
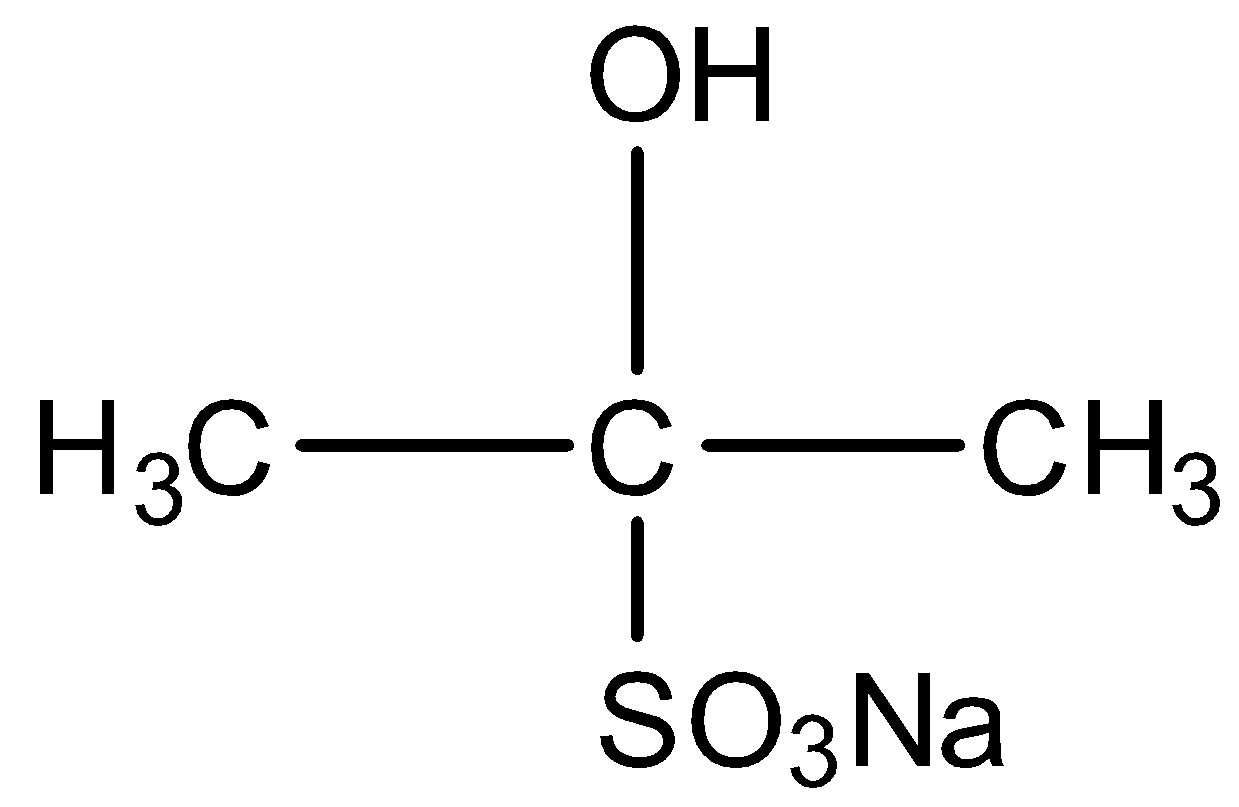
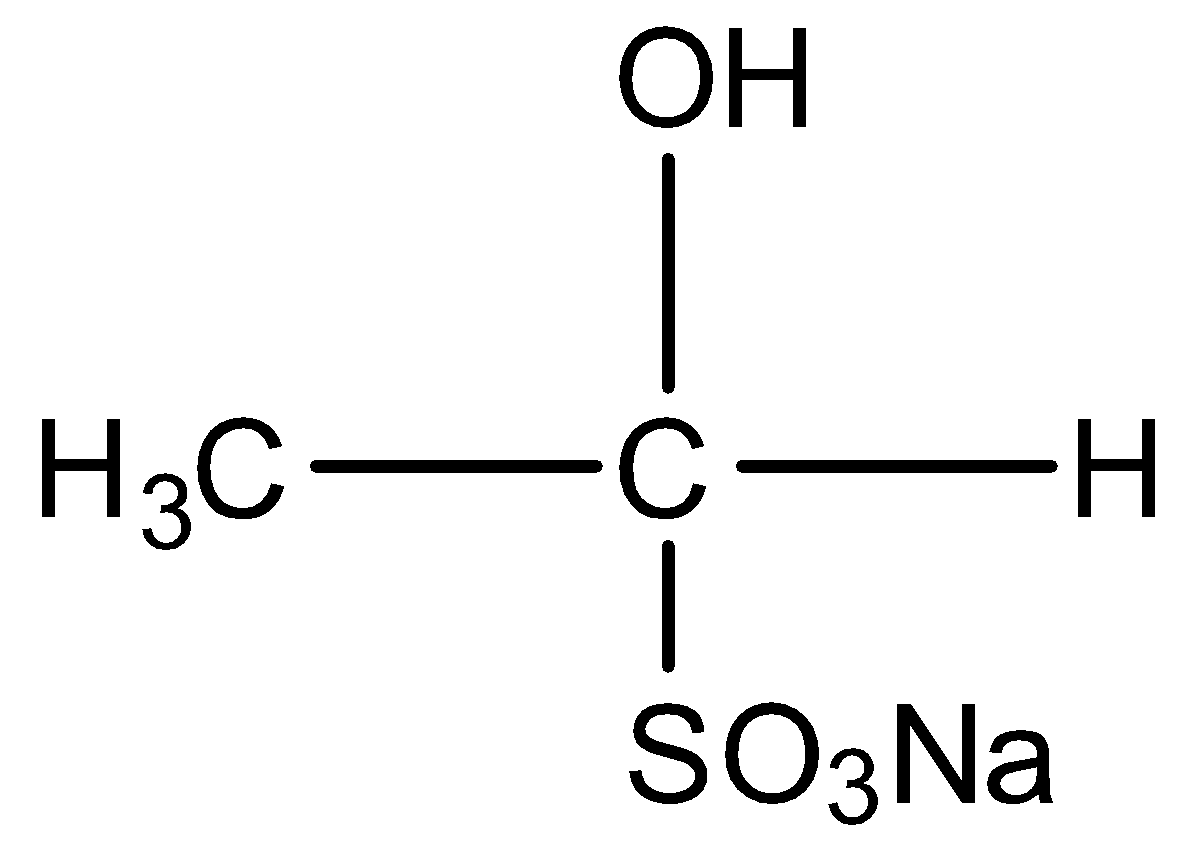
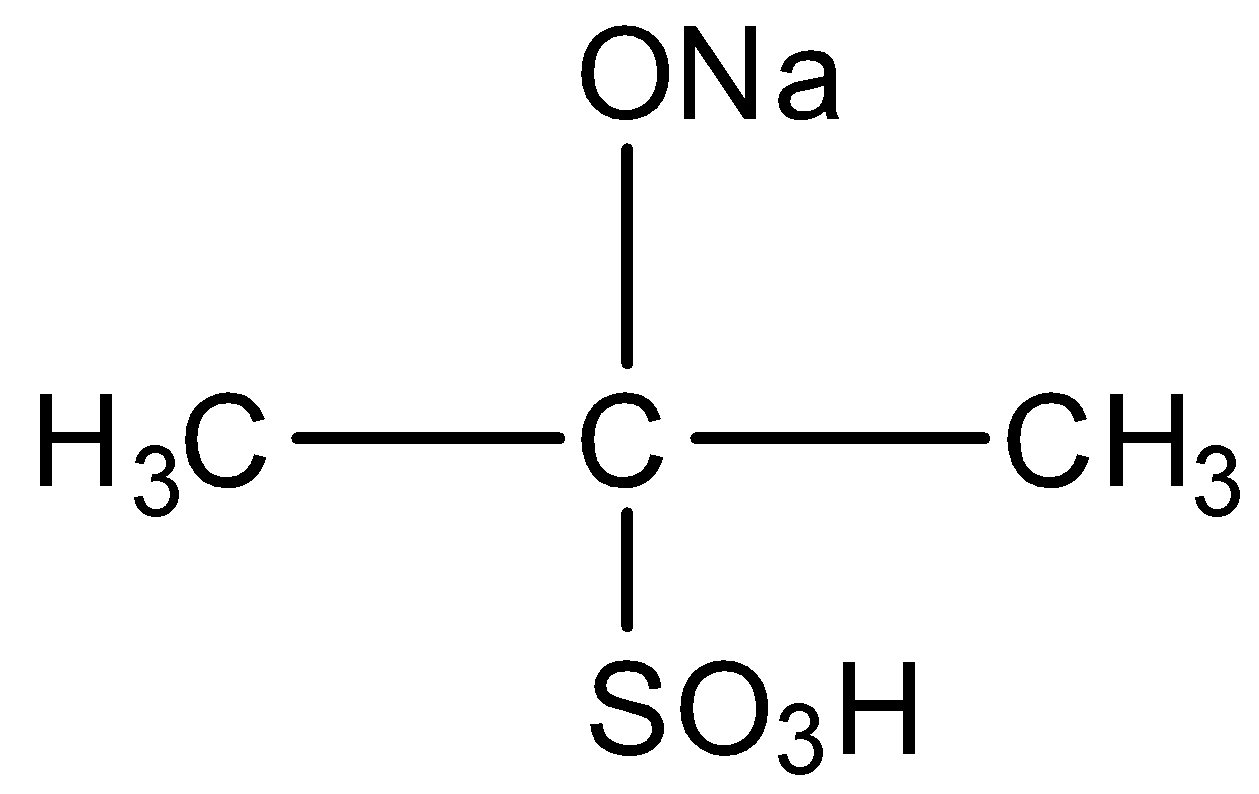
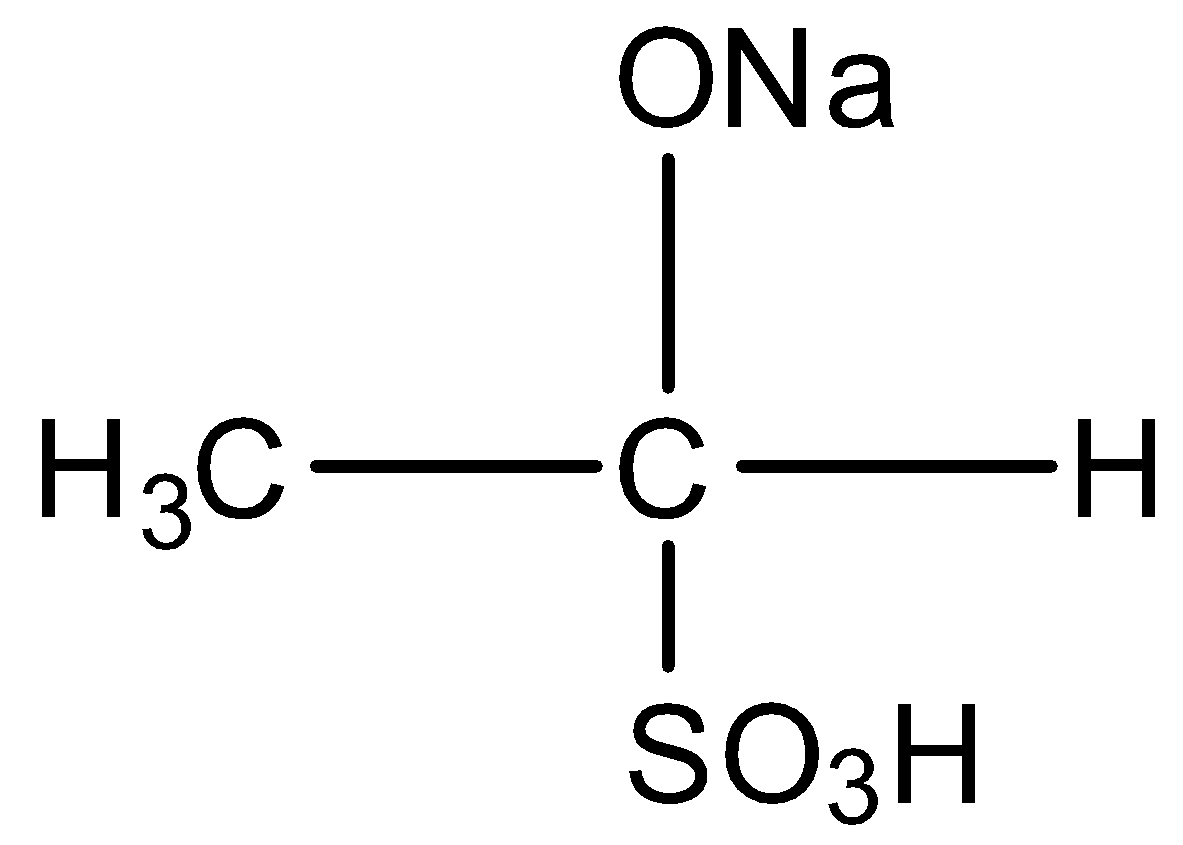
When acetone is treated with sodium bisulphite, the compound formed is :
A)
B)
C)
D)




Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: Acetone (systematically named $2 - $ propanone) is the organic compound with the formula ${\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}CO$ . It is a colorless, volatile, flammable liquid, and also it is the simplest ketone. Acetone is derived from propylene, either directly or indirectly. The cumene cycle helps produce approximately $83\% $ of the global acetone production. As a result, the production of acetone is based on the development of phenols. Benzene is alkylated with propylene in the cumene cycle to obtain the cumene, which is oxidized by the environment to create phenol and acetone.
Complete step by step answer:
Acetone is $C{H_3}COC{H_{3\,}}$ . On the addition of sodium bisulphite ($NaHSO_3^{}$), a nucleophilic addition reaction takes place. The compound formed is as shown in the chemical reaction below:
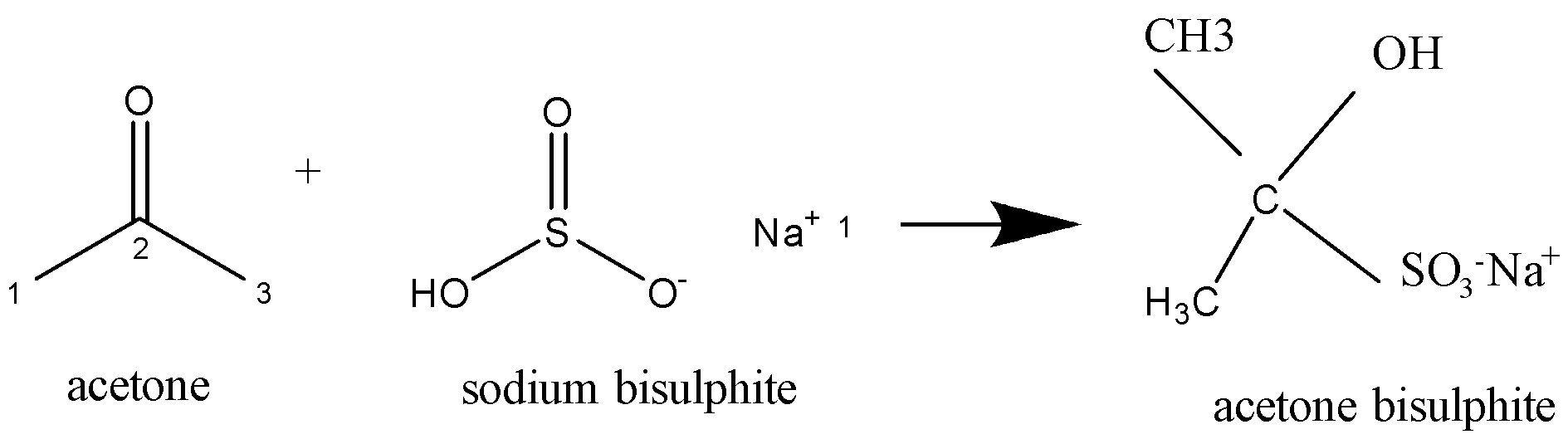
A nucleophilic reaction may be a chemical reaction within which a nucleophile forms a sigma bond with an electron-deficient species.
These reactions are considered important in chemistry since they allow the conversion of carbonyl groups into a spread of functional groups. Generally, nucleophilic addition reactions of carbonyl compounds may be softened into the subsequent three steps.
The electrophilic carbonyl carbon forms a sigma bond with the nucleophile.
The carbon-oxygen pi bond then gets broken, thereby forming an alkoxide intermediate. The bond pair of electrons are then transferred to the oxygen atom. The subsequent protonation of the alkoxide yields the alcohol derivative.
The carbon-oxygen covalent bond is directly attacked by strong nucleophiles to provide rise to the alkoxide.
However, when weak nucleophiles are used, the group must be activated with the assistance of an acid catalyst for the nucleophilic chemical reaction to proceed.
So, the correct answer is Option A .
Note: In carbonyl compounds, the carbon-oxygen bond is polar. Due to the relatively higher electronegativity of the oxygen atom, the electron density is higher near the oxygen atom. This results in the generation of a partial electric charge on the oxygen atom and a partial charge on the atom.
Since the carbonyl carbon holds a partial electric charge, it behaves as an electrophile. The partial charge on the oxygen atom may be stabilized via the introduction of an acidic group. The proton donated by the acid binds with the carbonyl oxygen atom and neutralizes the charge.
Complete step by step answer:
Acetone is $C{H_3}COC{H_{3\,}}$ . On the addition of sodium bisulphite ($NaHSO_3^{}$), a nucleophilic addition reaction takes place. The compound formed is as shown in the chemical reaction below:

A nucleophilic reaction may be a chemical reaction within which a nucleophile forms a sigma bond with an electron-deficient species.
These reactions are considered important in chemistry since they allow the conversion of carbonyl groups into a spread of functional groups. Generally, nucleophilic addition reactions of carbonyl compounds may be softened into the subsequent three steps.
The electrophilic carbonyl carbon forms a sigma bond with the nucleophile.
The carbon-oxygen pi bond then gets broken, thereby forming an alkoxide intermediate. The bond pair of electrons are then transferred to the oxygen atom. The subsequent protonation of the alkoxide yields the alcohol derivative.
The carbon-oxygen covalent bond is directly attacked by strong nucleophiles to provide rise to the alkoxide.
However, when weak nucleophiles are used, the group must be activated with the assistance of an acid catalyst for the nucleophilic chemical reaction to proceed.
So, the correct answer is Option A .
Note: In carbonyl compounds, the carbon-oxygen bond is polar. Due to the relatively higher electronegativity of the oxygen atom, the electron density is higher near the oxygen atom. This results in the generation of a partial electric charge on the oxygen atom and a partial charge on the atom.
Since the carbonyl carbon holds a partial electric charge, it behaves as an electrophile. The partial charge on the oxygen atom may be stabilized via the introduction of an acidic group. The proton donated by the acid binds with the carbonyl oxygen atom and neutralizes the charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




