride gives the halide complex:
A.Tetrahedral\[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\]
B.Trigonal\[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{3}}]\]
C.Linear\[H{{g}_{2}}{{I}_{2}}\]
D.Square planar\[{{K}_{2}}[HgC{{l}_{2}}{{I}_{2}}]\]
Answer
610.5k+ views
Hint:
To solve this question, first write the equation for the reaction. The given equation is an example of double displacement reaction. Then, through electronic configuration of the central atom of the complex, decipher the geometry.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us write the equation for the reaction given in the question.
According to the question, mercuric chloride reacts with excess potassium iodide solution to give a halide complex. Therefore,
\[HgC{{l}_{2}}+4KI\to {{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]+2KCl\]
So, the halide complex formed is Potassium mercuric iodide - \[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\]. This is an example of double displacement reaction.
Now, let us use the geometry of the complex.
Mercury is the central compound of the complex. The electronic configuration of Hg is –
\[Hg=[Xe]4{{f}^{14}}5{{d}^{10}}6{{s}^{2}}\]
In the complex, mercury has an oxidation state of +2.
\[H{{g}^{2+}}=[Xe]4{{f}^{14}}5{{d}^{10}}6{{s}^{0}}\]
It therefore has orbitals 6s and 6p for bonding.
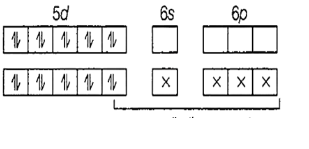
Since bonding takes place through 1 s-orbital and 3-p orbitals, the hybridization of the compound is \[s{{p}^{3}}\]. All \[s{{p}^{3}}\]hybridized compounds have a tetrahedral geometry.
Therefore, the answer is – option (a).
Additional Information: The IUPAC name of the halide formed is Potassium tetraiodomercurate(II).
Note:
The hybridization and geometry of any compound can be related as –
To solve this question, first write the equation for the reaction. The given equation is an example of double displacement reaction. Then, through electronic configuration of the central atom of the complex, decipher the geometry.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us write the equation for the reaction given in the question.
According to the question, mercuric chloride reacts with excess potassium iodide solution to give a halide complex. Therefore,
\[HgC{{l}_{2}}+4KI\to {{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]+2KCl\]
So, the halide complex formed is Potassium mercuric iodide - \[{{K}_{2}}[Hg{{I}_{4}}]\]. This is an example of double displacement reaction.
Now, let us use the geometry of the complex.
Mercury is the central compound of the complex. The electronic configuration of Hg is –
\[Hg=[Xe]4{{f}^{14}}5{{d}^{10}}6{{s}^{2}}\]
In the complex, mercury has an oxidation state of +2.
\[H{{g}^{2+}}=[Xe]4{{f}^{14}}5{{d}^{10}}6{{s}^{0}}\]
It therefore has orbitals 6s and 6p for bonding.

Since bonding takes place through 1 s-orbital and 3-p orbitals, the hybridization of the compound is \[s{{p}^{3}}\]. All \[s{{p}^{3}}\]hybridized compounds have a tetrahedral geometry.
Therefore, the answer is – option (a).
Additional Information: The IUPAC name of the halide formed is Potassium tetraiodomercurate(II).
Note:
The hybridization and geometry of any compound can be related as –
| Hybridization | Geometry |
| \[sp\] | Linear |
| \[s{{p}^{2}}\] | Trigonal planar |
| \[s{{p}^{3}}\] | Tetrahedral |
| \[s{{p}^{3}}d\] | Trigonal bipyramidal |
| \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\] | Octahedral |
| \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{3}}\] | Pentagonal bipyramidal |
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




