
Account for the following:
A) The ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than that in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{Cl}}$.
B) Chloroform is stored in closed dark brown bottles.
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond in chlorobenzene is $s{p^2}$ hybridised and the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond in methyl chloride is $s{p^3}$ hybridised. In the presence of light, chloroform $\left( {{\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ gets oxidised by air to form phosgene.
Complete step by step answer:
A) The structures of chlorobenzene and methyl chloride are as follows:
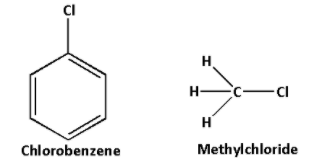
In chlorobenzene, the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond is attached to three groups. Thus, the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond in chlorobenzene forms three sigma bonds. Thus, the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond in chlorobenzene is $s{p^2}$ hybridised.
In methyl chloride, the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond is attached to four groups. Thus, the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond in methyl chloride forms four sigma bonds. Thus, the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond in methyl chloride is $s{p^3}$ hybridised.
In $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals, the s-character is more than that of in $s{p^3}$ hybrid orbitals. Thus, the $s{p^2}$ hybridised carbon atom withdraws the electron pair between the ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond with greater force than that of $s{p^3}$ hybridised carbon atom.
Thus, the ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than that in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{Cl}}$.
B) In the presence of light, chloroform $\left( {{\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ gets oxidised by air. This oxidation reaction of chloroform leads to formation of carbonyl chloride or phosgene $\left( {{\text{COC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$. Phosgene is extremely poisonous.
The reaction is as follows:
${\text{2CHC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}} + {{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Sunlight}}}}{\text{2COC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}} + {\text{2HCl}}$
Thus, to avoid the formation of phosgene, chloroform is stored away from light and air.
In closed dark brown bottles, no light and air can enter. Thus, oxidation of chloroform to phosgene can be avoided.
Thus, chloroform is stored in closed dark brown bottles.
Note: Apart from $s{p^2}$ and $s{p^3}$ hybrid orbitals there is presence of $sp$ hybrid orbitals also in which contribution of s and p orbitals is the same. Phosgene is an organic compound that is highly poisonous colourless gas. Phosgene damages skin, eyes, nose, throat and lungs.
Complete step by step answer:
A) The structures of chlorobenzene and methyl chloride are as follows:

In chlorobenzene, the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond is attached to three groups. Thus, the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond in chlorobenzene forms three sigma bonds. Thus, the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond in chlorobenzene is $s{p^2}$ hybridised.
In methyl chloride, the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond is attached to four groups. Thus, the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond in methyl chloride forms four sigma bonds. Thus, the carbon atom of ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond in methyl chloride is $s{p^3}$ hybridised.
In $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals, the s-character is more than that of in $s{p^3}$ hybrid orbitals. Thus, the $s{p^2}$ hybridised carbon atom withdraws the electron pair between the ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond with greater force than that of $s{p^3}$ hybridised carbon atom.
Thus, the ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than that in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{Cl}}$.
B) In the presence of light, chloroform $\left( {{\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)$ gets oxidised by air. This oxidation reaction of chloroform leads to formation of carbonyl chloride or phosgene $\left( {{\text{COC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$. Phosgene is extremely poisonous.
The reaction is as follows:
${\text{2CHC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}} + {{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Sunlight}}}}{\text{2COC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}} + {\text{2HCl}}$
Thus, to avoid the formation of phosgene, chloroform is stored away from light and air.
In closed dark brown bottles, no light and air can enter. Thus, oxidation of chloroform to phosgene can be avoided.
Thus, chloroform is stored in closed dark brown bottles.
Note: Apart from $s{p^2}$ and $s{p^3}$ hybrid orbitals there is presence of $sp$ hybrid orbitals also in which contribution of s and p orbitals is the same. Phosgene is an organic compound that is highly poisonous colourless gas. Phosgene damages skin, eyes, nose, throat and lungs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




