
Acetyl bromide reacts with an excess of CH3MgI followed by treatment with a saturated solution of NH4Cl gives:
A. acetone
B. acetamide
C. 2 - methyl - 2 – propanol
D. acetyl iodide
Answer
543.9k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept of preparation of alcohols. The simplest method to produce all primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol is by using a Grignard reagent.
Complete step-by-step answer: We know that to produce primary alcohol, the Grignard reagent is reacted with formaldehyde.

Methyl Magnesium Formaldehyde Ethanol
Bromide
Further reacting a Grignard reagent with any other aldehyde will lead to a secondary alcohol.
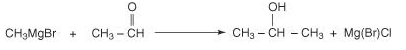
Acetaldehyde 2-propanal
Ultimately, reacting a Grignard reagent with a ketone will generate tertiary alcohol.
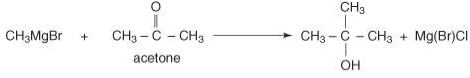
tert-butyl alcohol
For the reaction given in the question: Acetyl bromide reacts with an excess of \[C{H_{3}}MgI\;\] followed by treatment with a saturated solution of \[N{H_4}Cl\;\]gives tertiary alcohol which in the given option is 2-methyl-2-propanol. The mechanism can be visualized as follows:
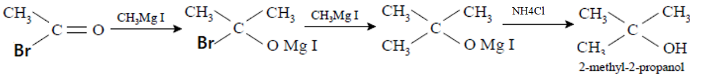
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option C.
Note: Grignard reagent refers to an organo-magnesium halide with the formula of ${\text{RMgX}}$, where X is a halogen, and R is an alkyl or aryl. Apart from preparation of alcohols, it is also used for determining the number of halogen atoms present in a halogen compound. Currently, another important use involves the chemical analysis of certain triacylglycerols.
Complete step-by-step answer: We know that to produce primary alcohol, the Grignard reagent is reacted with formaldehyde.

Methyl Magnesium Formaldehyde Ethanol
Bromide
Further reacting a Grignard reagent with any other aldehyde will lead to a secondary alcohol.

Acetaldehyde 2-propanal
Ultimately, reacting a Grignard reagent with a ketone will generate tertiary alcohol.

tert-butyl alcohol
For the reaction given in the question: Acetyl bromide reacts with an excess of \[C{H_{3}}MgI\;\] followed by treatment with a saturated solution of \[N{H_4}Cl\;\]gives tertiary alcohol which in the given option is 2-methyl-2-propanol. The mechanism can be visualized as follows:
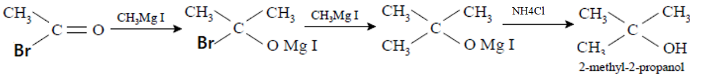
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option C.
Note: Grignard reagent refers to an organo-magnesium halide with the formula of ${\text{RMgX}}$, where X is a halogen, and R is an alkyl or aryl. Apart from preparation of alcohols, it is also used for determining the number of halogen atoms present in a halogen compound. Currently, another important use involves the chemical analysis of certain triacylglycerols.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




